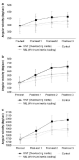
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to analyze the level and characteristics of physical activity (sedentary, light, and MVPA) of high school students according to physical education (PE) class (DWPE: days with PE class, DNPE: days with no PE class) and sex. METHODS Data were collected on 147 students (65 male and 82 female) from four high schools in Seoul city, and physical activity was measured using a three-dimensional accelerometer. The collected physical activity data were input into SPSS 25.0, and the descriptive analysis and two-way ANOVA according to PE class and sex were performed. RESULTS The descriptive statistical analysis showed that 31% (40.7% male and 23.4% female) of participants met the recommended physical activity durations (MVPA of 60 min/day). In the two-way ANOVA, sedentary activity, light activity, and MVPA showed statistically significant main and interaction effects according to PE class and sex. According to the results of the interaction effect analysis, the gap in physical activity between DWPE and DNPE was large in male students. For male students, light activity and MVPA significantly increased on the day of the PE class, and sedentary activity significantly decreased. However, for female students, DWPE and DNPE did not differ significantly in all levels of physical activity. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, the level of physical activity of Korean high school students was relatively low, and the effect of daily-life physical activity in the PE class was limited to male students. Accordingly, an alternative should be introduced to increase the physical activity of female high-school students through PE classes.
Purpose This study was designed to develop a curriculum for pre-service golf coaches at universities to enhance the coaches’ competencies to counsel athletes on the field. Methods This study was conducted in accordance with the revised and supplemented procedures for the national competency standard (NCS) based curriculum development outline under the level of application of individual instruction-level classes among the types of curriculum development. Results The results were as follows: First, the elements of the counseling competence were guided by conflict resolution counseling, psychological skills training, guidance counseling, coordination and Intervention, and relationship formation. Second, the curriculum was adopted as a curriculum for sports psychology, theory and practice of counseling, counseling practice and super-vision, and psychological skills training, and non-disciplinary activities were participation in group and personal counseling, and an open counseling case study. Third, the feasibility of the curriculum was calculated in the range of 0.8 to 1.0 for all areas to be reasonable. Conclusions The results of this study have structured the counseling competencies required for pre-service golf coaches. Based on this, the results of the study suggest counseling courses in the curriculum of university. This is expected to ultimately seek to improve the coaching field by enhancing the capacity of the coaches.
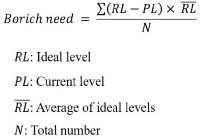



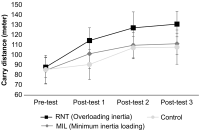
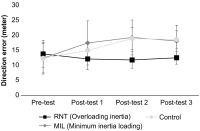
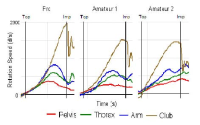
[Purpose] We examined the influence of reactive neuromuscular training (RNT) on golf swing coordination. RNT aims to induce proper coordinative movement by exaggerating the performer’s mistakes. Therefore, we applied RNT using inertia overloading to golfers who have problems with kinematic sequence during a golf swing. [Methods] To examine the effect of 12 weeks of RNT on golf swing coordination, we employed a ball tracking system (launch monitor) and motion analysis system (inertia sensors) were taken on four consecutive periods (pre-test and post-tests 4, 8, and 13 weeks later). Thirty Korean male cadets were divided into three groups based on inertial loading and practiced 7-iron golf swings combined with specific group tasks twice per week. [Results] At pre-test, most participants reached maximal angular velocity near the impact timing (95-100%). However, the deceleration timing of the maximum angular velocity of the proximal segments gradually moved toward mid-downswing as the training sessions proceeded, with the RNT group ultimately outperforming the two control groups. Additionally, the RNT group showed a significantly higher maximum angular velocity in the thorax and wrist. [Conclusion] Our results suggest that RNT can be sufficient to elicit and effective whole-body coordination pattern. Considerable follow-up research is needed on the use of RNT for various sports tasks and the effects of expertise on RNT results.



Purpose The purpose of this study is conducted to analyze the objectivity of the ski technical championships hosted by Korea Ski Instructor Association (KSIA) and to identify the error sources that affect the score of the competition. Methods To this end, we used the data from the 25th(2009) to 33rd(2017) ski technical championships held by the Korea Ski Instructor Association (KSIA). The data provided by Win Excel 2010 was used to sort out the missing data, such as abandonment, according to the data processing method. The collected data were analyzed by using SPSS 22.0 to calculate the mean and standard deviation of each season, event, and judges, and the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC). In addition, by using the single facet crossed design(p*j) of the generalizability theory’s G study, the variance component estimates for the participant(p) and the judges (j) are calculated, and the influence (%). Results As a result of the research, it was confirmed that the results of all the seasons and events from the 25th to the 33th events were very consistent, with the objective of .845~.986 higher than the recognition level of .80. In addition, the results show that the relative ratio of the judges to the error of the judging score is very low as a result of the error analysis through the dispersion component estimates. Conclusion In summary, the results of the KSIA evaluation are highly evaluated objectivity and have very low impact on the judges' errors.


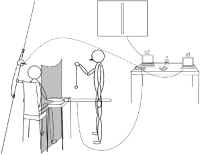
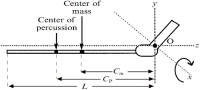
Purpose This study measured the haptic extroperception accuracy, that is, judging one hit position in a hand-held object. Especially, what factors associated the estimation of contact position when the impact is made at the grasped implement by hitting the ball. Methods Relative frequency and conditional probability based analysis verified that perceivers influenced not only the amount of pressure distinguished impressions by the coefficient of restitution but also the pressure distributions encoded impressions by the distance from the hand to the impact. Results Results conformed to previous invariant characteristic on dynamic touch in showing that perceiving the location of the impact of grasped objects, including dominant perceiving selectively modality, is constrained by inertial properties with such success requires appreciating the location of the implement’s center of percussion. Conclusion Investigated in this planes captured as a mechanical factor, we would suggest a broader hypothesis for further research into the effects of the rotational inertia related to haptic position accuracy in the hand-held object, and leading to different estimates of system function providing an account of generalization that accommodates of its varied aspects.

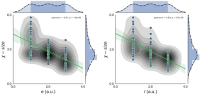
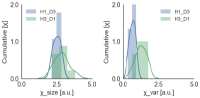
The objective of this study was to examine the relationships among preferred and perceived leadership behavior, their congruence, and satisfaction with leadership based on Chelladurai's(1978) Multidimensional Model of Leadership(MML). To achieve the study objective, 210 professional dancers from 6 professional dance teams located in Seoul and the suburbs participated in this study. For hypotheses testing, descriptive statistics, hierarchical multiple regression analyses, and a confirmatory factor analysis using SPSS and AMOS were used. Results showed that the congruence between preferred and perceived leadership behavior did not have statistically significant influence on dancers satisfaction. The results of the study were inconsistent with what MML suggested. However, the results were quite consistent with empirical evidences of previous studies that investigated the influence of the congruence between preferred and perceived leadership on satisfaction.
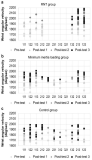
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the current injury status and traits, including damage area, cause of damage based on the situation, and type of occurrence by age group for middle and high schools, university, and professional athletes, in record competition sports (swimming, track and field, and weightlifting). METHODS The study included 503 athletes enrolled in the Korean Sport & Olympic Committee in 2020, and an online survey was conducted using the R statistical program. RESULTS Approximately 38.4% athletes suffered injuries with weightlifting (0.81 times at university) and weightlifting (7.02 times at university) during training. The lower extremities were the most affected areas in all age groups (53.8% in middle school, 48.6% in high school, 44.4% in university, and 47.4% in professional). The causes of damage found to occur most frequently were ‘lack of physical strength, overuse or lack of rest, and recurrence’ and external factors, including ‘facility programs and weather problems.’ The results showed that internal factors during training were mostly associated with ‘overuse or lack of rest and excessive attempts at skills’, while external factors were found to occur in ‘weather problems’. According to the classification of each event, the top priority of frequent damage according to the damaged area was skin bleeding of the head in swimming and muscle inflammation in the torso and upper and lower extremities. Track and field resulted in muscle inflammation in the head, torso, and upper and lower extremities. Weightlifting caused damage to the head and torso, resulted in spinal diseases (disc, spinal stenosis, etc.), and muscle inflammation in the upper and lower extremities. CONCLUSIONS This study highlighted changes in the training environment and training environment, including level-specific physical training, reinforcement programs, scientific access to specific skills, sufficient rest and recovery, and continuous improvement of facilities and equipment.
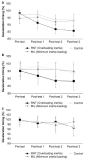
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate characteristics of levels of physical activity in considering gender and different types of competition-oriented physical activity classes using three-dimensional accelerometers. Methods A total of 981 students(505 male students, 476 female students) in six different types of physical education classes were participated in this study. All of the six different types of physical education classes were competition-oriented classes, and levels of physical activity were accessed by three-dimensional accelerometers. Data were analyzed using t-test and ANOVA. Results First, descriptive analyses of participation time of levels of physical activity showed that MVPA of physical education classes is 10.26 mins (22.89%) on average, and, MVPA showed differently in different types of physical education classes in the order of T ball(14.61 mins), flying disk(12.61 mins), soccer(10.78 mins), volley ball(10.56 mins), basketball(9.64 mins), and table tennis(5.73 mins). Second, female students showed significantly lower levels of MVPA in all the different types of physical education classes. Third, post-hoc analyses showed that significantly higher levels of MVPA were found in T ball physical education classes and significantly lower levels of MVPA were found in table tennis physical education classes, compared to other types of physical education classes. Conclusions MVPA in physical education classes is not satisfied with recommended MVPA, and MVPA in Korean physical education classes is lower than MVPA in same types of physical education classes in other countries. In addition, significant mean differences of MVPA are found between male and female students, and new sports physical education classes show higher levels of MVPA compared to classic sports physical education classes. These results indicate that competition oriented physical education classes widely used in Korea need to find ways to increase MVPA and to overcome different levels of MVPA between male and female students.
PURPOSE Players’ nonverbal behavior during a game may be expressed through selfregulatory and intentional processes, where nonverbal cues are strategically used to achieve specific outcomes. This study aimed to observe and explore the strategic and intentional nonverbal behaviors utilized by table tennis players. METHODS The study utilized a grounded theory methodology and involved purposeful sampling of ten adult table tennis players. Semi-structured face-to-face interviews were conducted. The collected data were analyzed using open, axial, and selective coding techniques. RESULTS The findings revealed that players’ intentional nonverbal behaviors are influenced by their confidence levels, physical condition, and perceptions of others’ nonverbal cues. Throughout this process, players underwent various emotional experiences, worked to maintain a positive mental state, and experienced changes in both their behaviors and psychological states, which impacted the flow of the game. CONCLUSIONS This study’s results provide valuable insights into the role of intentional nonverbal behaviors utilized by athletes during competitions. This suggests that understanding and incorporating intentional nonverbal behavior should be a key consideration in sports psychology counseling and psychological skills training.
PURPOSE This study aimed to verify the accuracy of three-dimensional (3D) motion data produced through artificial intelligence-based user motion recognition technology with images obtained using a smartphone monocular camera. This was done to explore the possibility of developing an application that can improve the reliability of the measurement of physical activity performing motions and feedback provision. METHODS To check the accuracy of the artificial intelligence-based 3D motion analysis system that utilized a semi-supervised learning method, a commercialized 3D infrared motion analysis system measured and compared motions on three movement planes, motions with limited joint movement, and fast motions in a wide moving range. RESULTS The motions on the coronal and sagittal planes produced through the 3D motion analysis application showed very high measurement accuracy; however, the accuracy of the measurement of motions on the horizontal plane, which could not be measured directly with a camera, was relatively lower than that of the coronal and sagittal planes. Accuracy in measuring 3D motion was moderate in moving motions and low in motions with limited joint movement. CONCLUSIONS For the developed 3D motion analysis system to be used in online physical education, the types of physical activities included in the program should be comprehensively composed through the analysis of the content system of the physical education curriculum and the resultant physical activities.