
The purpose of this study was to verify the effect on elementary school students in the exercise start stage by performing a sport psychological skill training to improvement of psychological skill and life skill. Participants were eight elementary school boys volleyball player. The program consisted of psychological skills and life skills in educational counseling model of Visek et al(2009). It was conducted 40-50 minutes a session in total for 22 sessions. Data was collected through a psychological test, worksheet and participant observation, in-depth interviews. The collected data was analyzed to verify difference by paird t-test after pre-middle-post test and to extract meaningful data category. Quantity analysis showed that a result of sport psychological skill test proved a significant difference in willingness to overcome, confidence, concentration, anxiety regulation. Life skill test were no significant differences in all factors. However, the rise of scores was observed on result of the pre-middle paired t-test of life skill during season. Quality analysis showed possibility of goal setting, concentration on the routine, decrease of competitive anxiety, increase of positive thinking, self-understanding and understanding of others, promotion of communication among team members. This sport psychology skill training had a significant effect on the psychological skills of elementary players change. But it seems to be necessary life skills in a more through review of the information.



Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a Korean Life Skills Scale for Sports (KLSSS) that original version is the LSSS developed by Cronin and Allen (2017). Methods The subjects were 899 middle school and high school students. The measurement tool was used with LSSS. The validation of KLSSS followed a three-stage of validation procedure; substantive stage, structural stage, and external stage. The result is as follows. Results First, In the substantive stage, KLSSS consisted of 47 items with 8 factors. As a result of the item clarity test, it was confirmed that all the items were appropriate. Second, in the structural stage, KLSSS was explored and confirmed as 5 factors and 18 items. Third, in the external stage, KLSSS showed discrimination and convergent validity. Conclusions KLSSS is composed of 5 factors and 18 items. The factors are teamwork (TW), goal setting (GS), time management (TM), social skills (SS), and leadership (LD). This scale can be used to obtain information on life skills in school physical education or sports.
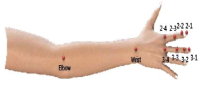
The purpose of this study was to determine how acute active pc-video game affects kinematic variables and muscle activities of adolescents. Fourteen middle school students(age: 15.9±0.7 yrs, height: 171.3±6.1cm, weight: 60.0±5.4 kg, right handed) who have no musculoskeletal disorder were recruited as the subject according to having experience in using the pc-video game for more than six months. Maximum angle, angular velocity, and muscle activity of the upper extremity were determined for each trial. For each dependent variable, a paired t-test was performed to test if significant difference existed between pre- and post a 60 minute active pc-video game(p<.05). This study found that one hour pc-video game hour may not affect on movement and ROM of the finger and the wrist, whereas it may have an effect on muscle activity of the upper extremity. It seems that repetitive movement pattern during an active pc-video game may hinder muscle activity of adolescents’ upper extremity. Part of the increase in musculoskeletal disorders is linked to the amount of time adolescents are allowed to play video games. This study found that an active pc-video game appears to have negative effects on the upper extremity muscles. Since wrist movements are continually repeated throughout the video game, carpal tunnel syndrome may possibly be caused by long-term exposure to video games.


PURPOSE This study examined the effect of sports life skills and life skills transfer of student-athletes and coaches, applying Actor-Partner Interdependence Model (APIM). METHODS Korean student-athletes and coaches from middle and high school sports teams participated in this study. There were 300 student-athletes (Mage=15.44, SD=1.64; male=218, female=82), with an average of 5.46 (SD=2.40) years of athletic career. Meanwhile, 33 coaches were (Mage=39.70, SD=8.36; male=26, female=7), with an average of 13.52 years of coaching career (SD=10.01). Measures included the Life Skills Scale for Student-Athletes (LSSSA; Jang et al., 2020) and Korean Life Skills Transfer Survey (KLSTS; Lim et al., 2018). Descriptive analysis, correlation, and APIM were undertaken by using the SPSS and AMOS programs. RESULTS First, the correlation between athletes’ and coaches’ life skills was not significant. Second, athletes’ life skills significantly affected their life skills transfer, similar to coaches’ life skills significantly affecting their life skills transfer. Fourth, coaches’ life skills did not significantly influence athletes’ life skills transfer, and the converse was not true either. CONCLUSIONS This study verified the effect of life skills development for two groups of athletes and coaches, on transfer in sports, and attempted statistical verification of whether it affects sports life skills and transfer between athletes and coaches. Although no statistically significant results were found in the partner effect, it is meaningful in that, it provided important implications for conducting a follow-up study on the relationship between athletes and coaches. In other words, it is expected to be a cornerstone for research on building a new model, along with investigating the interactive relations between athletes and coaches on life skills in the sports field.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to understand the athletic identity of youth football players and to trace its changing trend. METHODS Participants of this study included 93 players in 2005 and 94 players in 2021, who were in middle and high schools. All participants answered open-ended questionnaires. After the results of the inductive content analysis, the changing trend of the results was assessed. RESULTS The athletic identity of youth football players were collected from 811 raw data samples collected in 2005 and 741 collected in 2021 and categorized into 19 sub-categories and 5 categories. The results show a tendency to be specific to football. The athletic identity of a football player itself is weakening, being replaced by the identity of being a student. The role of the camp is also weakening, while more privacy and autonomy are allowed to the players. As a result, efforts to secure the players’ right to study were accepted by the players, and expected to decrease as camp life with limited privacy is on the decline, and as senses toward one’s physical competence are changing. CONCLUSIONS Sociocultural contexts, including changes in the system and social modifications, are reflected in the football player's athletic identity and its changes. The athletic identity of youth football players has changed from its 2005 version of unacademic camp life with limited privacy to the 2021 version, where the player leaves camp to be provided with privacy and attend classes.