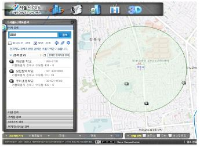
This study measured the accessibility of public exercise facilities within a residental area of a metropolitan community and examined how the accessibility can affect physical activity participation of residents. Initially, a total of 639 residents, who were aged between 19-70, visited Metabolic Syndrome Management Center of the Community Public Health Center, and registered for a Obesity Clinic Program, was listed as potential subjects. And those who responded to Physical Activity Questionnaire were selected for the analyses (n=92, 14.3% of 639). The relationships between physical activity level and accessibility to public exercise facilities were analyzed. Objective distance to public facility was related to ‘volume of participation to vigorous physical activity(r=.209)’, 'total volume of participation to physical activity(r=.206)’. And perceived distance to public facility was related to ‘volume of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.235)’. perceived transport time to public facility was related to ‘duration of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.239)’, ’volume of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.306)’, and ‘volume of participation to total physical activity(r=.273)’. In contrast, the difference between objective distance to public facility and perceived subjective distance to the facility was negatively related to ‘duration of participation to moderate-intensity physical activity(r=-.221)’. The perceived numbers of public facility was positively related to ‘frequency of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.237)’, ‘frequency of participation to walking(r=.273)’, ‘volume of participation to walking(r=.251)’ and 'total volume of participation to physical activity(r=.252)’. The predictor of 'total volume of participation to physical activity was perceived numbers of public facility(R2=.153, p=.046). The results revealed that the subjective accessibility to public health facilities was more influential to physical activity participation than the objective accessibility. Further research was warranted while using diverse populations as well as considering a inclusion of environmental factors.


PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the association of physical activity level with insomnia severity (Normal, Subthreshold, Moderate and Severe) in adolescents and to use it as a basis for insomnia prevention. METHODS This study was conducted on a cohort of 50 adolescents under the age of 20 (19 males, 31 females) recruited from Hospital N in Incheon, Korea. Participants were categorized into groups according to the severity of insomnia in both males and females using the Korean version of the Insomnia Severity Index-Korean (ISI-K). The Korean version of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire was also used to calculate participants’ weekly moderate and vigorous physical activity. RESULTS The participants’ characteristics did not differ by insomnia severity in males, but there were significant differences in weight (p=.008), BMI (p=.019), SBP (p=.004), and DBP (p=.019) in females by insomnia severity. In male adolescents, there was no significant difference in the amount of physical activity by insomnia severity, but there was a trend toward decreased amount of physical activity with increasing severity. Among female adolescents, there were significant differences in the amount of physical activity by insomnia severity: moderate (p<.05), high (p<.05), and moderate-high (p<.05). In the unadjusted model, adolescents who did not meet the recommended amount of physical activity (150 minutes per week) were more likely to have insomnia (OR=4.67, 95% CI=1.34–16.24) than those who met the recommended amount of physical activity. The model after adjusting for covariates (gender and body mass index) also showed an association between the recommended amount of physical activity and insomnia (OR=3.94, 95% CI=1.17–13.28). Negatice correlations was found between insomnia index and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (r=–.357, p=.013). CONCLUSIONS Adolescents are approximately 4.67 times more likely to suffer from insomnia if they do not meet physical activity recommendations, and there was a negative correlation between the insomnia index and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, suggesting that physical activity should be increased to reduce the insomnia index.

The purpose of this study was to explore Physically Activity Lifestyle pattern & constraints of high school girl in city, and then to propose P.A. promotional ways. I used International Physical Activity Questionnaire Long version and accelerometer to examine outline of P.A. pattern, and photo-voice as qualitative research techniques. The results were as followings. First, sedentary lifestyles of students in G girls' high school was terrible. Accelerometer was said that their inactive time were about 92.4%, however their moderate to vigorous time about 0.76% of the total time of a week. And, school domain of four domains(school, transportation, leisure, domestic chores) were the most active domain of all. Second, P.A. constraints were analyzed as 'because of something no'(time, effort, will, space, physical skills and person) and 'because of something'(smart phone, car, gaze, rules). The key cause were a shortage of time caused by academic based on school curriculum, sedentary leisure and transportation culture. Lastly, I proposed high school girl' P.A. promotional ways in basis of social ecological model.










Purpose The purpose of the study was to determine difference of body composition, bone mineral density and health-related fitness by physical activity level in young women. Methods A total of 90 women aged 19-29 years participated in this study. The subjects were divided into three groups (low, middle, and high level) according to the physical activity level estimated by bone-specific physical activity questionnaire(BPAQ). Body height and weight were measured. Body composition parameters including four sites of bone mineral density(BMD) were estimated by DXA (Hologic, QDR-4500, USA). Health-related fitness tests was assessed using sit & reach, grip strength, sit-ups, and VO2max. Statistical analysis was performed using SAS version 9.4. All data were presented in terms of means and standard deviations. One-way ANOVA was applied to determine difference of dependent variables by physical activity level. Duncan's multiple range test was used as a post-hoc test. The statistical significance level was set at p < .05. Results There were significant differences on body weight(F = 4.867, p = .01), body mass index(F = 5.053, p = .008) and fat-free mass(F = 8.364, p = .0001) among the three groups. Significant differences were found on whole body BMD(F = 16.730, p = .0001), lumbar BMD(F = 11.480, p = .0001), femur BMD(F = 42.182, p = .0001) and forearm BMD(F = 5.560, p = .005) among the three groups. There were also significant differences on sit and reach(F = 11.433, p = .0001), sit-ups(F = 17.972, p = .0001), VO2max(F = 3.106, p = .05) and duration of GXT(F = 7.479, p = .001). Conclusions There were differences on body composition, bone mineral density and health-related physical fitness by physical activity levels. Nevertheless, the questionnaire used in this study was not able to judge participation in various exercise types including aerobic exercise or resistance exercise. Therefore, in the future study, longitudinal study considering various types of physical activity and dietary intake will be needed.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate characteristics of levels of physical activity in considering gender and different types of competition-oriented physical activity classes using three-dimensional accelerometers. Methods A total of 981 students(505 male students, 476 female students) in six different types of physical education classes were participated in this study. All of the six different types of physical education classes were competition-oriented classes, and levels of physical activity were accessed by three-dimensional accelerometers. Data were analyzed using t-test and ANOVA. Results First, descriptive analyses of participation time of levels of physical activity showed that MVPA of physical education classes is 10.26 mins (22.89%) on average, and, MVPA showed differently in different types of physical education classes in the order of T ball(14.61 mins), flying disk(12.61 mins), soccer(10.78 mins), volley ball(10.56 mins), basketball(9.64 mins), and table tennis(5.73 mins). Second, female students showed significantly lower levels of MVPA in all the different types of physical education classes. Third, post-hoc analyses showed that significantly higher levels of MVPA were found in T ball physical education classes and significantly lower levels of MVPA were found in table tennis physical education classes, compared to other types of physical education classes. Conclusions MVPA in physical education classes is not satisfied with recommended MVPA, and MVPA in Korean physical education classes is lower than MVPA in same types of physical education classes in other countries. In addition, significant mean differences of MVPA are found between male and female students, and new sports physical education classes show higher levels of MVPA compared to classic sports physical education classes. These results indicate that competition oriented physical education classes widely used in Korea need to find ways to increase MVPA and to overcome different levels of MVPA between male and female students.
This article analyzes and compares the methodologies used in physical activity participation surveys from England, Australia, and South Korea. Specifically, it examines the “2021–22 Active Lives Adult Survey” from England, the “2021–22 AusPlay (15+)” from Australia, and the “2022 National Sports Participation Survey” from South Korea, highlighting both similarities and differences in their approaches. The analysis led to two key insights. First, there is a need to expand the scope of respondents in South Korea’s National Sports Participation Survey. Currently, the survey targets only 0.02% of the population aged ≥10 years, whereas the surveys in England and Australia gather data from a wider age range and more diverse regions. Therefore, South Korea should adopt online, postal, and mobile survey methods to widen the respondent pool and enhance the representativeness and reliability of the data collected. Second, South Korea needs to update its physical activity participation standards. The current benchmarks fall below international recommendations. Establishing new criteria that specify activity duration, intensity, and type is essential for effectively improving public health policies. The results of this study emphasize the importance of accurately assessing and enhancing physical activity participation in South Korea. These findings are expected to contribute to the development of effective sports policy standards in line with the World Health Organization’s global action plan.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of COVID-19 on elite youth athletes by investigating their activities and eating habits before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. METHODS This study included 917 elite adult athletes from 19 sports and were grouped into 6. The questionnaire included items regarding demographics, physical activity, sleep, and eating habits before and after COVID-19. A total of 44 questions requiring subjective short answers were included. Statistical significance was set at p< 0.05. RESULTS After COVID-19, vigorous and moderate activity decreased across all sports; however, light activity increased in almost sports. Time spent sitting increased across all sports. The difference in the number of meals consumed varied among sports, and the number of competitions decreased in all sports. CONCLUSIONS The COVID-19 pandemic appears to be finished but has not ended yet. Athletes must determine the best way to maintain their physical, physiological, and psychological states close to their original abilities. Determining this will provide the greatest impact on the return of athletes after COVID-19; this study will be helpful.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the moderate to vigorous physical activity(MVPA) and sedentary time measured by accelerometer. Furthermore, the level of physical activity and adherence rate of physical activity guideline(PAG) were compared with the self-reported questionnaire. Methods The MVPA, sedentary time, and adherence rate of PAG according to age and sex were examined to people who agreed to wear accelerometers among the participants of the 2014-2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. To compare the relationship between accelerometer and self-reported questionnaire, Chi-squared test and Spearman correlation analysis were performed. Results The MVPA of the accelerometer-total(AT) was 40.6 minutes/day for men and 31.1 minutes/day for women. Sedentary time was 502.9 minutes/day for men and 498.9 minutes/day for women. The MVPA of accelerometer-bout(AB) estimates was 16.4 minutes/day for men and 14.2 minutes for women. On the other hand, the MVPA of the self-report was 95.8 minutes for men and 64.3 minutes for women, and the sedentary time was 471.2 minutes for men and 455.2 minutes for women. The adherence rate of PAG was 55.6% of the self-report, 56.1% of the AT, and 21.4% of the AB. The correlation between self-report and accelerometer was statistically significant(p < 0.01), but showed a weak correlation coefficient(rho=0.112-0.351). There was no association between AB and self-report(p < 0.01). The sensitivity and specificity of the self-report were 71.3% and 48.6%, respectively. The positive and negative predictive values of the self-report were 27.5% and 86.1%, respectively. Conclusions As a result of this study, self-reported physical activity level by questionnaire had more MVPA and less sedentary time than the accelerometer-determined physical activity. In addition, the adherence rate of the PAG differed from accelerometer and self-report. The difference was significantly increased when comparing AB with the self-report. Therefore, great care must be taken when interpreting accelerometer and self-report questionnaire. Further research will be needed on specific methods that can be used by complementing the two measurement tools.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to explore the physical activity promotion plans for female student by revising and supplementing the SPARK program which is actively applied as a P.E physical activity improvement program recently. Methods To achieve this, this study followed the custom of action research and apprehended problem in female students' physical activity in SPARK soccer program(first action and examination), problem solving plan(replanning), execution and evaluation of replanned SPARK soccer program (second action and evaluation). The collection and analysis of data was conducted by sequential explanation strategy. Specifically, the study utilized 3 dimensional accelerometer to measure the physical activity in P.E class, and collected data which could apprehend the experience of students by utilizing qualitative study tools(observation, class note, interview). To analyze the collected data, the study utilized mixed-methods study analysis method developed by Greene(2007). Results The study results are as follows. As for the result of first action(October~November 2014), SPARK program increases the entire physical activity in P.E class, but the female students' activity was relatively lower than male students'. The reasons for lower physical activity of female students' were unmotivated class, burdensome class, alienated class. These were specified into teaching strategy to replan and execute the second action (May~June 2015). Compared to first action, the second action showed positive physical activity, and the MVPA of female students' showed statistical difference (<.01). As for the result of qualitative analysis, the positive grounds of second action are 1) motivative resource like "necessity", 2)hard but meaningful learning activity, and 3)kind P.E teacher. Conclusions In conclusion, the implementation of a soccer class with a modified supplement to the SPARK program can enhance physical activity of female middle school students.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore environmental constraints that hindered the physical activity of female students in daily life, and then to provide alternatives to improve the problems based on the social ecological model. Methods Research participants were twelve female students to be selected in two schools(Norang, Parang middle school), the process of data collection(orientation, photovoice implementation, focus group interview) and analysis(choosing a photo, contextualizing, subjecting) were conducted according to the Photo-voice. Results The constraints of physical activity in daily life were categorized on ‘playground as like a desert’(leisure domain), ‘space of recess and in-active play’(family domain), ‘transportation replaced by mom and dad car’(transportation domain), ‘space of the only exercise as well as reproduction of gender discrimination’(school domain). Conclusions The environmental constraints were analyzed as academic, physical, daily living, socio-cultural environment. Lastly, alternatives for promoting physical activity of female student were proposed in the level of organization, community, public policy based on the social ecological model.













