Purpose This study examines the Physical Education curriculum history of special schools, and then in-depth grasps the process of how the sports environment for the disabled has changed by age. Method The research method was literature review analyzing papers, reports and newspapers. For the concrete process, this study verified the relationship between the research subject and the collected data through experts and historians with disabilities to verify the sports data for the disabled. Results First, the process of physical education management of special schools is as follows. in the 1940's and 50's special schools, physical education was carried out simply by gymnastics. but, special schools were differentiated by the characteristics of the disabled, and the institutional foundation for physical education was also imitated by the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s, special schools were shortened in physical education time due to the increase in the number of courses and the strengthening of disability coping programs. in the 1990s, as special sports curriculum was established, customized prescription for students with disabilities was implemented. Second, the process of changing disability sports is as follows. In the 1960s and 1970s, disability sports were mainly focused on special schools, while in the 1980s, disability sports were expanded by the government. in particular, the hosting of the 88 Seoul Olympics and Seoul Paralympics provides an opportunity to equip the disabled with a system, organization and facilities. in the 1990s disability sports was meaningful in terms of academic progress, and with the quantitative growth of the 1980s and the academic foundations of the 1990s, disability sports in the 2000s provided a legal basis and improved welfare conditions for the disabled. In the future, it is necessary to find a way to solve the value of physical education for the disabled more reasonably.



Purpose The purpose of this research is to provide implications for the study of the physical education curriculum in Korea and China by comparatively analyzing the revised high school physical education curriculum in the two countries. Methods Using Bereday(1964)’s four steps of comparison model in education, this study focuses on the format and content of the general high school physical education curricula of Korea and China, each curriculum having been revised respectively in 2015 and 2017. Results First, in terms of format, both countries consider PE a necessity and share similarities in regard to course structure, credit allocation and document format. Nevertheless, though both countries are oriented toward competency-centered education, there are some differences with respect to official education curriculum documents, numbers of subjects and hours of study based on the reality and situation of each country. Second, in terms of content, both countries present various teaching methods and evaluation principles for the sake of acquiring core competence. However, the Korean curriculum prefers to advocate learning of the value of physical activity to achieve core competencies, while the Chinese curriculum prefers to focus on acquiring athletic skills and health knowledge for achieving core competencies. Conclusions After comparing physical education curriculum in both countries, two implications could be obtained. One is that the consistency problem in Korea should be solved between the core competency, the teaching and learning methods and evaluation standards. The other is that, in China, integrated value of physical education should be paid more attention and core competency as well as teaching and learning methods should be considered.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of training methods on body composition, isokinetic strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function, and anaerobic power in female judo players. Methods Subjects performed weight training (n=10) and circuit weight training (n=10) consisting of 10 sports items for 12 weeks. In order to analyze the effects of training, body composition, isokinetic strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function, and anaerobic power were measured and the effect of training was verified. Results First, the comparison of body composition between WT and CWT groups showed that significant interaction effect between group and period was found in all variables (weight: F=1082.694, p=.001, body fat mass F=199.999, p=.001; skeletal muscle mass F=2481.698, p=.001, and percentage body fat: F=496.246, p=.001). Second, there was a significant interaction effect between group and duration in shoulder muscle strength and knee endurance (EPTL: F=6.598, p=.019; EAPL: F=12.860, p=.002). Conclusions The result of this study showed that the interaction effect between period and group was not significant according to the training method but the overall effect of the circuit weight training group was more positive than the weight training group. Therefore, it can be concluded that the 12 weeks circuit weight training can contribute to improve the performance of female Judo players by improving body composition, strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function and anaerobic power.

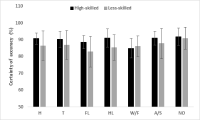
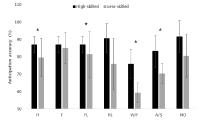
Purpose The purpose of this study was to establish the differences of anticipating accuracy and confidence according to fencing expertise and spatial occlusion region. Methods For the purpose of this study, the anticipation ability of 6 high-level fencing players and 6 low-level fencing players were analyzed. All subjects performed the 60 tasks of anticipating the attack positions(thorax, thigh, toe) from observing the fencing video screen using spatial occlusion technique. The spatial occlusion technique was used in 6 particular body of opponent’s movement. For statistic analysis, data was analyzed through independent T-test measure. Moreover, Paired t-test were used as follow-up analysis. Results The results of the study were as follows: In terms of accuracy anticipation, the main effect of expertise was significantly different. Specifically, when the spatial occlusion technique was applied in head, left leg, arm, and a foil, the accuracy of anticipation was significantly different. Moreover, comparing with no-occlusion condition, anticipation accuracy decreased when spatial occlusion technique was applied in arm and foil. In terms of confidence, there was no significant difference between level of expertise. Conclusions In order to effectively anticipate the opponent’s movement in fencing sports, it is necessary to focus on the visual cues of arm/shoulder, and the foil. Especially, focusing on the foil movement might provide the core informations on anticipation ability.



[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to provide the physiological characteristics of female adults in their 30s by comparing the body composition and the maximal strength of the knee extension and flexion and bilateral ratio and ipsilateral ratio(H/Q: Hamstring and Quadriceps ratio) depending on age. [Methods] Body composition was measured by Hv-ps 7681(GE medical systems Lunar, USA). Isokinetic lower limb muscular strength was measured by Isomed2000(D&R Ferstl GMBH, Germany). 92 volunteers who were chosen by our selection criteria agreed to participate in our study. The participants were divided into three groups depending on age and classified as female adults in twenties(n=30), in thirties(n=34), in forties(n=28). To evaluate differences according to age, One-way ANOVA was used. [Results] The result in the test for female adults is as follows. In body composition, there were significant differences in lean mass, bone mineral density in the legs area among groups(p<.05). In isokinetic test, there were significant differences in muscular strength among groups in extensor of knee(p<.05). [Conclusion] The finding revealed that strength training based on the characteristics depending on age is required and ipsilateral ratio needs to be improved.

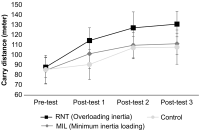
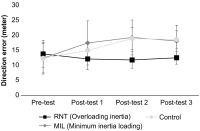
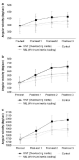
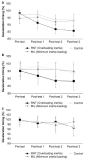
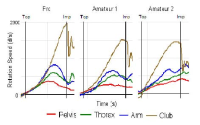
[Purpose] We examined the influence of reactive neuromuscular training (RNT) on golf swing coordination. RNT aims to induce proper coordinative movement by exaggerating the performer’s mistakes. Therefore, we applied RNT using inertia overloading to golfers who have problems with kinematic sequence during a golf swing. [Methods] To examine the effect of 12 weeks of RNT on golf swing coordination, we employed a ball tracking system (launch monitor) and motion analysis system (inertia sensors) were taken on four consecutive periods (pre-test and post-tests 4, 8, and 13 weeks later). Thirty Korean male cadets were divided into three groups based on inertial loading and practiced 7-iron golf swings combined with specific group tasks twice per week. [Results] At pre-test, most participants reached maximal angular velocity near the impact timing (95-100%). However, the deceleration timing of the maximum angular velocity of the proximal segments gradually moved toward mid-downswing as the training sessions proceeded, with the RNT group ultimately outperforming the two control groups. Additionally, the RNT group showed a significantly higher maximum angular velocity in the thorax and wrist. [Conclusion] Our results suggest that RNT can be sufficient to elicit and effective whole-body coordination pattern. Considerable follow-up research is needed on the use of RNT for various sports tasks and the effects of expertise on RNT results.



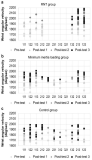
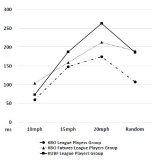
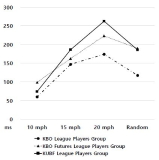
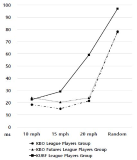
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of baseball expertise and stimulus speeds on coincidence-anticipation timing accuracy of batting. [Methods] Participants were 21 baseball batters, 7 of Korea Baseball Organization(KBO) League, 7 of Korea Baseball Organization Futures League, and 7 of Korea University Baseball Federation(KUBF) League. All of the participants were asked to swing the bat exactly at the time when the light arrived the target point of the runway. The Bassin Anticipation Timer was used to present stimulus with stimulus speed of 10, 15, and 20mph. Participants performed 10, 15, 20mph trials (3 kinds of speed per 5 times) and random trials (3 kinds of speed per 3 times randomly). The timing error of coincidence anticipation task was recorded and raw scores were transformed to constant error(CE), absolute error(AE) and variable error(VE). For data analysis, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures were used. And post-hoc test (Tukey HDS) were conducted. [Results] Results indicated a significant interaction on expertise and stimulus speeds for CE, AE and VE. The KBO League players group showed more accurate and consistent performance than the KBO Futures League players group and the KUBF League players group in baseball batting timing. [Conclusion] This findings revealed that coincidence-anticipation timing accuracy batting in baseball can be used as a factor to distinguish the ability of the other.


[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to investigate the process of Jang Changsun’s winning gold medal in the 1966 Toledo World Amateur Wrestling Championship and its meaning. [Methods] Jang Changsun and Katsumura Yasuo who had competed with Jang Changsun for the gold medal were selected as participants, a player and an executive who had participated in the Championship were selected as informants. Data had been collected by in-depth interview were analyzed firstly by using the Patton(1991)’s data analysis method, and the following conclusions were obtained by comparing with preceding studies, press releases, reports etc. [Results] Jang Changsun won a gold medal through the three stages of desperate struggles. The first struggle was to loose weight. Jang Changsun lost three times more weight than other players through fasting treatment, intensive training and dehydration in order to secure an advantageous position in the competition. His second struggle was the sparring itself. He made his mind to win gold medal 2 years before the Championship and started to strengthen his physical fitness and polish up his techniques to fight with strong players from powerful nation of wrestling. He finished the sparring by winning 4 games and tieing 2 games resulting in the same deduction points with Katsumura. It was inevitable for him to fight desperately to lose weight again to get gold medal. He eventually won the gold medal by losing his weight until he fainted because of injuries and serious dehydration. [Conclusion] The first gold medalist Jang Changsun contributed a lot to development of Korean sports by offering chance to consider significance of improving elite player’s exercising environment, scientific coaching, gaining self-confidence to win medal, and realizing the importance of sports informations.



Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine students’ perceptions of girls’ participation in physical education(PE) in elementary schools and examine the impacts of a girl-friendly integrated program on children’s participation in PE classes. Methods The participants were 10 fifth graders (5 girls and 5 boys) and their teacher in an elementary school. Data which were collected from in-depth interviews with students, students’ journal entries, field observation, and teacher’s reflective journal entries were analyzed inductively. Results Findings revealed that boys perceived girls’ participation as passive, possessing a low level of skills, and staying at the peripheral position. Meanwhile girls expressed their desire to demonstrate their strengths in PE classes and were afraid of boys’ criticism regarding their lack of skills. There were also misconceptions and misunderstanding on girls’ PE participation between boys and girls. In order to resolve these issues, a girls-friendly integrative program was designed. based on the four guiding principles drawn from students’ perception: (1) from ignorance to interest, (2) from misunderstanding to understanding, (3) from sport skills to sport values, and (4) from competition to cooperation. The program integrated boys and girls for promoting active interaction and also integrated competence, knowledge, and dispositions to accommodate students’ various ways of PE participation. Findings revealed that the program had: (1) diversified students’ perceptions of PE participation, (2) promoted students’ diverse and active participation, and (3) established classroom atmosphere which emphasized positive values.


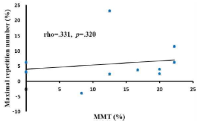
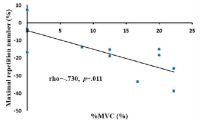
The purpose of this study was to determine whether maximum repetition number can be used as an indicator of strength imbalance. Eleven healthy, resistance-trained males were tested for one repetition maximum (1-RM) the chest-press exercise, and than manual muscle testing (MMT), two-arm at 80% of 1-RM and one-arm at 40% of 1-RM in the pectoralis major were measured for the maximum voluntary contraction (%MVC) and maximum number of repetitions during the chest press exercise. Exercise velocity was constantly 4 seconds (concentric: 2-s, eccentric: 2-s) per repetition. The changes in %MVC were significantly higher in non-dominant limb (NDL) compared with dominant limb (DL) pectoralis major during two-arm chest press (p < 0.01) and one-arm chest press exercise (p < 0.05). In contrast, the changes in MMT (p < 0.05) and maximum repetition number (p < 0.01) were significantly higher in DL compared with NDL during one-arm chest press exercise. There was no correlation between maximum repetition number and MMT (rho = 0.331, p = 0.320). However, maximum repetition number was significantly negative correlated with %MVC in two-arm chest press (rho = -0.730, p = 0.011). It is possible that maximum repetition number can be used as an indicator of strength imbalance.