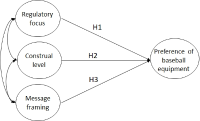
Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the propensity to consume the consumer of the baseball equipments who have difference of the product preference by regulatory focus, and who have construal level and suitable message framing. Methods Populations are consumers who have purchased the baseball equipments before, and the sampling groups, five different society baseball group’ league from Seoul and Kyeongi-do, were distributed, 318 copies, by convenience sampling. The questionnaire proceeded by three-way completely randomized design with stimulated sentences of four different advertisement compartmentalized by the regulatory focus, construal level and message framing. The analysis utilized SPSS 21.0 to perform the frequency analysis, manipulation check, independent t-test, two-way ANOVA, and Scheffe was used to post-hoc. Therefore, the result of this study is as below. Results First, after analyzing the distinction of the regulatory focus of the consumers of baseball equipments, the preference of the consumer who has improving focus was higher than that of consumer who has the prevention focus. Second, preference differentiation analyzed by construal level and the message framing of the consumer of the improving focus, the preference was higher when the message framing was positive, and the construal level was in short time. Third, preference differentiation analyzed by construal level and the message framing of the consumer of the prevetnion focus, there was no difference of the preference of the equipments followed by the construal level and message frame for prevention focus consumers.


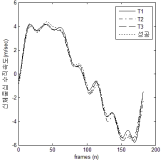
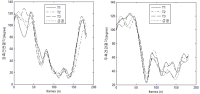
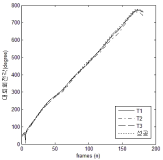
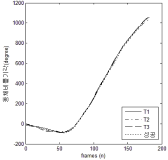
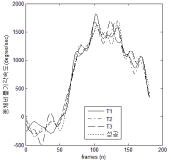
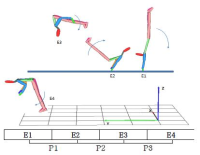
The research was a case study conducted in order to develop a new technique “YANG Hak Seon 2” for YHS athlete. A comparative kinematical three dimensional video analysis was performed with the use of high speed cameras. One successful trial and three of failure trials (T1: Falling backward while landing, T2: sitting reluctantly while landing, T3: Falling of sideways while landing). The result obtained from the study are as follows. Firstly when comparing the successful operation of the technique with failure trials, relatively higher landing angle was secured through increasing the thigh rotation and the body’s rotational velocity. Furthermore, despite increase in rotational velocity at twisting, stable landing was achieved through increasing the moment of inertia by spreading the left shoulder. Secondly, in case of failure trials while taking off the board, the thigh rotational angular velocity was comparatively less which ultimately affected the body position in the next phase of approach to the vault. Thus, due to the affected body position the athlete was not able to utilize the proper momentum of twist in positive direction Hence, it is considered that the velocity of center of mass might have also effected the operation not only the velocity while approaching the board.












This study classified and analyzed groups of spectators of professional baseball through market segmentation and predicted the sports consumer behavior by using artificial neural networks model and logistic regression model. The results of hierarchical cluster analysis, K-means cluster analysis, cross-tabulation analysis and one-way ANOVA using PASW 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 suggest five clusters of consumer segments and by using Modeler 14.1, artificial neural networks model was made to predict the data. By using artificial neural networks model and logistic regression model, hit ratio was grasped about the spectator satisfaction and future consumption behavior. The results are as follow: The hit ratio were high in ‘cluster 5’ for artificial neural networks model(spectator satisfaction: 71.3%, future consumption behavior: 99.3%) and logistic regression(spectator satisfaction: 71.8%, future consumption behavior: 96.5%). Furthermore, cross-tabulation and one-way ANOVA was performed to understand the cluster's characteristic which had highest hit ratio about the spectator satisfaction and future consumption behavior. And through this marketing strategy was suggested.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the optimal model for winning medal on vault event of men's gymnastics. Specifically, decision tree analysis was used to explore, first, for the optimal conditions for qualifying top 8th player that have high possibility into final round, and second, for the optimal model for obtaining the medal of the vault event. Methods Data were collected for five official competitions (Olympics, Asian games, and International championship, etc.) organized by the Federation of International Gymnastics (FIG) from 2013 to 2016. In this study, the data of 626 vault players were collected. Also all of these players performed 921 vault skills for qualifying round or final round. Five predictor variables for estimating for qualifying into the final round and for obtaining the medal of the vault event were selected; nationality, difficulty score, acting score, additional penalty score, final score. Results The results is as follows. Overall, it was confirmed that the optimal model for entering into the final round was the difficulty score of vault event. The optimal model for entering into the final round estimates 81.2% when condition would be the 5.6 or higher of difficulty score and 8.6 or higher of the acting score. The optimal model for winning medals was 86.7%, which means that when condition would be the 6.0 or higher of difficulty score and no additional penalty score. Conclusions This models can be used as a basic data for establishing a strategy for medal acquisition of vault event of gymnastics.



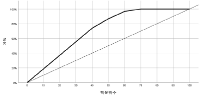
The purpose of this study was to analysis of moving distance during games, time and heart rate for hockey games using GPS (global positioning systems) by positions in Korea national female athletes. The subjects were Korea national female hockey players (n=13) including 4 forwards, 4 midfields, and 5 fullbacks that participated in five Korea vs. Japan international games. All subjects were wearing GPS throughout the games. The results were as follows: Firstly, the average total travel distance per game was approximately 5.7km and higher in the second half. Physical movement in the games was not different from positions where 70% of physical movement was performed at low intensity and 30% at moderate and/or vigorous intensity, suggesting that the subjects; physical movement was performed at the appropriate level of exercise intensity. Secondly, during the game, the subjects performed physical movement faster than 11km/h for 22 minutes, indicating that the subjects could maintain their physical movement at a relatively faster speed throughout the games. In particular, midfields showed a greater amount of physical movement at moderate speed. Thirdly, the average exercise heart rate was 145bpm, which was equivalent to 60% of HRmax. The subjects maintained their average exercise heart rate greater than 150bpm (above 60% of HRmax) for 40 minutes during the games, indicating that the players had an ability to maintain physical movement at high intensity throughout the games. In conclusion, in spite of the fact that Korea national female hockey players have an ability to maintain physical movement at a relatively faster speed and higher intensity, their physical movement and performance are often affected. Therefore, it is necessary to develop and apply the specific interval training program for national female hockey players that can facilitate the faster recovery from the repetitive physical movement requiring power and speed at high intensity.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to analyze the performance contents of men's floor exercise and to provide basic materials for achieving excellent results at world competitions. Methods Teams ranked 1 - 12 who participated in the World Championships' floor movement group competition selected a total of 59 players by the convenience sampling method and carried out technical statistics, frequency analysis, member variable variance analysis, and post hoc analysis. Results First, as a result of frequency analysis of the difficulty of each group, all the teams ranked 1 to 12 liked the most difficulty of C and found that they do not like the F difficulty the most. Secondly, there was a difference in average for each group's start score, ranking 1st to 4th> 5th to 8th> 9th to 12th place. Thirdly, there was a difference in average of difficulty levels for each group B, C, E, and it became very significant with E difficulty.Results of post hoc analysis B difficulty (9th to 12th> 1st to 4th, 5th to 8th), C difficulty (9th to 12th> 1st to 4th), E difficulty (1st to 4th> 5th to 8th ·9th to 12th). Conclusion These results show that in floor exercise, the art of more than C difficulty and the connection technology of A, B, C, difficulty, E and F, difficult difficulty such as difficulty, creative and dynamic performance composition is excellent It clearly states that it is a condition for getting results.
The purpose of this study was performance improvement through analysis of movement in elite field hockey players regarding positions using real-time GPS monitoring for compared training game and 2014 Incheon Asian Games. Fifteen elite women field hockey players (Defender: 4, Mid-fielder: 6, and Forward: 5) participated in this study. There were 2014 Incheon Asian Games Korean national team. Real-time GPS system analysis was completed during 10 training game appearances 5 2014 Incheon Asian Games appearances. The results of this study showed that in training game mid-fielder>forward>defender for 3, 4, 5, and 6 zone at speed zone by moving distance, in 2014 Incheon Asian Games forward>mid-fielder>defender for 6 zone at speed zone by moving distance. And moving distance by quarter increased all position in 2014 Incheon Asian Game more than training game. Therefore, These data might be useful to analysis of movement in field hockey players. Moreover improved performance and individual exercise ability by feedback for players distance, heart rate, and exercise trajectory. Thus, Gold-medal won at the 2014 Incheon Asian Games in field hockey.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to develop the estimating equations for 4 types of Wingate Anaerobic test setting. METHODS 80 male elite athletes performed 4 trials of the Wingate Anaerobic test by each type. Subjects were conducted the retest one week later. Data collected from the Wingate Anaerobic test included mean power, peak power, and power drop for 30s were measured. Coefficient of correlation was used for validity of type 1(DOS version) and the other types(ver. 2.24, 3.3.0, and 3.2.1). Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to examine the reliability of test and retest. Simple regression analysis was used for calculating the estimating equation. RESULTS There was significant correlation for absolute value(Watt, p<.01) and relative value(Watt/kg, p<.01) of mean power, absolute value(W, p<.01), relative value(Watt/kg, p<.05), and power drop rate(%, p<.01). Test and retest reliability was excellent for all test variables(p<.01). CONCLUSIONS From the all results, the estimating equation was calculated to convert all outputs from each type to the other types of the Wingate Anaerobic test setting. These findings suggest that the estimating equations are compatiable to 4 types of Wingate Anaerobic test setting.
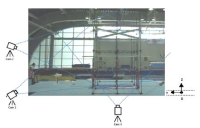
The purpose of this study was to identify the characteristics through technical analysis of dismount to perform the successful landing. The subjects in this study were male gymnastic players of the national team, hish-speed cameras were used to record the salto backward dismount on the parallel bars of the subjects and to study the qualitative and quantitative analysis. The evaluations including feedback of each subjects’problem were as follow: KHH showed early release timing compared to other players. It could be one of factors which can not decelerating the rotational speed, so the correction of posture is needed. NYI didn’t slide to the left at the release phase, and showed big rotation of body compared to other players so the center of mass moved to the rear. The correction of the hand position at flight phase is necessary to perform the V-shaped position. RSD landed in a state where the rotation is insufficient, so the training using elasticity of parallel bars at phase 2, and the correction of hand position are in need. PMS’s rotation angular velocity of body increased consistently, so showed instable land. Therefore the training to ensure the height of flight is required. PEJ showed high vertical position of CM at the release phase which is help for height of flight. He performed ideal V-shaped position, and took a relatively stable landing position. BGR also showed high vertical position of CM and performed ideal V-shaped position, so he landed in a posture in which the most stable. YHS should push vertically rather than horizontally at the moment of release. Especially, the hand position is not on the hamstring but on the back of the knee to perform the ideal V-shaped position. CJY showed little hip angle at the release phase, so he can’t take a position for vertical rise. Also he showed the lowest knee angle and performed rotation and landing in a state that cannot extend the knee. If such problems are corrected, it will be helpful to landing position not only in parallel bars but also in other events.


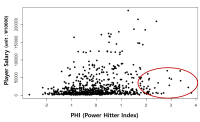
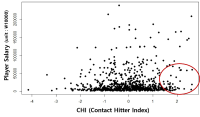
Purpose The main purpose of this current study is two-fold. Firstly, it attempts to develop a model to determine the true market value of Korean professional baseball players (hitters only) solely based on their athletic performances on the field. Secondly, it is to provide the evidential data for the market value of baseball players in Korea. Methods The statistical data and performance information were obtained from baseball almanac from KBO from 1997 to 2016. Seven hundred and ninety three players were included for data analysis. Principal component factor analysis was utilized to eliminate multicollinearity among 12 sabermetrics indices (OPS, GPA, SECA, TA, RC, RC/27, XR, ISO, PSN, sOBA, %OW, BABIP) and increase power of explanation of the proposed model with KMO(=0.77), p<0.001. Results The proposed model was successfully developed with YSalary = Years of Experience*921.5 + FA (free agent)*53528.9 + PHI(Power Hitter Index)*7313 + CHI(Contact Hitter Index)*5893.6. Furthermore, the proposed model explained 64.5% of variances of the market value for the Korean professional baseball players and proved to be statistically valid. Conclusions The newly developed model in this study was very helpful for us to identify the variables that affect the true market value of baseball players. It is expected that this model could make an important contribution in determining true market value of the baseball players in Korea.