The purpose of this study was to examine whether β-alanine ingestion for 8 weeks can regulate isokinetic knee strength, and 3km record in middle-long distance woman cyclists. Fourteen middle-long woman cyclists participated in this study and were divided into two groups; training group with beta-alanine ingestion and training group with placebo ingestion. All subjects took in beta-alanine or placebo supplement three times per a day for 8 weeks. Physical activity was evaluated by measuring the isokinetic muscular strength and 3km record before and after intervention for 8 weeks. As a results, in isokinetic test, there were significant interrelationships in peak torque of the right and left flexors at 60°/sec, peak torque of the right and left extensors at 180°/sec, peak torque of the right flexors at 180°/sec. In 3km record, result showed a significant interrelationship by groups and time. The results of present study provide evidence that beta-alanine supplement may be effective to increase physical activity and competition record in middle-long woman cyclists.

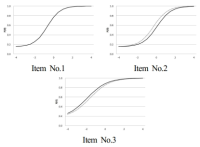
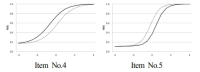
The purpose of this study was to analyze and confirm whether the items used in final paper and pencil test was determined to DIF when school sports clubs in each school operated by discriminatory curriculum in accordance with gender. Participants were 8th middle school students(male=135, female=141). They joined in school sports club every week from freshman to sophomore 1st semester. At that time, boys of them participated in soccer and basketball, and girls played dodge ball. They studied soccer unit at sophomore 1st semester, and had a final examination consisting of 5 soccer items. Using the data, differentially functioning item by the population difference between male and female were analysed quantitatively and qualitatively. The results showed that Mantel-Haenszel method(using classical test theory), comparison of item characteristic curve and likelihood ratio test(using IRT) determined item number 4 and 5 to differentially functioning item. Finally, item number 4 were identified differentially functioning item in favor of male students in intensive qualitative analyses. That item have low content validity and application-level of cognitive behavior classification. The result provides that application-level item can be functioning differentially to female students with little sports experience than male students in paper and pencil test of PE.






The purpose of this study was to verify the effect on elementary school students in the exercise start stage by performing a sport psychological skill training to improvement of psychological skill and life skill. Participants were eight elementary school boys volleyball player. The program consisted of psychological skills and life skills in educational counseling model of Visek et al(2009). It was conducted 40-50 minutes a session in total for 22 sessions. Data was collected through a psychological test, worksheet and participant observation, in-depth interviews. The collected data was analyzed to verify difference by paird t-test after pre-middle-post test and to extract meaningful data category. Quantity analysis showed that a result of sport psychological skill test proved a significant difference in willingness to overcome, confidence, concentration, anxiety regulation. Life skill test were no significant differences in all factors. However, the rise of scores was observed on result of the pre-middle paired t-test of life skill during season. Quality analysis showed possibility of goal setting, concentration on the routine, decrease of competitive anxiety, increase of positive thinking, self-understanding and understanding of others, promotion of communication among team members. This sport psychology skill training had a significant effect on the psychological skills of elementary players change. But it seems to be necessary life skills in a more through review of the information.




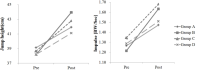
The purpose of this study was to find which percentage of 1RM for squat to improve the result of squat jump most effectively after plyometric training with different percentage of 1RM for squat. 24 men in their twenties were measured 1RM for squat and separated in 4 groups by 6 participants. Group A, B, C, and D used 0, 15, 30, and 45% of 1RM, respectively in the plyometric training. All groups had 1 hour training 3 days per week for 8 weeks(24 sessions). This study designed to increase the number of sets of exercises gradually. In week 1 and 2, participants trained 1 set of plyometrics with no load. The number of sets increased 2 to 4 in the week 3-4 to 7-8. The jump height(cm) and vertical impulse(%BW) of squat jump before and after plyometric training were measured by 3D motion capture system and force plate. All 4 groups showed the improvement of squat jump height and vertical impulse, but specially group B was most improved(p<0.5).

Purpose This study was conducted to analyze the differences of physical characteristics focused on the physique, strength, and power for cycling national athletes (Sprint cyclists and Road race cyclists). Methods We measured various factors (e.g., height, weight, body fat ratio, thigh circumference, waist circumference, anaerobic power, isokinetic muscular strength, muscle power, squat jump by 1RM intensity, and so on) for a total 11 male cycling national athletes (5 Sprint cyclists and 6 Road race cyclists). Results First, the body composition showed the significant differences only in weight (p=0.31) and BMI (p=.001) for Sprint cyclists. Second, the values of the anaerobic power for the Sprint cyclists were significantly higher than those for the Road race cyclists only at peak power (p=0.28), whereas there was no significant difference in average power, isokinetic muscular strength, and muscle power between the two groups. Third, the isokinetic trunk flexion muscle (p = .016) for the Sprint cyclists were significantly higher than those for the Road race cyclists. Fourth, the significant difference in Time to Peak Torque was not found between two groups. Fifth, the values for the Sprint cyclists showed the significant difference in all 5 intensity groups (0%, 30%, 50%, 60%, and 80%) (p=.001) of the squat jump. Also, there was a statistically significant difference only in 0% velocity between the two groups, except for exercise intensity. Conclusions From the various measures between two groups, the Sprint cyclists relatively showed the high weight, BMI (muscle mass), and maximum power. Additionally, the isokinetic trunk flexion muscle and the squat jump were higher in the Sprint cyclists than the Road race cyclists. These data may be used as basic data to improve the physical fitness factors related to the athletic performance of the athletes by reflecting them in the effective training plan and evaluation of the athletes.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate user perceptions regarding the mobile healthcare application of public health centers by using big data. METHODS The study data included 1,089 users’ reviews (from September 27, 2016 to December 23, 2021), which were analyzed using Python, Textom, KrKwic, UCINET 6, and the Net-draw program. RESULTS First, the evaluation of the application showed a higher number of “Good” responses (677 times) compared to “Bad” (329 times) and “Normal” responses (83 times). Second, network structures related to “Good” were “Like,” “Health care,” “Help,” “A sense of purpose,” “Grateful,” “Diet management,” “Exercise management,” “Easy,” “Recommendation,” “Satisfaction,” “Diet,” “Useful,” and so on. Third, network structures related to “Bad” were “Execution error,” “Request improvement,” “Question,” “Slow speed,” “Interlocking error,” “Lack of food type,” “Login error,” “Inconvenience,” “Delete and reinstall,” “Update error,” “Irritation,” “Connection error,” “Problem occurred,” “Direct input request,” “Not available,” “Waste of stars,” “Lack of function,” “Not enough,” “Stuffy,” “Lack of exercise,” and so on. Fourth, as a result of structural equivalence analysis, four clusters appeared: cluster 1 (negative function), cluster 2 (negative emotion), cluster 3 (positive function), and cluster 4 (positive emotion). CONCLUSIONS It is necessary to respond quickly in order to reflect on the users’ reviews, and active efforts are required to improve the program quality so that users can use it conveniently.
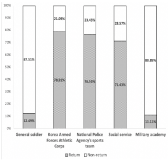
Purpose The purpose of this study is to identify the negative effects of long-term exercise (training and competition) suspension of male elite athletes due to compulsory military service on athletic performance, and to provide a basis for enhancing the importance of providing support systems and social conditions for maintaining athletic performance. Methods In this study, 17,418 male athletes aged 18 to 21 who were registered as athletes for the Korean Sports & Olympic Committee from 2003 to 2005 were enrolled. The athlete registration data includes information about the athlete's gender, age, sport and affiliation. According to the continuity of registration and belonging information, the compulsory military service type was classified into a manipulator. According to the form of Compulsory military service performed by male elite athletes, the return rate was confirmed and the career (year) was calculated. Results As a result of the survey, 12.49% of the athletes who served as general soldiers returned to the athletes after compulsory military service, showing a relatively low return rate compared to 78.91% of the Korea Armed Forces Athletic Corps, 76.55% of the National Police Agency's sports team, and 71.43% of the social service. Also, Athletes who served as general soldiers had a career of 2.46 years (± 1.94), while the Korea Armed Forces Athletic Corps was 10.21 years (± 3.58), the National Police Agency's sports team was 9.45 years (± 3.26), and the social service was 5.86 years (± 4.06), The exemption was 11.08 years (± 2.27), and the compulsory military service exception was 9.79 years (± 5.55). Conclusions Male elite athletes' decrease in athletic performance after compulsory military service is a natural result, as confirmed through the results of this study, and it is necessary to seek a support system between compulsory military service to maintain athletic performance.


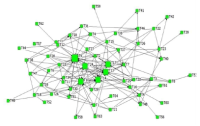
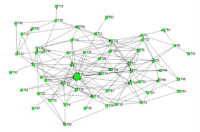
Previous work has shown that coaches sought information from several sources; however, there was a strong reliance on learning from other coaches within their social networks. There has been limited research examining the nature of these social networks with other coaches (Trudel and Gilbert 2004). Thus the purpose of this study was to examine the structures of coaches’ social networks of Korean rhythmic gymnasts. Research questions were: (1) What are the network structures of Korean rhythmic gymnasts’ coaches? (2) What structural parameters contribute to coaches’ network structures, and (3) Is there an association between coaches’ network and flow of information in their networks? A total of 37 coaches of youth rhythmic gymnasts (6-18 years old) participated in this study. Each of those coaches was asked to complete a Name Generator Questionnaire (i.e., list four names that you have a close relationship with) and general socio-demographic survey. Data were analyzed using social network analysis tools such as UCINET, p-net, and Quadratic Assignment Procedure. Analysis of network centrality, density, and strong components showed that (1) homophily was identified in the structure of coaches’ social networks (2) homophily (e.g., by gymnasts’ ranking, mentor coaches) contributed to the total social network of coaches, and (3) interacting only with close coaches in the network, coaches received information about coaches/coaching from the strong ties rather than weak ties (Granovetter, 1973). This study also has strong links to Wenger’s (1998) community of practice which posited that groups of people share a common characteristic in practice.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore environmental constraints that hindered the physical activity of female students in daily life, and then to provide alternatives to improve the problems based on the social ecological model. Methods Research participants were twelve female students to be selected in two schools(Norang, Parang middle school), the process of data collection(orientation, photovoice implementation, focus group interview) and analysis(choosing a photo, contextualizing, subjecting) were conducted according to the Photo-voice. Results The constraints of physical activity in daily life were categorized on ‘playground as like a desert’(leisure domain), ‘space of recess and in-active play’(family domain), ‘transportation replaced by mom and dad car’(transportation domain), ‘space of the only exercise as well as reproduction of gender discrimination’(school domain). Conclusions The environmental constraints were analyzed as academic, physical, daily living, socio-cultural environment. Lastly, alternatives for promoting physical activity of female student were proposed in the level of organization, community, public policy based on the social ecological model.















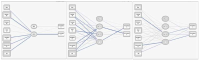
This study examined whether or not regulatory focus can predict motivation level. 141 Ssireum player completed Korean self-regulatory focus of Hong(2005)assessing their self-regulatory focus, and Behavioral Regulation in Sport Questionnaire(BRSQ) of Lonsdale, Hodge & Rose(2008) accessing motivation level based on self-determination theory. Artificial neural network analysis was utilized to find motivation factors that determine the regulatory focus, and the option was multi-layer perception. The result represented promotion focus predicted intrinsic motivation. Also, the prevention focus predicted extrinsic motivation. This result provided that self-regulatory focus can predict player’s motivation level and promotion focus related to intrinsic motivation.