Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of 8 weeks of circuit exercise training on blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and metabolic syndrome risk factors in 40~50s male bus drivers. Methods Twenty-nine bus drivers were randomly assigned to one of two groups, i.e., circuit exercise training group (TR: n=14) and control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR participated in circuit exercise training 30-40 min per session, three sessions per week for 8 weeks, whereas subjects in CON were asked to maintain their normal life pattern for same intervention period. The variables regarding body composition, blood lipids, insulin resistance, cardiovascular function, and number of metabolic syndrome risk factors were measured and compared between two groups as well as between pre- and post-test. Data were analyzed using repeated two-way ANOVA with post hoc test. Results Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Waist circumference, waist-hip ratio, body mass index, and percent body fat decreased significantly in TR. 2) LDL-C decreased and HDL-C increased significantly in TR. 3) Fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR decreased significantly in TR. 4) Regarding cardiovascular function, diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial pressure decreased significantly in both TR and CON. hs-CRP were not changed significantly; however, it tended to be decreased TR. 5) Number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased significantly in TR(2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76). Conclusions It was concluded that 8 weeks of circuit exercise training would be beneficial for improvement of blood lipid profiles and insulin resistance, resulting in preventing metabolic syndrome. In particular, it would be very clinically meaningful that number of metabolic syndrome risk factors decreased from 2.86±0.86 to 1.50±0.76 by the circuit exercise training.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to apply the Self-Assertiveness Training based on Solution-Focused to student-athletes caused by violence in sports. Methods Participants were five Taekwondo athletes in this study. They were consisted of offenders, a accuser, and a victim. The head coach of the team asked for counseling to resolve the conflict. Data was collected with quantitative, qualitative data, and group dynamics. The group counseling program was conducted for 90 minutes a week for eight weeks. Results The results are as follows. First, (application process) the 8-week Self-Assertiveness Training based on Solution-Focused was assessed to be applied step by step and systematically. Second, (qualitative evaluation) as a result of analyzing the observation journal and the interview data, the participants experienced the change of attitude and thought of group members in a short period of time by focusing on enhancing self-assertiveness. Third, (quantitative evaluation) self-assertiveness and attitude of school violence measured by questionnaires were higher in post-survey than pre-survey. In addition, participants' satisfaction with the program was found to be very positive. Discussions and Suggestions Self-Assertiveness Training based on Solution-Focused was found to have a significant effect on conflict resolution among the student-athletes who have experienced violence in sport. This programs was expected to increase the value of use in the sport field. Based on this case study, We suggested for future research.


PURPOSE The purpose of this review was to summarize the current knowledge on the trends in athletes’ health problems (and their preventive strategies) caused by low energy availability (LEA) and relative energy deficiency in sports (RED-S). METHODS In this narrative review, we summarized previous studies by searching the literature in the PubMed, Google Scholar, and Science Direct databases. RESULTS Energy availability (EA) refers to the amount of energy from caloric intake used for exercise, and a LEA is considered as a surrogate marker of RED-S. In several previous studies, chronic low energy availability in female athletes has been reported to cause health problems such as endocrine dysfunctions, immunosuppression, and psychological disorders, and to also affect the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPC) axis and bone health. Moreover, it has been suggested that an increase in injury risk and a decrease in exercise performance may occur. CONCLUSIONS Since it can be difficult to recover from the health deteriorations caused by RED-S, early detection (of related signs and symptoms) and prevention are very important. Therefore, athletes, coaches, and parents need to develop educational programs that ease the recognition of the problems caused by various symptoms related to RED-S and promote educational interventions.
PURPOSE This study aims to critically read the film <Run-Off 2> in a manner in which its narrative represents and constructs the multicultural subject as the fearful and compassionate “other,” and its structure and meanings reconciles with the concept of cultural citizenship. METHODS This research is informed by two methods: 1) text analysis by deconstructing the narrative structure and flow, and 2) contextual interpretation focussing on understanding the significance of the filmic representation in the Korean historical, political, social, and cultural contexts. RESULTS The narrative of the film portrays and constructs the multicultural subject as a cultural other, with specific styles of representation, in which stereotypical description, otherizing tropes of double process, and recognition struggle for cultural citizenship. CONCLUSIONS The study summarized the present research and laid out some suggestions for critical studies of sport films from an interdisciplinary approach and cultural studies-based methods.

The purpose of this study was to verify the effect on elementary school students in the exercise start stage by performing a sport psychological skill training to improvement of psychological skill and life skill. Participants were eight elementary school boys volleyball player. The program consisted of psychological skills and life skills in educational counseling model of Visek et al(2009). It was conducted 40-50 minutes a session in total for 22 sessions. Data was collected through a psychological test, worksheet and participant observation, in-depth interviews. The collected data was analyzed to verify difference by paird t-test after pre-middle-post test and to extract meaningful data category. Quantity analysis showed that a result of sport psychological skill test proved a significant difference in willingness to overcome, confidence, concentration, anxiety regulation. Life skill test were no significant differences in all factors. However, the rise of scores was observed on result of the pre-middle paired t-test of life skill during season. Quality analysis showed possibility of goal setting, concentration on the routine, decrease of competitive anxiety, increase of positive thinking, self-understanding and understanding of others, promotion of communication among team members. This sport psychology skill training had a significant effect on the psychological skills of elementary players change. But it seems to be necessary life skills in a more through review of the information.



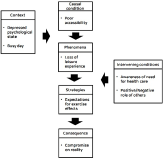
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the alienation and the overcoming process of the physical activity participation of people with Adventitious Visual Impairment(AVI) Methods 21 Adults with AVI were recruited and one on one semi-structured interview was conducted. Ground theory was used to analyze the data. Member check, peer debriefing was conducted to enhance the trustworthiness of this study. Results As a result, a total of 203 concepts were derived. This consisted of 21 subcategories and the common themes of the subcategories were categorized into nine categories. Specific results are as follows. First, the physical activity of people with AVI was directly affected by the sports facilities, physical activity programs, and professional instructor. This causal condition resulted in the loss of leisure experience in the context of the busy daily life and the depressed psychological state. Second, due to the perceived need of health care and the positive involvement of others, people with AVI came to expect the effect of exercise. Third, people with AVI participated in physical activity again as a tool to achieve the purpose of health improvement. This type of physical activity has a limitation that it can not guarantee the continuity of physical activity due to the limitation that it does not contain autonomy and interest of people with AVI. Conclusions Based on these results, the following suggestions were made. First, it is necessary to improve the environment for ensuring participation in physical activity of people with AVI. Moreover education and promotion of the effects and values of the exercise should be carried out for people with AVI and their guardians. Second, it is necessary to diversify physical activity types and reconstruct existing exercise programs.

PURPOSE This study aimed to verify the criterion validity of the two-minute step test in older Korean adults, develop an equation for predicting VO2max, and verify cross-validation. METHODS A submaximal exercise test and the two-minute walk test were performed on 150 older adults (74 males and 74 females) aged 65 years or older. Correlation analysis was performed to confirm criterion validity. An equation for estimating VO2max was developed through multiple regression analysis, and cross-validation was confirmed by performing a correlation analysis between measured and predicted values of VO2max. RESULTS The correlation coefficient between VO2max and the two-minute step test was 0.457 (p<.001). The adjusted R2 of the developed VO2max prediction equation was 0.430 (p<.001), and the explanatory variables finally selected were sex, age, number of steps in the two-minute step test, and percentage of body fat. The correlation coefficient between the measured VO2max (19.08±4.36) and the predicted VO2max (19.73±3.36) was 0.654 (p<.001). CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the criterion validity of the two-minute step test in older Korean adults, and the cross-validation of the developed VO2max prediction formula was verified. The explanatory variables of the prediction equation will be easy to apply in the field, and more meaningful results will be derived if the validity of the prediction equation developed for a larger number of participants is verified.
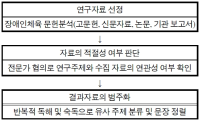
Purpose This study examines the Physical Education curriculum history of special schools, and then in-depth grasps the process of how the sports environment for the disabled has changed by age. Method The research method was literature review analyzing papers, reports and newspapers. For the concrete process, this study verified the relationship between the research subject and the collected data through experts and historians with disabilities to verify the sports data for the disabled. Results First, the process of physical education management of special schools is as follows. in the 1940's and 50's special schools, physical education was carried out simply by gymnastics. but, special schools were differentiated by the characteristics of the disabled, and the institutional foundation for physical education was also imitated by the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s, special schools were shortened in physical education time due to the increase in the number of courses and the strengthening of disability coping programs. in the 1990s, as special sports curriculum was established, customized prescription for students with disabilities was implemented. Second, the process of changing disability sports is as follows. In the 1960s and 1970s, disability sports were mainly focused on special schools, while in the 1980s, disability sports were expanded by the government. in particular, the hosting of the 88 Seoul Olympics and Seoul Paralympics provides an opportunity to equip the disabled with a system, organization and facilities. in the 1990s disability sports was meaningful in terms of academic progress, and with the quantitative growth of the 1980s and the academic foundations of the 1990s, disability sports in the 2000s provided a legal basis and improved welfare conditions for the disabled. In the future, it is necessary to find a way to solve the value of physical education for the disabled more reasonably.




Purpose: This study was to verify the relationship between coaching behavior(autonomy/controlling behavior), self-regulation motivation and performance. Method: 356 athletes (from middle to work and professional team) in individual and team sport completed coaching behavior scale developed by this researchers assessing autonomy and controlling coaching behavior perceived by players, Korea Basic Pyshoclogical Needs Scale (KBPNS) assessing basic psychological needs, Behavioral Regulation in Sport Questionnaire (BRSQ) assessing sports motivation level based on self-determination theory, and sport performance score. To estimate the relationship between coaching behavior, self-regulation motivation and performance, this study employed the structure equation modeling analysis. Results: The relationship between psychological needs, regulation motivation and performance showed that autonomy coaching behavior tend to reinforce competence and autonomy of player. These variables have a positive effect on more inner regulation motivation. Moreover, the intrinsic motivation through stimulation experience was a key factor leading to a positive performance by improving the performance strategy and skill of athletes. Conclusion: These results are meaningful as an empirical evidence that relationship between motivation and performance can be changed according to the type of coaching behavior, and that autonomous coaching behavior play an important role in maximizing the performance of player that provided theoretically form.

PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate how a 10-week online live Pilates training held during the COVID-19 pandemic affected body composition, cardiovascular function, and physical fitness in sedentary middle-aged obese women. METHODS Thirty obese women, aged 30 to 49 years (BMI : 25kg/m2 or more; waist circumference: 85cm or more) who were leading a sedentary lifestyle for more than 8 hours a day were assigned to one of two groups—that is, the Pilates training group (TR) and the control group (CON). Four participants were dropped from the study during the intervention period. Participants in the TR group (n=13) performed online live mat Pilates exercises (3 sessions per week; 60 minutes per session for 10 weeks, whereas participants in the CON group (n=13) were asked to maintain their normal lifestyles during the same intervention period. Independent variables related to body composition, cardiovascular function, venous function in the lower body, physical fitness, and 1-RM (repetition maximum) were measured at pre-test and post-test, and data were compared between the two groups and between the two tests. RESULTS 1) Regarding body composition, body weight, body mass index, fat mass, and waist circumference decreased significantly in the TR group. 2) Regarding cardiovascular function, stroke volume and cardiac output increased significantly in the TR group, and total peripheral resistance decreased significantly in the TR group. 3) Regarding venous function in the lower body, blood flow velocity and blood flow volume of the parenchyma area increased significantly in the TR group. 4) Regarding physical fitness, cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular endurance, flexibility, and balance improved significantly in the TR group. 5) 1RM of biceps curl, lat pull-down, leg curl, and leg extension increased significantly in the TR group. CONCLUSIONS It was concluded that the 10-week online live Pilates training had positive effects on the body composition, cardiovascular function, venous function in the lower body, and physical fitness of middle-aged obese women leading sedentary lifestyles.