In the field of Adapted Physical Activity, there is a dearth of research that has attempted to critically explore ethical issues arising in the field of practice. The reason why ethical considerations are needed in the field of practice is that adapted physical activity instructors can negatively affect other people's lives, such as students with disability, regardless of their intentions. Purpose Therefore, the purpose of this study is to apply ethical theories on ethical issues that may appear in the adapted physical activity practice field and consider their implications. Methods Through ethics theory, researcher attempted to critically examine what is right, wrong, or good or bad in the field of adapted physical activity practice. Results As a result of the research, ethical theories were considered and the contributions and limitations that each theory could offer to adapted physical activity practice were discussed.
This study aims to find the alternative to increase the participation rates of physical activities and to analyze socio-demographic factors that determine sporting participation in Korea. We estimates the sporting participation model with ʼ2012 national sport participation survey in Korea' and binary logit analysis. The results are as follows: sporting participation is positively related to gender(male), age, education level, household income, health status, leisure time in weekday, proximity to public and private sports facilities. The most significant factors influencing the raising the participation rates of physical activities factors are age and proximity to sports facilities. Therefore, to make many people to participate in sports activities, we need to supply the public sports facilities that in proximity to house and the facilities needs to be taken into participant's age such as elderly group. Also, we make effort to improve the accessibility to sports facilities of poor and unhealthy people.
PURPOSE This study analyzed research on physical activities for elementary school students 1st and 2nd-graders to explore teachers’ perceptions and instructional practices in physical activity classes. METHODS Twelve studies published in academic journals conducted between 2000 to 2022 were selected for analysis. RESULTS The research articles were categorized into three domains: perception of physical activity in lower grades, operational features, and factors influencing practices from a didactic perspective. Challenges identified include dilemmas between curriculum documents and actual practice, a lack of practical teaching expertise, and a teaching culture discouraging physical activity in lower grades. Operational patterns were restructured into “avoidance-style classes,” “ad-hoc classes,” “textbook-dependent classes,” and “textbook-reorganization classes.” Factors influencing physical education for early elementary students included “teacher support factors,” “environmental factors,” and “administrative factors.” CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, this study advocates for policies that systematically improve perception, administration, and support classes for activating physical activities in lower elementary school students. The findings suggest the need for strategies such as adapting integrated curricula, creating training programs and educational materials, ongoing professional development activities for teachers, and specific research focused on physical activities for lower grade elementary students.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to analyze the level and characteristics of physical activity (sedentary, light, and MVPA) of high school students according to physical education (PE) class (DWPE: days with PE class, DNPE: days with no PE class) and sex. METHODS Data were collected on 147 students (65 male and 82 female) from four high schools in Seoul city, and physical activity was measured using a three-dimensional accelerometer. The collected physical activity data were input into SPSS 25.0, and the descriptive analysis and two-way ANOVA according to PE class and sex were performed. RESULTS The descriptive statistical analysis showed that 31% (40.7% male and 23.4% female) of participants met the recommended physical activity durations (MVPA of 60 min/day). In the two-way ANOVA, sedentary activity, light activity, and MVPA showed statistically significant main and interaction effects according to PE class and sex. According to the results of the interaction effect analysis, the gap in physical activity between DWPE and DNPE was large in male students. For male students, light activity and MVPA significantly increased on the day of the PE class, and sedentary activity significantly decreased. However, for female students, DWPE and DNPE did not differ significantly in all levels of physical activity. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, the level of physical activity of Korean high school students was relatively low, and the effect of daily-life physical activity in the PE class was limited to male students. Accordingly, an alternative should be introduced to increase the physical activity of female high-school students through PE classes.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the association of physical activity level with insomnia severity (Normal, Subthreshold, Moderate and Severe) in adolescents and to use it as a basis for insomnia prevention. METHODS This study was conducted on a cohort of 50 adolescents under the age of 20 (19 males, 31 females) recruited from Hospital N in Incheon, Korea. Participants were categorized into groups according to the severity of insomnia in both males and females using the Korean version of the Insomnia Severity Index-Korean (ISI-K). The Korean version of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire was also used to calculate participants’ weekly moderate and vigorous physical activity. RESULTS The participants’ characteristics did not differ by insomnia severity in males, but there were significant differences in weight (p=.008), BMI (p=.019), SBP (p=.004), and DBP (p=.019) in females by insomnia severity. In male adolescents, there was no significant difference in the amount of physical activity by insomnia severity, but there was a trend toward decreased amount of physical activity with increasing severity. Among female adolescents, there were significant differences in the amount of physical activity by insomnia severity: moderate (p<.05), high (p<.05), and moderate-high (p<.05). In the unadjusted model, adolescents who did not meet the recommended amount of physical activity (150 minutes per week) were more likely to have insomnia (OR=4.67, 95% CI=1.34–16.24) than those who met the recommended amount of physical activity. The model after adjusting for covariates (gender and body mass index) also showed an association between the recommended amount of physical activity and insomnia (OR=3.94, 95% CI=1.17–13.28). Negatice correlations was found between insomnia index and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (r=–.357, p=.013). CONCLUSIONS Adolescents are approximately 4.67 times more likely to suffer from insomnia if they do not meet physical activity recommendations, and there was a negative correlation between the insomnia index and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, suggesting that physical activity should be increased to reduce the insomnia index.
PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze factors associated with physical activity (PA) in older adults based on social ecological theory. METHODS Secondary analysis was conducted using raw data from the 2021 Community Health Survey. after excluding 129 non-responses in the PA domain, a total of 74,363 individuals were included in the final analysis. A total of eight factors, including personal (level of depression, history of falls), relational (relationships with neighbors, living alone), community (satisfaction with the local community system, safety), and environmental factors (living environment, natural environment), were selected in accordance with the key points of social ecological theory. To analyze social ecological factors related to the PA of older adults, we conducted a decision tree analysis using Chi-square automatic interaction detection (CHAID). RESULTS The average PA level among older adults was approximately 136 minutes, but the mode and median were both 0 minutes. A total of 20.2% of older adults met the physical activity recommendations, while 79.8% did not. According to the first split of the decision tree, living alone was the most relevant factor associated with the PA of older adults, followed by depression and falls. Older adults living alone, with a depression score of 10 or higher, and who had experienced a fall within the past year, were least likely to meet the PA recommendations. CONCLUSIONS This study urgently suggests that PA programs should target older adults living alone, experiencing depression, and falls.

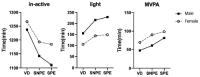
Purpose The purpose of this study is to measure the daily physical activity of male and female middle school students according to the period (VD: vaction day, SNPE: school day no PE, SPE: school day with PE) by using 3-axis accelerometer, and to compare the characteristics of adolescent physical activity according to gender and period. Methods The subjects were 130 middle school students (68 male, 62 female students). Data collection was performed using a 3-axis accelerometer(GT3X model, ActiGraph). Collected data were converted into time by intensity and rate using physical activity analysis program (Actilife v6.11.9) and analyzed by statistical program (SPSS 25.0). One-way ANOVA and independent sample t-test were used for statistical analysis. Tukey's HSD was used as a post analysis. The statistical significance level was .05. Results As a result, during each periods(VD, SNPE, and SPE), except for MVPA(moderate to vigorous physical activity) time on SPE, sedentary and MVPA time were significantly higher in female students, and low intensity and total physical activity time were significantly higher in male students. For male students, total physical activity time was higher in the order of SPE, SNPE, and VD, and for female students, physical activity time during the semester(SNPE and SPE) was significantly higher than VD. For male students, MVPA time was significantly high in order of SPE, SNPE, and VD, and for female students, it was high in order of SPE, SNPE, and VD but only significant difference occurred between SPE and VD. For both male and female students, sedentary time was high in the order of VD, SNPE, and SPE, but the sedentary time during vacation was significantly higher than during the semester. Conclusions When summarizing the results, first, it was confirmed that school and physical education classes as a physical activity space play a significant role in physical activity, especially MVPA, of male and female middle school students, second, the physical activity effect of physical education class was found to be more effective in male students. Based on the results of this study, it is necessary to conduct studies on various grades and to explore various factors affecting physical activity in a complex way.


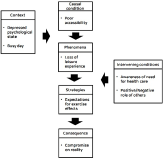
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the alienation and the overcoming process of the physical activity participation of people with Adventitious Visual Impairment(AVI) Methods 21 Adults with AVI were recruited and one on one semi-structured interview was conducted. Ground theory was used to analyze the data. Member check, peer debriefing was conducted to enhance the trustworthiness of this study. Results As a result, a total of 203 concepts were derived. This consisted of 21 subcategories and the common themes of the subcategories were categorized into nine categories. Specific results are as follows. First, the physical activity of people with AVI was directly affected by the sports facilities, physical activity programs, and professional instructor. This causal condition resulted in the loss of leisure experience in the context of the busy daily life and the depressed psychological state. Second, due to the perceived need of health care and the positive involvement of others, people with AVI came to expect the effect of exercise. Third, people with AVI participated in physical activity again as a tool to achieve the purpose of health improvement. This type of physical activity has a limitation that it can not guarantee the continuity of physical activity due to the limitation that it does not contain autonomy and interest of people with AVI. Conclusions Based on these results, the following suggestions were made. First, it is necessary to improve the environment for ensuring participation in physical activity of people with AVI. Moreover education and promotion of the effects and values of the exercise should be carried out for people with AVI and their guardians. Second, it is necessary to diversify physical activity types and reconstruct existing exercise programs.

The frailty, characterized by reduced physiological function is closely related to a fall, disability, institutionalization, hospitalization, and mortality in the elderly. A reduced physical fitness is a major phenotype of the frailty. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship among pre-frailty, physical activity (PA) and functional fitness in the community dwelling elderly women. The study participants were elderly women (n=338, 70.6±4.2years) aged over 65 who took part in the Korean Healthy Fitness Criteria study for the National Fitness Award Project in 2015. The pre-frailty was defined using the Cardiovascular Health Study frailty criteria. PA was assessed using the International PA Questionnaire (IPAQ). The participants were classified as regular PA participants if they meet the World Health Organization (WHO) PA recommendation for the elderly. Functional fitness was assessed using the composite of the National Fitness Award fitness testing for the elderly. Quality of life was evaluated using EuroQoL visual analogue scale and WHO quality of life assessment. As the results, the pre-frail elderly women were significantly older and obese (body mass index, percent body fat, waist circumference) than the healthy elderly. The pre-frail elderly presented significant decreases in walking, moderate intensity, and total PA compared to the healthy elderly even after adjusted for age and percent body fat. However, no significant difference was found in vigorous-intensity activity between the pre-frail and healthy elderly. Also, the pre-frail elderly women showed the decrease in functional fitness and quality of life compared to the healthy elderly. Regular PA was associated with high levels of muscular endurance and coordination in healthy and pre-frail elderly. In pre-frail elderly, high levels of cardiorespiratory endurance was associated with PA. In conclusion, regular PA is inversely associated with fitness decline in healthy and pre-frail community-dwelling elderly women. Regular PA might attenuate fitness decline in pre-frail elderly women.
The purpose of the study is to find the impact of social and economic factors in physical activity of children and youth. This study utilized the data from 4th Korean Children and Youth Panel Study(KCYPS), and the analysis were carried out based on the starting sample of 2,009 from ‘the elementary 4 panel’ and 1,978 from the ‘middle school 1 panel’ and 1,984 from the ‘high school 1 panel’, 5,971 full data were used in the final analysis. Data were processed using hierarchical regression analysis and it was statistically validated at the significance level of 0.05. First, Pearson r and Spearman ρ showed that all variables are statistically significant correlations. Second, among the first factors of personal and family characteristics, household income level(B=.113), family composition(B=-.049) and parental education (B=.060) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, parental education (B=.027) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Third, among the second factors of community-level characteristics, Gini coefficient (B=-.810), wealth concentrating (B=.120) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, the Gini coefficient (B=-0.315) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Additional factors that determine the coefficient of variation in the level 2 were found to be 0.623 and 0.001 respectively. Therefore, second factors of community-level characteristics are added such as Gini coefficient, wealth concentrating were explained to children and youth exercise time during physical activity 62.3%(p<.01) and subjective evaluation of physical education in grades 0.1%(p<.01). predictive power to