PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of accelerated rehabilitation exercise on physical fitness, lower extremity isometric strength, and blood variables in older adult women diagnosed with degenerative osteoarthritis. METHODS A total of 29 older adult women diagnosed with degenerative osteoarthritis residing in G city participated in the study, and 19 participants, excluding dropouts, took part in the experiment. They underwent exercise twice a week for 60 minutes per session over a period of 12 weeks. Pre- and post-experiment, the older adult fitness assessment (SFT), lower extremity isometric strength, and blood variables were measured. Data analysis was performed using SPSS 25.0, and paired sample t-tests were conducted to examine the effects before and after exercise. RESULTS The study results showed significant differences in body mass index (BMI) before and after exercise (p<0.05), and the older adult fitness assessment (SFT) showed significant differences in all items (p<0.01). Lower extremity isometric strength showed significant differences in absolute (Nm) and relative (%BW) values of 20° right flexion muscle (p<0.01). In terms of blood variables, significant differences were observed in creatine and ESR before and after exercise (p<0.01). CONCLUSIONS This study’s results suggest that regular physical activity and rehabilitation exercise programs can positively impact the muscular strength, cardiovascular endurance, exercise function, and blood composition of older adult women diagnosed with degenerative osteoarthritis. It is indicated that conducting future research, including periodic exercise programs, could be beneficial in promoting sustained exercise participation.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to analyze the level and characteristics of physical activity (sedentary, light, and MVPA) of high school students according to physical education (PE) class (DWPE: days with PE class, DNPE: days with no PE class) and sex. METHODS Data were collected on 147 students (65 male and 82 female) from four high schools in Seoul city, and physical activity was measured using a three-dimensional accelerometer. The collected physical activity data were input into SPSS 25.0, and the descriptive analysis and two-way ANOVA according to PE class and sex were performed. RESULTS The descriptive statistical analysis showed that 31% (40.7% male and 23.4% female) of participants met the recommended physical activity durations (MVPA of 60 min/day). In the two-way ANOVA, sedentary activity, light activity, and MVPA showed statistically significant main and interaction effects according to PE class and sex. According to the results of the interaction effect analysis, the gap in physical activity between DWPE and DNPE was large in male students. For male students, light activity and MVPA significantly increased on the day of the PE class, and sedentary activity significantly decreased. However, for female students, DWPE and DNPE did not differ significantly in all levels of physical activity. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, the level of physical activity of Korean high school students was relatively low, and the effect of daily-life physical activity in the PE class was limited to male students. Accordingly, an alternative should be introduced to increase the physical activity of female high-school students through PE classes.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to analyze the type of and interest in home training video contents using the YouTube platform. METHODS Web crawling was performed using Python and a total of 3,937 sets ofvideo information (title, content, number of views, upload date) were obtained, 3,155 of which were finally selected for the study material. Overlapping and unrelated content were excluded. The data of text underwent 3 stages of preprocessing, the TF and TF-IDF of the keywords were calculated to identify the main keywords, and the LDA algorithm was applied in the topic modeling to successfully identify the types. In order to understand the level of interest by type, the number of views was subdivided into the percentage of the assigned type. RESULTS First, the types of home training videos were classified into bare whole body exercise for aerobic and muscular power strengthening, Pilates exercise for core and upper body strengthening, upper body exercise using tools, lower body line exercise, posture correction and upper body stretching exercise for pain relief, hip-up exercise, dance and tabata exercise for diet, diet and lower body correction stretching exercise for diet, and bare body exercise for core and lower body strengthening. Second, it was found that the proportion and interest were high in the contents of bare whole body exercise for aerobic and muscular power strengthening, dance and tabata exercise for diet, diet and lower body correction stretching exercise for diet. CONCLUSIONS The findings of this study may provide baseline data about the development of the active online home training videos in the market.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to compare the dynamic postural control of youth athletes with and without a history of lateral ankle sprains. METHODS Twenty-eight youth athletes (14 lateral ankle sprain, 14 healthy control) participated in this study. All participants answered the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure questionnaire and were subject to the Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) for dynamic postural control evaluation to collect the joint angles of the lower extremity, a center of pressure (COP) path, and COP velocity. Independent sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U-test were performed to analyze the difference between the groups. RESULTS The lateral ankle sprain group (LAS) was found to have a long experience in participating in sports, and low Foot and Ankle Ability Measure scores were identified when compared to the healthy control (CON; p<0.05). LAS was observed with a short reach distance, less hip flexion, and dorsiflexion angles during the anterior direction of SEBT when compared to CON (p<0.05). Furthermore, LAS showed a slower anteroposterior and mediolateral center of pressure velocities in the posteromedial aspect of SEBT and a slower anteroposterior COP velocity in the posterolateral aspect of SEBT when compared to that of CON (p<0.05). There were no differences between the groups with respect to the other variables (p>0.05). CONCLUSIONS Based on these results, decreased anterior reach distance of SEBT may be affected by changing the dynamic posture control strategy of the lower extremity joint on the sagittal plane in LAS.
PURPOSE This study aimed to apply a capacity building program to sport life skill leaders and to provide cases of this process. METHODS The study participants included four leaders (male=2, female= 2, Mage=37.5) who were managing a sport life skills program at a university. They participated in a capacity building program, which consisted of (a) understanding (leader seminar), (b) application (managing the sport life skills program), and (c) evaluation (leader’s self-reflection), which were conducted in eight sessions. Four leaders conducted self-evaluations using program quality assessment (PQA) during every session, and quantitative and qualitative data were collected. Qualitative data were derived using a cross-case analysis, and quantitative data were used for calculating the effect size after performing the paired t-test. RESULTS Analyzing the reported cases of sport life skill leaders, the use value of the capacity building program was identified. Furthermore, the cases reported by the four leaders enabled observation of how the leader’s capabilities were strengthened. In the paired t-test, the effect size of physical and psychological safety, appropriate structure, supportive relationship, opportunities to belong, support for efficacy mattering, opportunities for life skill building, excluding integration of family, school, and community effort, were all significant. All effect sizes were found to have “very large effects.” CONCLUSIONS The capacity building program played a positive role in strengthening the leaders’ life skill coaching capabilities. These findings have practical implications—chiefly, it is important to strengthen leaders’ or coaches’ capabilities in order to foster life skill development and transfer of student-athletes.
PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze physical activity (sedentary, light, moderate to vigorous physical activity [MVPA]) characteristics of middle school students based on region (urban and rural) and sex. METHODS Data were collected from 216 students across 6 middle schools located in medium-sized urban (3 schools) and rural areas (3 schools), and the relevant physical activity was measured using a three-dimensional accelerometer (GT3X model). The collected data were inputted into the SPSS 20.0, and descriptive analysis and two-way ANOVA based on region and gender were performed (<.05). RESULTS The descriptive statistical analysis resulted in the following achievement rate of the physical activity standard (MVPA 60 minutes/day): 9.4%. The two-way ANOVA showed that the main effect according to gender was found in sedentary activity (F=5.258), light activity (F=6.790), and MVPA (F=32.274); furthermore, the main effect according to region was found in light activity (F=10.888) and MVPA (F=7.876). Interaction effect according to region and gender was found at all intensities, and the gap between rural and urban in male students was larger compared to that of female students. CONCLUSIONS After COVID-19, the level of physical activity among adolescents has worsened; this study found the problem of "decrease in physical activity; increase in sedentary activity" to be more serious among male students in urban areas.
PURPOSE Recreation specialization theory, which is characterized by a unique development process and progress, has been found to have varied pathways that develop in different patterns based on each dimension of recreation specialization. This study aimed to investigate how each sub-dimension of specialization changes as the degrees of experiential participation (frequency, period, and intensity of participation) and goods investment (expenditure) of the scuba divers increase. METHODS In the summer of 2021 (May-August), a purposive sampling method was used to collect samples from young scuba divers, and 278 copies of valid data were used for the final analysis. Frequency analysis, descriptive statistical analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, curve estimation analysis, and hierarchical regression analysis were performed using SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 24.0 ver. RESULTS The findings were as follows. First, the quadratic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the scuba divers’ participation intensity and cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations based on experience. Second, the cubic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the participation period, frequency of participation, and cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations of scuba divers. Third, the cubic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the expenditure cost of scuba divers and the cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations in the center of the goods. As the period, frequency, and expenditure of scuba diving participants increased, the relevant cognitive, behavioral, and affective specializations did not progress in a linear manner; instead, they went through an intermediate maintenance stage and developed to a higher level. CONCLUSIONS Progressive and meaningful consumption of experiences and goods further promotes recreation specialization. Any future follow-up study should identify a trade-off point in the development of the recreation specialization in a step by step manner.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of midsole hardness on gait mechanisms by wearing a backpack. Methods Ten healthy adult males(age:23.20±1.33yrs, heights: 1.72±0.03cm, weights: 67.60±5.95kg) participated in this study. Subjects walked at a speed of 1.5m/s in an 8m section wearing randomly selected midsole hardness (Soft, Medium, Hard) shoes and backpack (30% of body weight). For measurement of body movement, 10 infrared cameras (Vicon motion capture system, UK) and force plate (AMTI, ORG-6, US) were used. Results First, in the shock phenomenon change, the ground contact time was longer when wearing a backpack. Second, in the shock absorption strategy, the pack plantarflexion velocity at the ankle joint was faster in Hard than Soft, and the pack dorsiflexion moment decreased when wearing a backpack (p<.05). Also, the pack extension moment of the knee increased significantly when wearing a backpack. Fourth, in the mechanical negative work, the ankle joint performed less work than the medium soft, and the knee joint increased as the backpack was worn (p<.05). Conclusion As a result of this study, the difference in the hardness of the midsole used in this study does not seem to affect the biomechanical movement of gait even when wearing a backpack. In future studies, it is necessary to investigate the effect of the midsole through the presence or absence of shoes or inducing muscle fatigue.

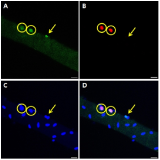
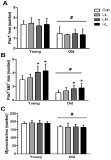
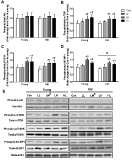
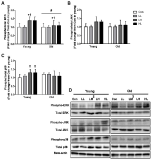
Purpose This is the first study to examine whether age impacts the response of single muscle fibers to high/low frequency and high/low volume electrical pulse stimulation. We performed in vitro experiments to evaluate the effect of low-frequency high-volume electrical pulse stimulation (EPS) on mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, and satellite cell activation in singles fibers of young and aged muscles. Methods Isolated single fibers from gastocnemius in 12-wk (n=21) and 72-wk (n=21) old male C57BL/6 mice were divided into four groups: 1) control (Con) received no EPS, 2) low-frequency low-volume EPS (LL), 3) low-frequency high-volume EPS (LH), and 4) high-frequency low-volume EPS (HL) were made to contract using independent EPS protocols. Satellite cell activation and anabolic pathway (mTOR and MAPK signaling) were measured before and after EPS. Results The number of quiescent (Pax7+/Ki67-) and active (Pax7+/Ki67+) satellite cells, myonuclear content and the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and ERK were higher in young when compared with old. However, regardless of age, LH and HL EPS significantly increased the number of activate satellite cells (142%, both) and phosphorylation of mTOR (129% and 133%, respectively), p70S6K (133% and 136%, respectively) and 4E-BP1 (140% and 129%, respectively) compared with Con. The protein expression of ERK phosphorylation only increased by LH EPS in both the young and old groups (123% and 125%, respectively). Conclusion Low-frequency high-volume EPS stimulated satellite cell activation and the mTOR signaling pathway in older similar to young muscle.

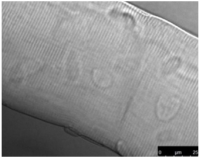
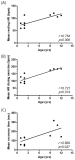
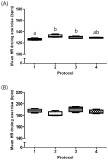
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate changes of the cardiovascular system by comparing heart rate (HR) and blood responses to exercise in younger and older adult dogs and to verify the value of dogs as aging model in exercise science research. Methods A total of 11 healthy beagles were divided into 2 groups according to age: younger adult dogs (1~2 years old, 7 animals) and older adult dogs (9~11 years old, 4 animals). Each animal exercised on the treadmill for 25 minutes, twice a week, and for 4 weeks. The exercise intensity was gradually increased by applying four different protocols. Resting HR, HR during exercise, and HR recovery time were determined as HR parameters. Biochemical analysis was performed on blood samples. The independent Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA were used to analyze the mean difference of each variable. The associations between age and HR parameters were determined using Spearman‘s analysis. Results Older adult dogs showed higher HRs during rest and exercise than younger adult dogs. HR recovery time was significantly longer in older adult dogs than in younger adult dogs. A strong positive relationship was observed between beagles’ age and resting HR, HR during exercise, and HR recovery time, respectively. The heart rate response to the treadmill exercise was similar between the 1st week and 4th week in younger and older adult dogs. Exercise significantly reduced the white blood cell level in older adult dogs and increased the alkali phosphatase level in younger adult dogs. Conclusions The results of this study demonstrated that short-term treadmill exercise may have a positive effect on the aerobic capacity, inflammation, and bone formation, suggesting that dogs are valuable as aging model in exercise science research.