PURPOSE By analyzing trends in Taekwondo demonstrations, specifically in breaking and performances, to date, this study aims to offer timely insights and set the groundwork for future research. METHODS We used Korean abstracts from a total of 425 papers containing the keyword “Taekwondo demonstrations” spanning 20 years from April 2004 to April 2023. We employed Python 3.5.2 to conduct dynamic topic modeling (Latent Dirichlet Analysis, LDA) and to examine the correlation between the topic distribution by section and the publication year. RESULTS The main findings from the LDA are as follows. Topic 1 (10%): “The development of demonstrations: performance in culture and art, ” Topic 2 (11%): “The development of formalized rules and judgments in a demonstration event,” Topic 3 (08%): “A study on the educational courses and professionalism of Taekwondo coaches,” Topic 4 (11%): “Technical movements and kinematic characteristics,” Topic 5 (09%): “A study on marketing perspectives of demonstration performances,” and Topic 7 (33%): “Global exchange: the development and rise of internationalization.” In the correlation analysis between the topic share by section and the publication year, Topics 1 to 5 exhibited no statistically significant correlation. However, Topic 6, “A study on the attainment of events, training, and the psychological factors influencing athletes” and Topic 7, “Global exchange: the development and rise of internationalization,” also displayed a very statistically significant but negative correlation. CONCLUSIONS Future research should focus on studies on the psychological management of athletes during the performance of specific techniques and training methods. Further research considering the global characteristics of Taekwondo may be required.
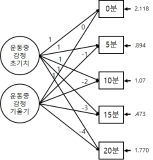
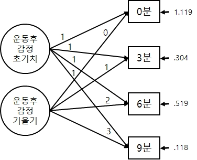
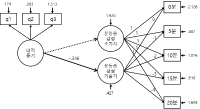
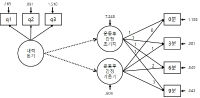
Recent research on exercise and affect has examined participants` affective changes during and after exercise with a longitudinal approach. With regard to this viewpoint, a theoretical model (Dual Mode model) has been presented to explain the different change of affect in an exercise setting and the model identified the impact of psychological factors on the affective changes. However, not only there is little empirical studies on the dual-mode model, but some relevant research has used an inappropriate statistical method (ANOVA), which cannot effectively explain the overall trends in affective change during and after exercise. Exiting research has a limitation to generalize the DM model examining only a certain gender such as active male or inactive female participants. Thus, the aim of present study was to investigate the effect of intrinsic motivation on affective change during and after exercise in participants who do not take part in regular exercise considering gender based difference. 51 inactive university students (M: 36, F: 15) responded a survey measuring intrinsic motivation for running activity and participated in moderate-intensity running exercise to examine affective change during exercise. Therefore, present study examined the influence of intrinsic motivation as a psychological variable on the trend of affective changes during and after exercise based on the dual mode model. Results from the latent curve model analysis revealed that there were decreasing trends of affect during exercise and the trends were individually different. Importantly, the decreasing trends were weaker in the participants with higher intrinsic motivation[FL=-.34, p=.000]. Additionally, participants` affective responses were positively changed after the exercise in general, but the changes were not influenced by intrinsic motivation. Therefore, the decreasing trend of affective change during exercise was weaker in the participants with higher intrinsic motivation, and the positive change in affect after exercise was not influenced by intrinsic motivation.


Purpose: This study was to verify the relationship between coaching behavior(autonomy/controlling behavior), self-regulation motivation and performance. Method: 356 athletes (from middle to work and professional team) in individual and team sport completed coaching behavior scale developed by this researchers assessing autonomy and controlling coaching behavior perceived by players, Korea Basic Pyshoclogical Needs Scale (KBPNS) assessing basic psychological needs, Behavioral Regulation in Sport Questionnaire (BRSQ) assessing sports motivation level based on self-determination theory, and sport performance score. To estimate the relationship between coaching behavior, self-regulation motivation and performance, this study employed the structure equation modeling analysis. Results: The relationship between psychological needs, regulation motivation and performance showed that autonomy coaching behavior tend to reinforce competence and autonomy of player. These variables have a positive effect on more inner regulation motivation. Moreover, the intrinsic motivation through stimulation experience was a key factor leading to a positive performance by improving the performance strategy and skill of athletes. Conclusion: These results are meaningful as an empirical evidence that relationship between motivation and performance can be changed according to the type of coaching behavior, and that autonomous coaching behavior play an important role in maximizing the performance of player that provided theoretically form.

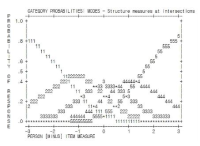
The purpose of present study is to develop the'Golf Mental Scale'that measures and assesses golf players' cognitive, emotional, behavioral response per golf mental factor experienced while competing in depth. In order to achieve this research purpose, Researcher collected raw data of golf mental question through literature review and interview with 8 members of Korean male national golf team and gathered questions per factor through Deductive-Inductive Content Analysis for the raw data. Then, Researcher conducted first and second questionnaire survey targeting 253 of elite & pro golf players and conducted Rasch Model and Confirmatory Factor Analysis for the data collected using SPSS 21.0, Winsteps Ver. 3.65 Program, AMOS 18. The conclusion reasoned out through these research process was as follows: First, golf players' psychological factor structure identified was revealed as Concentration, Self-confidence, Anxiety and Arousal control, Emotion control, Thought control. Total 37 questions were determined. Second, 5 point scale was revealed to be a good fit for Golf Mental Scale. Third, the result of Construct Validity Verification of CFA showed that Golf Mental Scale model was a good fit. Fourth, Reliability of Golf Mental Scale showed high level by recording Cronbach' α value .936. Fifth, Internal Consistency of Convergent Validity and Discriminant Validity was revealed to be satisfied. Eventually, Golf Mental Scale is expected to be used practically as a functional test tool that provides participant's response toward each situation-specific questions concretely and an objective evaluation of participant's golf mental ability per factor considering questions'level of difficulty and participants'characteristic.

PURPOSE This study seeks to explore the subjectivity regarding leisure constraints perceived by college student-athletes. METHODS Based on Q methodology as an analysis framework, 25 Q-samples and 25 P-samples suitable for the research purpose were selected, and Q-classification and Q-factor analysis were conducted. RESULTS The leisure constraints were categorized into “Type Ⅰ: Psychological constraints,” “Type Ⅱ: Financial constraints,” and “Type Ⅲ: Spatio-temporal constraints.” The three types provided discussions on “strong athlete identity of student-athletes,” “role conflict between students and athletes,” “core competencies of student-athletes,” “current student-athlete support project,” and “school sports camp training.” CONCLUSIONS College student-athletes’ leisure constraints are closely related to strong athlete identity, anxiety about enjoying leisure, cost burden, and closedness of camp training, and each type provided new perspectives on discussions related to Korean student-athletes.
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop a model for life skills transfer in sport. METHODS A literature review of research on life skills transfer was conducted. The prior representative studies on sport life skills and transfer models were selected and discussed to improve the validity of this study. RESULTS First, based on the basic psychological needs of the internalization and generalization of life skills, the model for life skills transfer should consider the influence of the explicit and implicit climate and environment. Furthermore, access to cognitive processes is required based on the conceptualization and integration of transfer. Second, the concept of a transfer was defined, and key issues of the cognitive processes that support the connection between the sport domain and out of the sport domain were discussed. Third, the model for life skills transfer in sport was presented. In this model, life skills transfer occur through sport context, cognitive process, promoting factors, and out of sport context. CONCLUSIONS Since the 2000s, research on life skills and transfer in sport has developed quantitatively based on positive youth development theory. Unfortunately, research on this area in South Korea is very insufficient. This study suggests a model for life skills transfer in sport based on an extensive and systematic analysis of the prior research, and this model can be used for future research.
PURPOSE This study investigates the effectiveness of biomechanics information on intermediate golfers driver swing learning. It analyzes changes in center of pressure (COP) patterns, GRF Direction Inclination, driver performance, and learners psychological responses to determine the learning effects. METHODS Subjects were 32 right-handed male golfers (handicap 15-23) who had no difficulty in performing the golf driver swing (Full swing). Four groups were selected, BF (Biomechanics Feedback group), BVC (Biomechanics Verbal Cue group), CB (Combination group), and CT (Control group), and assigned randomly. Driver swing learning showed results after 6 weeks,and a transfer test was conducted 1 week after the completion of the learning. RESULTS Analysis of COP patterns and GRF Direction Inclination indicated changes in the BF, BVC, and CB groups. Furthermore, analysis of driver distance (m), club head speed (km/h), and ball spin rate (rpm) revealed that during the 6-week acquisition phase, all three groups (excluding the control group) showed improvements in driver distance, club head speed, and ball spin rate. However, there were no statistically significant differences among the groups. In contrast, the transfer test showed statistically significant differences among the groups, with the CB group exhibiting the highest driver distance. Learners' psychological responses during the learning process were trust, understanding, and satisfaction. The understanding factor was relatively higher in the CB and BVC groups compared to the BF group. CONCLUSIONS In summary, biomechanics information (BI) was effective in improving driver performance, and changesappeared in the COP pattern and GRF Direction Inclination, indicating a change in movement. Therefore, BI can be fully utilized for athletes or high-level advanced players and for motor learning for intermediate-level students.However, BI can only improve learning effects by strengthening learners' “understanding” when visual feedback forms and verbal cues are provided together.

Purpose This study was designed to develop a team building program that helps freshmen student-athletes to adapt to college life and enhance team function and process and to examine the effects of this program. It could provide basic information of a team building program that effectively accelerates team function in the college team sports domain. Methods The program was developed through this process. First, an open-ended questionnaire was utilized to discover the needs of the program. Second, the results of needs of the program and important factors of team-building program were taken into consideration. Third, expert meetings were conducted. Consequently, the program consisted of three stages of total 10 sessions which was 90 min long. The questionnaires(Group Cohesion Questionnaire and Coach-Athlete Relationship Questionnaire), experience report, and program evaluation form were used as measures to identify the effects of the developed program. SPSS version 24.0 and inductive analysis were used to analyze the data. Results The results of this study are as follows. First, there was no statistically significant influence between developed program and the level of group cohesion. In contrast, the level of coach-athlete interaction was significantly increased. Second, the analysis of experience report revealed that this program reduced interpersonal conflict between team members and formed positive interpersonal relationship by mind of respect and consideration. Conclusion In conclusion, the hierarchical culture was strongly formed and team member suffered from the dual role of athlete and student in Korean college team sports. Thus, these should be resolved in order to enhance team function and process. As a results, this process could increase team performance as well as offer psychological stability to college student-athletes.

PURPOSE This study first investigated how different types of sport team logos (emblem vs. mascot) influence consumer behavior through warmth and competence and then examined the moderating effects of consumer characteristics (gender) and contextual cues (perceived competence) on these relationships. METHODS A nationwide sample of adults age 20 was selected using quota random sampling based on gender. A 2 (logo type: emblem vs. mascot) × 2 (gender) × 2 (contextual cue: high competence vs. low competence) experimental design was employed, with participants randomly assigned to each group. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) with Mplus 8 was employed to assess the measurement model’s reliability and validity, and hypothesis testing was conducted through structural equation modeling (SEM), measurement invariance tests, and multigroup SEM analysis. RESULTS Findings indicate that anthropomorphized mascot logos, compared to emblem logos, generate more positive attitudes and psychological responses (warmth and competence) to the team. Gender’s moderating effect on the relationship between logo type and consumer perceptions (warmth and competence) was not significant, but contextual cues’ moderating effect was partially significant. CONCLUSIONS This study highlights of perceived warmth and competence’s crucial role in shaping consumer attitudes toward sports teams through logo design. These findings offer meaningful insights for sports teams and marketers to optimize branding strategies and enhance fan engagement.
Recent studies focus on Metabolic Equivalent Task (MET) to measure levels of and areas of peoples’ physically active lifestyle because MET more readily translate peoples ’subjectively perceived physicality into standardized scores. MET also allows researchers to clearly understand the relationships between peoples’ physicality and psychological variables. Thus, the purpose of this study was to understand the levels of and areas of MET among Korean middle school students and to analyze the relationships between MET scores and physical self-efficacy. A total of 278 questionnaires were analyzed using SPSS 18.0. Exploratory factor analysis, descriptive analyses, and regression analyses indicated that middle school students’ physically active lifestyle occurred in the order school, leisure, housework, and transportation areas. Female students did more physical activity in the areas of housework and transportation, compared to male students. In contrary, male students did the majority of physical activity in the areas of school and leisure. Physical self-efficacy affected students’ MET scores, especially for vigorous intensity activity. With regard to gender differences, physical self-efficacy affected male students’ MET scores in the area of leisure while female students’ MET scores were affected in the areas of school and housework. The results were discussed in light of methodological and pedagogical perspectives, and future research suggestions were provided in the discussion.