PURPOSE This study aimed to a) develop suitable screening tools for identifying gambling severity in Korea and b) explore factors that affect the gambling severity index in order to prevent Korean sports betting users from easily falling into gambling addiction, thus providing practical and useful guidelines in this regard. METHODS This study examined Korean sports fans who had experiences of participating in sports betting (Sports Toto), a legal sports betting system in Korea. Toward this end, an online survey was conducted from May 10 to June 25, 2022. A total of 214 questionnaire results, excluding 23 who gave insincere and/or incomplete answers, were analyzed for normal distribution through skewness and kurtosis, and subscale scores were calculated after performing exploratory factor analysis and reliability analysis using Cronbach’s α. RESULTS A psychological gambling severity index and behavioral gambling severity index were developed based on a stepwise regression analysis, which was conducted using the demographic characteristics of domestic sports betting participants and their lifestyle habits (e.g., smoking and drinking, problem gambling severity index, self-control scale, and gambling expectation scale). CONCLUSIONS First, factors affecting the psychological gambling severity index were identified (having a job, job stability, and security) along with lifestyle habits (smoking and drinking). Second, gender, occupational characteristics, full-time employment, confidence in self-control, and desire for self-improvement were indicated as significant factors that influenced the behavioral gambling severity index.
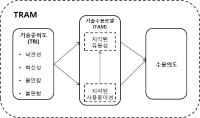
The current study was aimed to examine acceptance intention of sports Wearable products using the Technology Readiness and Acceptance Model. Data were drawn from 271 consumers in their 20s and 30s. Data were analyzed through frequency analysis, exploratory factor analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, simple regression analysis and multiple regression analysis using SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 program. The results were as follows: First, optimism had a positive effect on perceived usefulness but innovativeness, discomfort and insecurity did not affect perceived usefulness. Second, optimism and innovativeness had a positive effect on perceived ease of use and discomfort had a negative effect on perceived ease of use but insecurity did not affect perceived ease of use. Third, perceived ease of use had a positive effect on perceived usefulness. Fourth, perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use had a positive effect on acceptance intention.


PURPOSE This study both validated the Characteristics of Resilience in Sports Teams Inventory (CREST) scale for use in Korean sports and analyzed the impact of team resilience on teamwork and performance. METHODS The study surveyed 462 elite football players by using the CREST scale to measure team resilience in Korean sports. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, exploratory factor analysis (EFA), reliability analysis, correlation analysis, multiple regression analysis, and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). RESULTS First, results confirmed that the CREST scale’s two main factors—resilient characteristics and vulnerabilities under pressure—can be meaningfully applied in the Korean context. Second, resilient characteristics showed positive correlation with life skills, whereas vulnerabilities under pressure showed negative correlation. Third, resilient characteristics positively predicted life skills, whereas vulnerabilities under pressure negatively affected life skills. CONCLUSIONS The CREST scale was found reliable and valid in the Korean sports context, demonstrating that team resilience significantly impacts life skills. Thus, the study contributes to evaluation of resilience in Korean sports teams and provides strategicinsights to improve team performance.
PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the decision-making process for consumers participating in sports centers based on an extended goal-directed behavior model (EMGB), and to provide empirical data for establishing effective operation strategies for sports centers, including additional risk perception of consumers during pandemic. METHODS A total of 446 surveys were used as the final sample. For data analysis, SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 were used for frequency analysis, correlation analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation model analysis. RESULTS Except for hypothesis 2 and 9, all of the hypothesis were chosen. CONCLUSIONS The findings suggested that extended goal-oriented behavior models can increase consumers' cognitive and emotional factors through emotional aspirations, suggesting that a lower risk perception of COVID19 increases their desire to participate in sports centers, and provides academic fundamental data on how to increase and activate sports centers.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to verify their effectiveness as we develop and apply worksheets for improving life skills and resilience of collegiate Taekwondo athletes. Methods The study went through three stages: developing, applying, and evaluating. In the developing stage, literature review, expert meeting, and pilot test (n=25) were conducted to develop the worksheets. In the applying stage, 37 athletes participated in life skills program using the worksheets. Data were collected by survey and in-depth interview. In the evaluating stage, paired t-test, word cloud analysis, and inductive content analysis used to identify the effect of worksheets. Results First, the worksheets were composed of 3 stages (plan, acquisition, implementation) and 15 sessions including 12 factors of life skills. Second, the worksheets were applied in each phases such as planning, acquiring, and implementing. In the planning phase, they understood life skills knowledge and set goals. In the acquisition phase, students learned specific life skills’ strategies. In the practice phase, the acquired life skills were applied and practiced in real life and relationships. Third, the result of paired t-test showed that all the factors of life skills and 6 factors of resilience were significantly improved. In addition, word cloud and in-depth interviews revealed that the participants' cognitive and psychological changes were most prominent. Conclusions The life skills worksheets consists of 12 factors in 15 sessions and can be considered as an effective intervention tool for improving the resilience and life skills of collegiate Taekwondo athletes.

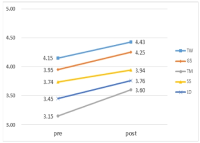
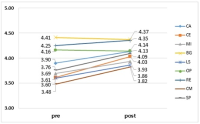










This study was to verify the structure of efficacy related to performance perceived by short-track athletes when playing a match. Therefore, 50 players answered open questionnaires and 200 players participated in construct validity verification, a total of 250 players of short-track members of national, business and university team were sampled during the research phase. The data was analyzed through the study procedures. The results were as follows: First, efficacy structure of players during the match were categorized into three groups as game managing strategy(including course management, race control, match management and selective attention ability), psychological control ability(including positive imagery, match competition, competitive spirit, ability to handle hardship, anxiety control, and patience), and physical usage of ability(including physique, endurance, and quickness). Second, the result of the first construct validity verification through exploratory factor analysis showed 7 factors in 29 items as game management, course management, psychological control, physical use, coping with hardship, speed control and psychological stability. Finally, as a result of confirmatory factor analysis, short-track self-efficacy showed the 5 factor in 15 items except for coping with hardship and psychological stability.

Purpose Recently, studies associated with the negative physical and mental effects of athletes’ pain have received extensive attention. This study confirmed the validity of the pain catastrophizing scale (PCS) developed in clinical settings and is widely used in the sports field, and examined their relationship between the perceived stress levels and fear of pain. Methods The pain catastrophizing consisted of 13 items of three factors which are Helplessness (6 items), Rumination(4 items), Magnification(3 items). To verify the validity, PSC was revised by following the recommended revision guideline procedures. To test the validation of pain catastrophizing, 206 adult athletes were recruited including the collegiate, professional, and national levels. The participants were instructed to complete questionnaires to assess the level of pain catastrophizing, perceived stress, and fear of pain. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to test the fit of measurement model was adopted to examine three higher-order three-factor measurement models. Results In results, confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the Korean version of the pain catastrophizing scale demonstrated a good model fit of measurement when removing one item with a significantly lower factor load as well as the reliability of the scale was reasonable. The pain catastrophizing had a meaningful positive direct relation with perceived stress level and fear of severe pain. In addition, construct validity and predictive validity of PCS showed valid. Conclusions Based on the results of this study, the Korean sports pain catastrophizing scale can be used to measure the subjective pain intensity of Korean athletes. In addition, it is expected to provide fundamental information for evaluating athletes’ post-injury rehabilitation processes.
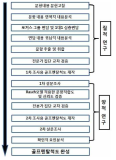
The purpose of present study is to develop the'Golf Mental Scale'that measures and assesses golf players' cognitive, emotional, behavioral response per golf mental factor experienced while competing in depth. In order to achieve this research purpose, Researcher collected raw data of golf mental question through literature review and interview with 8 members of Korean male national golf team and gathered questions per factor through Deductive-Inductive Content Analysis for the raw data. Then, Researcher conducted first and second questionnaire survey targeting 253 of elite & pro golf players and conducted Rasch Model and Confirmatory Factor Analysis for the data collected using SPSS 21.0, Winsteps Ver. 3.65 Program, AMOS 18. The conclusion reasoned out through these research process was as follows: First, golf players' psychological factor structure identified was revealed as Concentration, Self-confidence, Anxiety and Arousal control, Emotion control, Thought control. Total 37 questions were determined. Second, 5 point scale was revealed to be a good fit for Golf Mental Scale. Third, the result of Construct Validity Verification of CFA showed that Golf Mental Scale model was a good fit. Fourth, Reliability of Golf Mental Scale showed high level by recording Cronbach' α value .936. Fifth, Internal Consistency of Convergent Validity and Discriminant Validity was revealed to be satisfied. Eventually, Golf Mental Scale is expected to be used practically as a functional test tool that provides participant's response toward each situation-specific questions concretely and an objective evaluation of participant's golf mental ability per factor considering questions'level of difficulty and participants'characteristic.

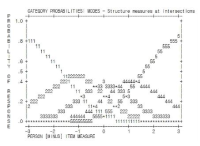
PURPOSE This study aims to develop a coach presenteeism scale with scientifically proven reliability and validity. METHODS In order to achieve the research purpose, preliminary questions were drafted using previous studies (Lee & Kim, 2022) and existing presentation questionnaires (SPS-34, SPS-6, SPS-13). The preliminary set of questions was composed of 23 questions, which were deliberated through a meeting with subject experts. After which, a survey involving 183 coaches was conducted. In this study, statistical verification procedures were conducted through construct validation, exploratory factor analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, internal consistency analysis, convergent validation and discriminant validation. RESULTS Finally, a 2-factor (DRA 5 items, DTP 5 items), 10-item coach presenteeism scale was developed. CONCLUSIONS In this study, a scale with verified reliability and validity was developed to support and investigate the presenteeism phenomenon experienced by coaches. These may be used by coaches themselves to check their presenteeism status and may guide future research to effectively train athletes.
PURPOSE The outdoor camping market size is expected to hit a new high in 2021 as the popularity of outdoor activities surges due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The purpose of this study was to investigate the structural relationships among servicescape, perceived value, flow and behavioral intention, focusing on participants of international outdoor camping exhibition. METHODS Demographic analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation modeling analysis were perfomed. RESULTS The findings suggest that (1) all servicescape factors (attractiveness, cleanliness, accessibility and responsiveness) have a positive effect on perceived value, (2) attractiveness, cleanliness and responsiveness are significant predictors of flow, (3) perceived value affects both flow and behavioral intention, and (4) flow also significantly impacts behavioral intention. CONCLUSIONS These findings highlight that high quality servicescape can result in enhancing a positive perceived value and flow, and in turn leading to behavioral intention of consumers. Hence, it is recommended for practitioners and staff of the exhibitions to considering the strategies for improving servicescape factors in order to achieve their goal.