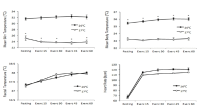
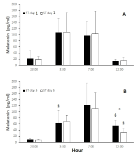
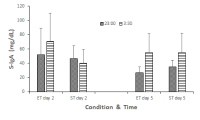
Whether a nocturnal exercise with concomitant increase of body temperature (Tb) would intensify circadian phase delay compare to exercise with a suppressed Tb increase was examined. Seven healthy men (20.57 ± 2.88 yrs, 174.43 ± 4.05 cm, 70.13 ± 6.07 kg, 10.74 ± 1.92% fat) participated in two tests. Each lasted 5-days. On the day of 1 of each test, subjects maintained habitual sleep time (23:00-07:00, 0.2 lux) in laboratory. From day 2 thru 5, they biked for 60 min at 55% of maximal capacity beginning at 01:30 (15 lux). Then they went to bed at 04:00 and woke at 12:00. During test, they exercised either at 26℃ with elevating Tb (ET) or at 17℃ with cooling devices for suppressing Tb (ST). Two tests were counter balanced and separated by 2 weeks. During exercise, rectal (Tre) and skin (Tsk) temperatures, and heart rate were continuously recorded. Body weight changes during exercise were measured. Urine volume and saliva sample were collected. Blood samples were taken at 23:00, 03:30, 07:00, and 12:00 on day 1 and 5 of tests and analyzed for melatonin. The average weight loss for 4 days of exercise in ET and ST was 0.62 ± 0.09 and 0.22 ± 0.07 kg, respectively (p<.001). Tre increased during exercise but not different between conditions. Tsk maintained at 32℃ in ET and 24℃ in ST (p<.001). Tb were higher in ET than ST during exercise (p<.05). The average total urine volume passed was 0.07 ± 0.07 in ET and 0.11 ± 0.07 liter in ST (p<.05). The melatonin concentration at day 1 was 23 ± 26, 107 ± 45, 98 ± 46, and 14 ± 5 in ET and 18 ± 10, 108 ± 65, 103 ± 75, and 14 ± 12 pg/ml in ST for each time period. At day 5, it was 9 ± 3, 64 ± 41, 122 ± 73, and 54.1 ± 17.8 in ET and 8 ± 1, 68 ± 21, 111 ± 52, and 32 ± 14 pg/ml in ST. Differences of melatonin between ET and ST at day 5 of 12:00 as well as between day 1 and 5 at 12:00 of both conditions were noticed (p<.05). Salivary cortisol and immunoglobulin-A were not different. A nocturnal exercise induced a circadian phase delay in both conditions. However, body temperature increase during exercise intensified the shift indicating the importance of thermal load during exercise for circadian shift.

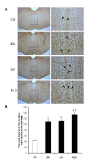
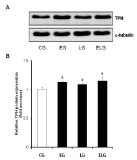
The main purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of treadmill exercise and bright light exposure on serotonin expression in rat brain. Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly assigned into four groups (n=9 in each group), specifically, control group (CG), exercise group (EG), light group (LG), and exercise+light group (ELG). Rats in EG were subjected to treadmill exercise (5 days/week, 30 min/day), LG rats exposed (5 days/week, 30 min/day, 10,000 Lux), ELG rats subjected to treadmill exercise in combination with exposure, and CG rats remained sedentary over a four-week period. We observed a significant increase in serotonin expression in the raphe obscurus nucleu and the midbrain of rats in EG, LG, and ELG, compared to CG. Interestingly, serotonin expression was significantly increased in ELG, compared to EG and LG in the raphe obscurus nucleu via immunohistochemistry. In the western blot, it showed a increased pattern in ELG, compared to EG and LG. The overall results showed that treadmill exercise and/or bright light had positive effects on serotonin expression in the brain. Therefore, we suggest that moderate exercise or exposure to bright light during a growth child may be beneficial in brain action.

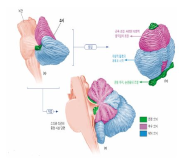
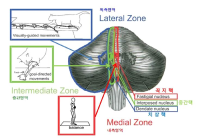
The cerebellum is one of the major parts of the brain involved in the motor control including motor coordination, muscle tone, balance, and the learning of motor skills. The purpose of this review paper was to explore of pathophysiology, anatomical function and neurophysiological mechanism for cerebellum. For this, we sought to examine of previous study related cerebellar disease. Specifically, this paper suggested that motor deficiency of limb movements, coordination, gait/posture balance, adaptation of during movement execution through information proprioception or kinaesthesia, and motor planning and programming of cerebellar patients. We expect that this review will be able to offer the useful information to research. For example, movement scientists will provide an academic information about cerebellar ataxia. Patients and their families will provide relevant information to the daily life (e.g., management and rehabilitation exercise).




PURPOSE This study examines how fitness centers’ care services affect the MZ generation’s perceived value, exercise attitude, and exercise commitment and how perceived value mediates this impact. METHODS Patrons aged 20–30 who used fitness centers in the Seoul and Gyeonggi regions participated in a questionnaire survey from January to February 2024, providing a total of 233 responses. Using SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0, the data underwent frequency analysis, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling. RESULTS First, perceived caring services had a significant effect on perceived value. Second, perceived value had a substantial influence on exercise attitude. Third, perceived value had no significant effect on exercise commitment. Fourth, exercise attitude significantly drives exercise commitment. Fifth, perceived caring services did not significantly affect exercise attitude or commitment. Sixth, perceived value fully mediates the relation between perceived caring services and exercise attitude. Seventh, perceived value had a full mediating effect on the association between perceived caring services and exercise commitment. Finally, tailored services and emotional support were identified as key factors in fostering MZ individuals’ positive exercise experiences and commitment. CONCLUSIONS Fitness centers should develop strategic services reflecting their customers’ goals and values to enhance their exercise attitudes and commitment and ultimately secure long-term customer loyalty.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of continuous exercise and the accumulation of short-duration exercise for 12 weeks on body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease indices in overweight men in their 30s. METHODS Participants in the continuous exercise group (CE; n=13) performed a circuit exercise program of 30 min/session, 3 sessions/week for 12 weeks. Participants in the accumulation of short duration exercise group (ASE; n=12) performed the same exercise time of 30 min per day, divided into three sessions of 10 min. Body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease indices were measured pre- and post-test and were compared by utilizing a repeated two-way ANOVA. RESULTS 1) Regarding body composition, body weight, body mass index, skeletal muscle mass, waist circumference, and fat mass decreased significantly, while hip circumference increased significantly in the CE group. Waist circumference and skeletal muscle mass decreased significantly, while hip circumference increased significantly in the ASE group. 2) Regarding physical fitness, right grip strength, sit and reach, sit up, and maximal oxygen uptake increased significantly in both groups. 3) Regarding hypertension indices, there were no significant differences in both groups, but they showed a tendency to improve. 4) Regarding hyperlipidemia indices, triglycerides (TG) decreased significantly in both groups, and total cholesterol (TC) decreased significantly in the CE group. 5) Regarding diabetes indices, there were no significant differences in both groups, but a tendency to improve was noticed. 6) Regarding arteriosclerosis indices: TG/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio decreased significantly in both groups, and the TC/high density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio decreased significantly in the CE group. CONCLUSIONS We concluded that both the accumulation of short duration exercise and continuous exercise can be effective in improving body composition, physical fitness, and lifestyle disease in overweight men.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 8-week aerobic exercise and polyphenol intake on body composition, cardiovascular response, vascular endothelial function, and physical fitness at rest and during exercise in prehypertensive men. METHODS The study included twenty-eight males in their 20-30 years of age with prehypertension. Participants in the aerobic exercise + polyphenol intake group (EX + PP; n = 14) performed aerobic exercise three sessions/week, 30 min/session, at 65% of the heart rate reserve, and consumed polyphenol (grape seed extract 300 mg) for 8 weeks. Participants in the aerobic exercise + placebo intake group (EX + PL; n = 14) performed the same aerobic exercise; however, they consumed placebo instead of polyphenol. All independent variables were measured at pre-test and post-test, and the data were analyzed. RESULTS The main results of the study were as follows: 1) SBP and MAP at rest decreased significantly in EX + PP, while MAP decreased significantly in EX + PL group. 2) In the EX + PP group, CO increased significantly, whereas DBP, MAP, and TPR decreased significantly during the hand grip exercise. In contrast, CO decreased significantly, while DBP and TPR increased significantly in the EX + PL group during the hand grip exercise. 3) Regarding vascular endothelial function, % FMD increased significantly in EX + PP group. 4) Sit-up increased significantly in both EX + PP and EX + PL groups; however, sit-and-reach in EX + PP group was significantly higher than that in EX + PL group at post-test. CONCLUSIONS The findings of this study showed that the 8-week aerobic exercise would have positive effects on body composition, cardiovascular response, and physical fitness at rest and during exercise in hypertensive men. Additionally, polyphenol intake would contribute more towards reduction of blood pressure at rest and during exercise and improvement of vascular endothelial function.
PURPOSE Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for home training, with exercises or workouts at home, has steadily increased. As a result, the popularity of home training YouTube content, which shows how to use exercise equipment or workouts without professional influence, has also increased. Therefore, this study focused on the characteristics of YouTube home training content (specialization, diversity, and interaction), personal health awareness, exercise awareness, and expectation-confirmation model to identify which required exercise continuation intention through YouTube home training. METHODS SPSS and AMOS software were used to conduct frequency, reliability, and confirmatory factor analyses, as well as to conduct correlation analysis and construct a structural equation model. RESULTS First, health and exercise awareness had a positive effect on confirmation. Second, among the characteristics of home training content, only specialization had a positive effect on perceived usefulness. Third, confirmation had a positive effect on perceived usefulness and viewing satisfaction, perceived usefulness had a positive effect on viewing satisfaction and exercise continuation intention, and viewing satisfaction had a positive effect on exercise continuation intention, which proved the expectation-confirmation model in this study. CONCLUSIONS To increase exercise continuation intention through home training YouTube content, creators need to produce professional content that can stimulate viewers' internal motivation.
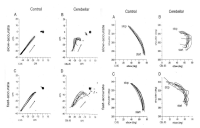
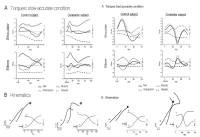
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of trunk stabilization exercise (TSE) with abdominal expansion maneuver (AEM) that lasted for 8 weeks on postural stability and functional movement in college athletes. METHODS Twenty college athletes participated in the program (AEM=9, Control=11) and were subjected to 8-week TSE. The AEM group performed exercise by applying AEM techniques during TSE, and control group performed TSE without breathing-related instructions. Both groups measured postural stability with lower-quarter Y-balance test (LQYBT) and functional movement with functional movement screen (FMS) before and after applying TSE to verify the interaction before and after this study with the two groups. Two-way repeated analysis of variance was performed to evaluate the differences between groups and time for an absolute value of LQYBT and FMS, followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests for post-hoc analysis. RESULTS As a result of the left and right LQYBT, there was a significant difference between the time x group (p=.041, p=.033), and post-hoc analysis indicated that there was a significant difference between the AEM and control groups (p=.000, p=,000). Furthermore, the FMS total score indicated that there was a significant difference between the time × group (p=.039), and the post-hoc analysis showed the AEM group had significant results (p=.001), while there were no significant results in the control group (p=.255). CONCLUSIONS Application of AEM during TSE seems to be effective with regard to postural stability and functional movement in college athletes.
PURPOSE Blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive individuals is reduced by the accumulation of post-exercise hypotension (PEH) induced by a long period of training. This study aimed to investigate the effects of intensity of two different aerobic exercises with identical energy expenditure on post-exercise blood pressure and cardiovascular function in prehypertensive men. METHODS Eleven prehypertensive men in their 30s participated in two trials repeatedly. In the first trial, the exercise was moderate in intensity and continuous (MICE) with 70% of VO2max, and the exercise in the second trial was high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE) with 50% and 90% of VO2max. Each exercise was performed for 30 min, and the variables related to BP and cardiovascular function were measured at certain times for 1 hr during the recovery phase. RESULTS Our main findings are as follows: (1) Systolic blood pressure was significantly lower at 30 and 45 min of recovery time than the baseline in the HIIE trial, and systolic blood pressure was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 10, 15, and 30 min of recovery time. (2) The rate pressure product was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of recovery time. (3) The heart rate was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of recovery time. (4) Stroke volume was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 30 min of recovery time. (5) Cardiac output was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 min of recovery phase. (6) Total vascular conductance was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 and 30 min of recovery phase. (7) Total peripheral resistance was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 and 30 min of recovery phase. CONCLUSIONS The HIIE shows a higher cardiovascular stress than MICE; however, HIIE contributes to the augmentation of PEH and improvement of cardiovascular function. Therefore, HIIE rather than MICE should be suggested in BP control and enhancement of cardiovascular function in prehypertensive males.
PURPOSE With participants in recreational sports clubs, this study clarified positive psychological capital’s mediating effect on the relationship between exercise commitment and perceived stress. METHODS A survey conducted with individuals actively engaged in recreational sports a yielded data for statistical analysis from 296 respondents. Data processing involved frequency analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, structural equation modeling, and testing for mediating effects using the SPSS 29.0 and AMOS 29.0 programs. RESULTS First, results showed that exercise commitment did not significantly impact perceived stress. Second, exercise commitment positively influenced positive psychological capital. Third, positive psychological capital negatively impacted perceived stress. Fourth, positive psychological capital mediated completely between exercise commitment and perceived stress. CONCLUSIONS This research encourages participation in physical activities, especially among those with low physical activity levels, because it positively affects both physical and mental well-being, ultimately enhancing social benefits and overall quality of life.