
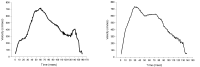
The purpose of this study is to establish the efficient defensive strategy from analyzing the goalkeeper’s gaze behavior and defensive motion in both field hokey penalty corner and penalty stroke. To achieve this goal, 3 national team goalkeepers’ gaze behavior and defensive motions were analyzed, as well as the player’s visual strategies from their interview contents. For the apparatus, multi-channel integrational system were used for analyzing goalkeeper’s reaction movement and personal visual strategies. The result is as follow: First of all, In the penalty stroke, goalkeepers were tended to focus on the bottom of the shooter’s hokey stick. Second, national hokey players had quicker anticipating saccadic movement. For this reason, their visual fixation locations were arrived in targets earlier than the hockey ball. Lastly, in the interview contents, they were reported to focus just on the ball from not disturbed by other various objects(body, hockey stick). However, they actually observed various body parts of shooters. These results imply that we need to develop an effective perceptual skill training in order to anticipate the shooting performance more accurately and rapidly. These types of perceptual and cognitive skill training should be conducted with information on knowing their specific visual cues in anticipating shooting direction.



This study aimed to analyze the patterns of service return and the 3rd stroke in relation to the winning and losing points in Badminton men's doubles matches. Especially the comparison of the patterns between rally point and service server game systems was made. Video records of 12 top elite teams were analyzed. As a result, there were significant differences in the total stroke patterns between the rally point system and the server game, and there was a higher offensive stroke tendency. After classification of situations with ‘after the service trial’ and ‘after the service return’, there were high number of winning ratio and offensive stroke in the after the service situations. There were no significant difference in the winning/losing points and winning ratio when the types of 3rd shot attempts were analyzed. I case of the win and lose in service return, there was a significant difference in the server game while not in the rally point system. Offensive stroke ratio in the server’s return categories and the service return strokes’ categories, and was no difference in shots after the return of service in the server team. From the investigation of offensive stroke ratio and winning ratio, there was a high ratio in the rally point system game but no difference in the server game. When aggressive service return took place, rally point system had higher winning ratio, but the server game system did not display such characteristic. Based on these results, recommendations of service anticipation and aggressive plays for Korean Men's doubles game have been suggested.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of auditory stimulus using white noise on stability and balance during sit-to-stand and standing tasks of chronic stroke patients. Methods Eighteen chronic stroke patients participated in this study. They asked to perform the tasks of sit-to-stand, standing with eyes open and standing with eyes closed before and after listening to white noise. Eight infrared cameras and one force plate were used to evaluate the stability and balance before and after the white noise stimulus during each task. Results There was no significant difference between before and after white noise stimulus in all tasks. On the other hand, the anteroposterior range of CoP was significantly decreased after white noise stimulus in standing with eyes-closed (p<.05), and the sagittal angle of CoP-CoM was significantly decreased after white noise stimulus in standing with eyes-open and eyes-closed (p<.05). Conclusion Auditory stimulus using white noise improves the balance of chronic stroke patients. Therefore it is thought to be helpful for the independent daily life of chronic stroke patients.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of coupled high frequency rTMS and prism illusion in elderly stroke patients, based on the result of previous studies which discovered the effect of bilateral training, mirror rehabilitation treatment, and rTMS. Methods This is a case study of 4 stroke patients who were homogeneous on the basis of selection criteria such as brain injury area, duration of onset, degree of upper limb movement function. A total of 24 rehabilitation sessions were conducted three times a week during the training period, and TMS(transcranial magnetic stimulator), EMG, motion analysis system, and prism optical glasses were used for apparatus. Results The results of the study were as follows: Combined rehabilitation exercises were found to be beneficial to restore upper limb function in stroke patients. Particularly, the maximum speed of stretching and JTT(Jebsen-taylor Test) performance showed improvement after training. The amount of total map volume and MEP(megnetic evoked potential) increased in evaluation of neurophysiology. Conclusion The upper limb dysfunction of stroke patients could be restored by combine rehabilitation exercises.








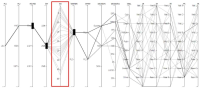
This study aims to visualize the data regarding the entire rally and the final 5 strokes in a badminton single match and to present its analysis method using the parallel coordinate system. For this study, were used the videos of three games of the final, semifinal, quarterfinal in the '2014 National Fall Badminton Championship’ where the L Player of Gyeonggi C university won championship. Herein, the data was collected utilizing a tagging technique of Dartfish (Ver 8.0), in terms of shuttlecock ball direction, judgment of final kill stroke, and used technique. The data collected were classified and condensed using Excel 2013 program, and the parallel coordinates, which is provided with free open source through D3js.org, was utilized as a data visualization tool. As the results; first, the entire rally of single matches in badminton was visualized; second, as an analysis method of data visualization in relation to final 5 strokes, game pattern analysis, attack success course analysis by players and techniques, attack failure course analysis by players and techniques, and a plurality of selected condition analysis by players and techniques could be presented. In future, when processing subsequent studies that can provide us together with numerically analyzed data as well as visualization through a parallel coordinate system, it is expected that this study could be applicable to a variety of events and utilized in the actual sports games.







PURPOSE Blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive individuals is reduced by the accumulation of post-exercise hypotension (PEH) induced by a long period of training. This study aimed to investigate the effects of intensity of two different aerobic exercises with identical energy expenditure on post-exercise blood pressure and cardiovascular function in prehypertensive men. METHODS Eleven prehypertensive men in their 30s participated in two trials repeatedly. In the first trial, the exercise was moderate in intensity and continuous (MICE) with 70% of VO2max, and the exercise in the second trial was high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE) with 50% and 90% of VO2max. Each exercise was performed for 30 min, and the variables related to BP and cardiovascular function were measured at certain times for 1 hr during the recovery phase. RESULTS Our main findings are as follows: (1) Systolic blood pressure was significantly lower at 30 and 45 min of recovery time than the baseline in the HIIE trial, and systolic blood pressure was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 10, 15, and 30 min of recovery time. (2) The rate pressure product was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of recovery time. (3) The heart rate was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min of recovery time. (4) Stroke volume was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 30 min of recovery time. (5) Cardiac output was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 min of recovery phase. (6) Total vascular conductance was significantly higher in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 and 30 min of recovery phase. (7) Total peripheral resistance was significantly lower in the HIIE trial than the MICE trial at 15 and 30 min of recovery phase. CONCLUSIONS The HIIE shows a higher cardiovascular stress than MICE; however, HIIE contributes to the augmentation of PEH and improvement of cardiovascular function. Therefore, HIIE rather than MICE should be suggested in BP control and enhancement of cardiovascular function in prehypertensive males.
PURPOSE This study seeks to contribute to the enhancement of the performance of domestic wheelchair racers by producing 3D-printed customized gloves and verifying their application effect. METHODS A total of three male wheelchair racers who belong to the T54 and have won gold medals in the National Para Games within the last three years were selected as subjects. Each subject performed three session s of muscle activity and maximum speed measurements before and after applying a 3D-printed glove during the stroke and recovery phases of wheelchair racing, focusing on the pectoralis major (PM), triceps brachii (TB), and erector spinae (ES) muscles. To standardize the muscle activity measurement data, the relative muscle activity level (%) for each section was calculated by maximum voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC) for each subject. All maximum speeds of each round of driving were calculated by the average record for comparative analysis. In addition, to verify the effectiveness of applying the 3D-printed glove, the Wilcoxon signed rank test, which is a non-parametric test method, was performed on all measured values using SPSS 24.0. RESULTS This study derived the following results. First, a statistically significant difference was observed in the muscle activity of each major muscle before and after using the 3D-printed glove. In common, an increase in muscle activity of the PM, TB, and ES was confirmed in the stroke section, and an increase in muscle activity of the TB was confirmed in the recovery section. Second, a statistically significant difference was documented in the maximum speed before and after using the 3D-printed glove. When using 3D-printed gloves, the maximum speed increased by 4.57, 3.63, and 1.06km/h for Payer A, and by 5.9, 6.04, and 7.86km/ h for Player B. In the case of Player C, the speed increased by 6.73, 2.27, and 0.83km/h, and all three players improved their maximum speed through the 3D-printed gloves. CONCLUSIONS Our study suggests that the application of 3D-printed customized gloves can have a positive impact on the performance of wheelchair racers. If the application of 3D-printed customized equipment is extended to athletes in a wider range of sports in the future, this could significantly contribute to the improvement of performance in domestic disability sport.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the technique and power of the Korean national athletes and international athletes in the start phase of the 500 m speed skating to improve the performance and to understand the relationship between the biomechanical variables affecting the record. Method The subjects were 8 Korean national athletes (Korean athletes) and 6 international athletes (international athletes). For the three dimensional motion analysis, 5 high-speed cameras were used to capture the 40 m start phase of the athletes participating in the international competition. The variables selected for analysis were the kinematic chain, 100 m net time, time to 9 strokes, horizontal position of center of mass after 2.5 sec, range of motion of trunk, knee, push-off angle, net power output, total power loss. Results The correct kinematic chain ratio of Korean athletes was 61.2%, which was lower than 76.0% of international athletes. The time to 9 strokes was 2.82±0.25 sec for Korean athletes, which was significantly lower than 2.53±0.11 sec for international athletes (p=.001). The range of motion of the push-off angle was 60.15±2.75° for Korean athletes, which was significantly lower than 64.76±2.55° for international athletes (p=.001). The net power output was 887.2±269.9 W for Korean players and 1103±264.1 W for international players (p=.021). The variables related to the 100 m net time were the horizontal position of center of mass after 2.5 sec (r=-.956, p=.001), the net power output (r=-.931, p=.001), and the total power loss (r=-.904, p=.001). Conclusion In order to improve the start performance of Korean athletes, it is necessary to maximize the efficiency of skating through skill training to use the correct kinematic chain. Also power enhancement training is needed to improve leg power because the net power output related with 100 m net time.



The purpose of this study was a investigate the endothelial function of prehypertensive during dynamic exercise. Hypothesis of this study was to impair the endothelial function in prehypertensive compared to normtensive during dynamic handgrip exercise. Eleven healthy prehypertension (24±2 yrs) and ten healthy normotensive (25 ± 2 yrs) were recruited in this study. Participants were performed dynamic handgrip exercise in one contraction per second at 30% of maximum voluntary contraction for three minutes. Vascular (blood vessel diameter, blood flow) and cardiar response (stroke volume, heart rate and cardiac output) were measured at rest and during exercise. Flow mediated dilation (FMD) was decrease significantly in prehypertensive less than normotensive (p<0.05) at rest, and vasodilation of prehypertensive was reduced significantly less than normitensive during exercise (p<0.05). All the cardiovascular responses were aot significantly different at rest and during exercise between prehypertensive and normotensive. These results suggest that endothelial function is impaired in prehypertensive compared to in normotensive

Purpose : The purpose of this study was to investigate coaching information with which coaches provided players during badminton competition. Methods : To this end, we generated an open-ended questions and presented it to 88 high school athletes registered in the Badminton Korea Association. The survey was conducted during a tournament and immediately after the tournament to collect the data. The collected data were categorized through inductive content analysis. Results : As a result of this study, a total of 480 raw data points collected through the open-ended survey were categorized into four general areas: psychological information, technical information, tactical information, and game operation information. Specifically, psychological information was divided into six subdivisions: concentration, confidence, relaxation/stabilization, mental toughness, play thought, and passion; technical information was broken into four subdivisions: strokes, footwork, swing and posture, and position preparation; tactical information had four subdivisions: coping to opponents, play changes, rotation, and manipulation of opponents; and, game operation information was divided into two subdivisions: taking the lead in a game and changing atmosphere. Conclusions : In other words, in badminton competition, the coaches strengthened psychological skills that promote psychological stability to attain the athletes’ peak performance and modified the athletes’ motion into the action necessary for achieving accurate techniques. Furthermore, they provided a variety of coaching information so that the athletes will respond appropriately to their opponents’ play, take the lead in games and induce a positive mood. The psychological, technical, tactical and game operation information offered by badminton coaches are the main factors influencing the performance of badminton players and suggest a need for the proper management and control of the coaches as well as athletes for the peak performance.