PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of an 8-week online yoga training on body composition, muscle activity, flexibility, and balance in males (n=7) and females (n=15). METHODS Twenty-two participants were recruited and divided into two groups (Exercise group, n=11 and control group, n=11). All participants had two visits. During the visits, body composition, muscle activity for forward and back-bending poses, flexibility for sitting-forward and back-bending poses, and balance for one-leg standing were determined. After 8-week yoga training, all measurements were re-performed. An independent t-test was performed to determine the difference between the exercise and control groups. A two-way repeated measures of ANOVA was used to assess the interaction effects (group*time). All values were represented as mean ± standard deviation. An α level was set at 0.05 for all analyses. RESULTS First, the height significantly increased (F=16.573, p=0.001) and body fat mass (F=7.109, p=0.015) and body fat percent (F=7.667, p=0.012) were significantly decreased after the 8-week online yoga training. Second, the muscle activity for vatus lateralis doing a back-bending pose (F=6.140, p=0.022) significantly increased after the 8-week online yoga training. Third, the flexibility on sitting-forward bending pose (F=4.661, p=0.043) and back-bending pose (F=11.650, p=0.003) were statistically increased after the 8-week online yoga training. Lastly, balance on the Center Of Pressure (COP) X (F=5.769, p=0.026) and the Center Of Pressure (COP) Y (F=4.365, p=0.05) significantly increased after the 8-week online yoga training. CONCLUSIONS This study will provide scientific evidence on improving exercise programs using online yoga training on physical activity.

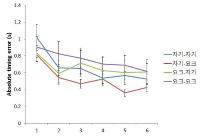
Purpose The present study was set up to investigate the effect of self-regulated learning and selection of feedback on learning of the relative and absolute timing. Methods 48 university student volunteers participated in the experiment and were randomly assigned four groups (n=12 for each) depending on practice task and feedback, namely: 1) self-regulated practice task - self-controlled feedback (self-self), 2) self-regulated practice task - york-controlled feedback (self-york), 3) york-regulated practice task - self-controlled feedback (york-self), and 4) york-regulated practice task - york-controlled feedback (york-york). The task was to examine the temporal timing error and the task goal was to press a computer keyboard 'J' and 'K' alternatively corresponding to time set. Prior to the experiment, the participants had a pre-practice session and then practiced one of three timing tasks provided by an experimenter in the acquisition phase. There were two transfer test to assess adaptability aspects of performing changes related to learning after 24 hours of the acquisition phase. Serial practice was applied in the transfer 1 and an effector transfer was examined in the transfer 2. The dependent variables were a relative timing error that is susceptible to discrepancy between the participant’s key press and the goal patterns and an absolute timing error that is susceptible to discrepancy in the time required to perform the sequence compared to the goal absolute time. Results The results showed that in the pre-test there was no significant difference in both the relative and absolute timing error across four groups. However, in acquisition phase there was a significant difference in both the relative and absolute timing error across block. The relative timing error was different across the group in the transfer test 1, however it was different only between the self-self and york-york group. Lastly, the absolute timing error was not different across the groups in the transfer test 2. Conclusion The findings revealed that the self-regulated strategy is effective to learn the relative timing in the effector transfer.









PURPOSE This study examines organizational autonomy through a public sports governance lens and diverse theoretical perspectives by discussing the longstanding conflicts between the Korea Sports Council and the Ministry of Culture, Sports, and Tourism (MCST) in the context of the Korean Sport and Olympic Committee’s (KSOC) reorientation under President Ryu Seung-min in 2025. METHODS This research adopted Verhoest et al.’s (2004) analytical framework of organizational autonomy to perform a comprehensive literature review that includes scholarly articles, government reports, public institution disclosure documents, and media sources. Expert meetings were also conducted using the naturalistic inquiry method to gather opinions. RESULTS First, this study redefined sport governance as a collaborative partnership between the government and public sport organizations rather than being based merely on traditional government-centric control. Second, public sport organizations’ organizational autonomy has five dimensions: managerial, structural, legal, interventional, and financial autonomy. Third, the KSOC shows high structural and legal autonomy, moderate managerial and interventional autonomy, and low financial autonomy. Fourth, the KSOC’s unique organizational attributes and history allow it to maintain a relatively higher autonomy compared with other public organizations. CONCLUSIONS Amid ongoing debate over its autonomy and independence, the KSOC must balance autonomy with accountability and foster stronger collaborative relations with the MCST to reassert its foundational mission as a public sport organization and help develop stronger and more effective public sport governance.
PURPOSE This study examined Julsil impact on self-management and the moderating effect of achievement goal orientation in adolescent male athletes. METHODS Adolescent male athletes (n=248) registered with the Korean Sports & Olympic Committee participated in a survey. After exclusion of data from seven respondents who provided insincere responses, 241 responses were used for the final analysis. After verification of the measurement tool’s construct validity, technical statistical analysis and correlation analysis were performed. Finally, multiple regression analysis and PROCESS Macro (Model 1) were used to verify the research hypothesis. RESULTS 1) Male adolescent athletes’ Julsil and 2) task goal orientation had significant positive effects on self-management,, but ego goal orientation did not. 3) The moderating effect of task goal orientation on the relationship between Julsil and self-management was significant, but that of ego goal orientation was not. CONCLUSIONS 1) Male adolescent athletes’ Julsil and 2) task goal orientation had significant positive effects on self-management,, but ego goal orientation did not. 3) The moderating effect of task goal orientation on the relationship between Julsil and self-management was significant, but that of ego goal orientation was not.
PURPOSE This study analyzed the relationship between the center of pressure (CoP) trajectory area and ankle inversion/eversion movement across different walking speeds and established a new assessment method for predicting ankle instability. METHODS Twenty-seven healthy young adult males (20 yrs) performed treadmill walking trials at three speeds (slow, normal, and fast). Their cumulative CoP trajectory area and ankle inversion/eversion angles were analyzed, with particular focus on the third quadrant area (3QA). RESULTS During slow walking, mediolateral CoP range (p < .05) and 3QA (p < .05) increased significantly compared to normal and fast walking. Concurrently, ankle inversion/eversion angle (p < .05) and range of motion (p < .05) also increased. Furthermore, 3QA exhibited significant negative correlations with maximum ankle eversion angle (p = .001) and eversion angular velocity (p = .005). CONCLUSIONS This study provides findings that the CoP trajectory’s cumulative area, specifically 3QA, serves as a critical predictor of ankle joint eversion kinematics. These findings have potential implications for ankle instability assessment, prevention, footwear design, and rehabilitation protocols.
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the mediating effect of psychological needs in the relationship between multiple coaching styles and teamwork among college football players. METHODS This cross-sectional study involved 526 elite football players. Descriptive statistics, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, path analysis, and macroprocess were performed using statistical software to test the mediation effects of the data collected. RESULTS The findings suggested that autonomy-supportive and structure coaching styles positively correlated with and impacted psychological needs satisfaction and teamwork. Conversely, control and chaos coaching styles negatively correlated with and impacted psychological needs satisfaction and teamwork. In addition, autonomysupportive and structure coaching styles negatively correlated with and impacted psychological need frustration, while control and chaos styles positively correlated with and impacted psychological needs frustration. Furthermore, psychological needs satisfaction and frustration were found to partially mediate the relationships between autonomy support and teamwork, structure and teamwork, control styles and teamwork, and chaos styles and teamwork. CONCLUSIONS Autonomysupportive and structure coaching styles positively influenced teamwork by satisfying psychological needs. In contrast, control and chaos coaching styles negatively impacted teamwork by contributing to psychological needs frustration.
PURPOSE This study investigated the correlation between anaerobic power and maximum muscle strength in relation to core muscle strength among Korean national golfers. METHODS A total of 96 national golfers (53 females and 43 males) participated in the study. Body composition was assessed using multi-frequency impedance devices, while core and lower extremity muscle strength (extension, flexion, flex/ex ratio) was measured using isokinetic strength tests. Anaerobic power was evaluated through peak power, average power, and power drop rate tests conducted on bicycle ergometers, along with one-repetition maximum (1RM) tests for squats and bench presses. Mean and standard deviation values were calculated for all variables, and linear regression analysis was performed to verify correlations, with statistical significance set at α=.05. RESULTS The comparison of physical characteristics between male and female national golfers revealed significant differences in age, height, body fat percentage, lean body mass, and weight. There was a strong correlation between core muscle strength and isokinetic lower extremity muscle strength. Additionally, a strong correlation was observed between core muscle strength and anaerobic power and between peak power and average power. Furthermore, there was a high correlation between core muscle strength and bench press and squat maximum muscle strength. CONCLUSIONS This study highlights the correlation between various professional physical fitness variables of Korean national golfers over the past decade. The findings are expected to provide valuable insights for coaches and players in developing future training programs.
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop physique and basic physical fitness evaluation criteria for middle school soccer players, providing a foundation for training and player development to be used by coaches in the field. METHODS The study involved 440 middle school soccer players (Grade 1=178, Grade 2=132, and Grade 3=130). Measurements were conducted on seven physique and ten basic physical fitness factors. Measurement results were organized using Windows Excel 2021 and descriptive statistics were performed using Windows SPSS 26.0. Based on the descriptive statistics of the measurement results, the Cajori 5-Grade evaluation method was applied to establish evaluation criteria for each grade and fitness component. RESULTS The study results provide evaluation criteria for middle school soccer players based on the measured data, considering grade, physique, and basic physical fitness. CONCLUSIONS The criteria established in this study are expected to be widely utilized by coaches in the field to set training goals for areas such as player selection, development, injury prevention, and rehabilitation.
PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the factors affecting job stress in fitness instructors, and to elucidate the mediating effects of mindset on the relationship between self-reflection and job stress. METHODS Using convenience sampling, a survey was conducted with 217 male and female fitness instructors nationwide. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 25.0 for descriptive statistics, frequency analysis, and reliability analysis, and AMOS 22.0 for confirmatory factor analysis to validate the measurement tools. SPSS PROCESS Macro v4.0 (Model 4) was utilized to verify the mediating effects of the research model. RESULTS Self-reflection among fitness instructors was found to significantly reduce job stress. A growth mindset was found to have a partial mediating effect on the relationship between self-reflection and job stress among fitness instructors, whereas a fixed mindset did not have a significant impact . CONCLUSIONS The results confirm that self-reflection and having a growth mindset significantly influence the reduction of job stress in fitness instructors.
PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze the differences in ground reaction forces (GRF) and pelvis and trunk kinematic patterns between groups based on ball speed during pitching. METHODS Twenty-nine males were recruited for this study. Participants were categorized based on ball speed into high (HG), medium (MG), and low (LG) ball speed groups. Statistical analysis was performed using one-dimensional statistical parametric mapping (SPM1D) one-way analysis of variance to compare GRF and pelvis and trunk kinematic patterns, followed by Bonferroni post-hoc tests. RESULTS Drive leg anterior and resultant GRF were greater in the HG than in the LG (p<0.001). The posterior GRF of the stride leg in the HG was greater than in the LG (p<0.008). Additionally, the vertical GRF of the stride leg was greater in the HG than in the LG (p<0.003), as was the resultant GRF of the stride leg (p<0.003). CONCLUSIONS The GRF of the drive and stride legs was significantly related to ball speed, indicating that a pitching strategy to maximize the GRF of the drive and stride legs is required.