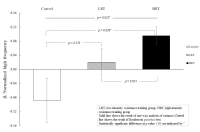
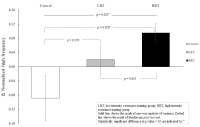
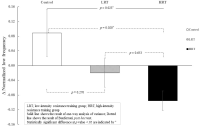
The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of resistance training with different exercise intensities on heart rate variability(HRV) in habitual smokers. Twenty-eight healthy young smokers participated in this study were randomly divided into three groups; CON(control), LRT(low-intensity resistance training; 50% 1RM), and HRT(high-intensity resistance training; 70%1RM), respectively. LRT and HRT groups performed an 8-week resistance training(4 upper- and lower body exercises) using weight training machines, whereas CON group maintained their regular activities. All groups were evaluated basal body composition, hemodynamic parameters, HRV as autonomic nervous function, and muscular strength (1RM and isokinetic test) before and after the 8-week training. To assess the effect of 8-week training with different intensities on autonomic regulation, time and frequency domain indices of HRV were calculated from 5min R-R interval recording. As results, both LRT and HRT groups increased baseline 1RM and isokinetic strength compared to CON group. Meanwhile, high-frequency power reflecting parasympathetic activity was significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. In addition, normalized low frequency power(LF nu) indicating a shift of sympathovagal balance towards sympathetic predominance significantly decreased while normalized high frequency power(HF nu) which reflects vagal predominance significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. Furthermore, improved cardiac autonomic regulation and parasympathetic activation had significant association with increased muscular strength. Overall, the 8-week training has enhanced muscular strength in both training groups, particularly autonomic balance improved in young habitual smokers with high intensity resistance training.

PURPOSE Recreation specialization theory, which is characterized by a unique development process and progress, has been found to have varied pathways that develop in different patterns based on each dimension of recreation specialization. This study aimed to investigate how each sub-dimension of specialization changes as the degrees of experiential participation (frequency, period, and intensity of participation) and goods investment (expenditure) of the scuba divers increase. METHODS In the summer of 2021 (May-August), a purposive sampling method was used to collect samples from young scuba divers, and 278 copies of valid data were used for the final analysis. Frequency analysis, descriptive statistical analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, curve estimation analysis, and hierarchical regression analysis were performed using SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 24.0 ver. RESULTS The findings were as follows. First, the quadratic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the scuba divers’ participation intensity and cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations based on experience. Second, the cubic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the participation period, frequency of participation, and cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations of scuba divers. Third, the cubic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the expenditure cost of scuba divers and the cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations in the center of the goods. As the period, frequency, and expenditure of scuba diving participants increased, the relevant cognitive, behavioral, and affective specializations did not progress in a linear manner; instead, they went through an intermediate maintenance stage and developed to a higher level. CONCLUSIONS Progressive and meaningful consumption of experiences and goods further promotes recreation specialization. Any future follow-up study should identify a trade-off point in the development of the recreation specialization in a step by step manner.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of visual color perception on autonomic nervous activity and exercise capacity in healthy male college students. METHODS The subjects who were healthy male college student (n=10) were participated in 4 visual colors using by randomized crossover; clear color group (CG), red color group (RG), blue color group (BG) and green color group (GG). All subjects wore goggles for five minutes prior to the exercise to adjust to color, and they did not take off goggles until recovery after exercise. Significant differences between groups were determined by two-way repeated measures ANOVA. RESULTS As a result of this study, the low frequency (LF) was significantly higher in RG than those in GG. But the high frequency (HF) was significant higher in BG compared to GG. Exercise capacity such as maximum strength, muscle endurance, reaction time, power, agility and aerobic performance did not differ significantly between all groups. CONCLUSIONS Therefore, our findings suggested that perception of the visual color might be change autonomic nervous activity, while don’t influence exercise capacity.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to analyze the performance contents of men's floor exercise and to provide basic materials for achieving excellent results at world competitions. Methods Teams ranked 1 - 12 who participated in the World Championships' floor movement group competition selected a total of 59 players by the convenience sampling method and carried out technical statistics, frequency analysis, member variable variance analysis, and post hoc analysis. Results First, as a result of frequency analysis of the difficulty of each group, all the teams ranked 1 to 12 liked the most difficulty of C and found that they do not like the F difficulty the most. Secondly, there was a difference in average for each group's start score, ranking 1st to 4th> 5th to 8th> 9th to 12th place. Thirdly, there was a difference in average of difficulty levels for each group B, C, E, and it became very significant with E difficulty.Results of post hoc analysis B difficulty (9th to 12th> 1st to 4th, 5th to 8th), C difficulty (9th to 12th> 1st to 4th), E difficulty (1st to 4th> 5th to 8th ·9th to 12th). Conclusion These results show that in floor exercise, the art of more than C difficulty and the connection technology of A, B, C, difficulty, E and F, difficult difficulty such as difficulty, creative and dynamic performance composition is excellent It clearly states that it is a condition for getting results.
PURPOSE This study investigated the correlation between anaerobic power and maximum muscle strength in relation to core muscle strength among Korean national golfers. METHODS A total of 96 national golfers (53 females and 43 males) participated in the study. Body composition was assessed using multi-frequency impedance devices, while core and lower extremity muscle strength (extension, flexion, flex/ex ratio) was measured using isokinetic strength tests. Anaerobic power was evaluated through peak power, average power, and power drop rate tests conducted on bicycle ergometers, along with one-repetition maximum (1RM) tests for squats and bench presses. Mean and standard deviation values were calculated for all variables, and linear regression analysis was performed to verify correlations, with statistical significance set at α=.05. RESULTS The comparison of physical characteristics between male and female national golfers revealed significant differences in age, height, body fat percentage, lean body mass, and weight. There was a strong correlation between core muscle strength and isokinetic lower extremity muscle strength. Additionally, a strong correlation was observed between core muscle strength and anaerobic power and between peak power and average power. Furthermore, there was a high correlation between core muscle strength and bench press and squat maximum muscle strength. CONCLUSIONS This study highlights the correlation between various professional physical fitness variables of Korean national golfers over the past decade. The findings are expected to provide valuable insights for coaches and players in developing future training programs.
PURPOSE This study aims to analyze research trends on the social capital in sports. METHODS A total of 69 papers published until December 2020 were selected as research subjects. Further, Excel, KrKwic software, and NetDraw function of the UCINET 6 program were used for analysis. RESULTS First, social capital research on sports has shown quantitative growth since 2010. Second, the studies were conducted on sports participants such as general, elderly, college students, adolescents, foreigners, and the disabled, showing the highest frequency of research subjects. Third, quantitative research conducted based on the research method were several. Fourth, single-author studies were the highest. Fifth, as the result of the analysis on the publication journal, the Journal of the Korean Physical Education Association was shown the highest. Sixth, due to frequency analysis of the thesis keywords, “social capital,” “sports participation,” “action intention,” “social capital type,” “living sports participation,” and “youth” were shown the highest. Seventh, as a result of centrality analysis between keywords through the network analysis, “sports participation” in connection centrality, “health-promoting lifestyle” in proximity centrality, and “sports participation” in mediation centrality were found as the highest. CONCLUSIONS The significance of social capital in sports is more important than others because it is a fundamental element for creating a culture where more people can enjoy sports moderately in Korea, where capitalism and liberal democracy were adopted as the governing system. Therefore, this study can be a vital resource significantly contributing to the understanding and active use of social capital, a significant factor in developing sports in Korea.
Purpose The current study investigated the effects of exercise information using social network service(SNS) to identify changes of physical activity and psychological variables among inactive college students. Methods Inactive college students(30 experimental group, 30 control group) were voluntarily participated in the 12-weeks intervention. During this period, the experimental group received exercise information through SNS. And all study participants’ physical activity, stages of physical activity, self-efficacy, motivation, and perceived benefits and barriers were measured at the pre, mid and post intervention. Frequency analysis, chi-square test, 2-way ANOVA RM were conducted to analyze data obtained in the study. All procedures were performed by using SPSS 23.0. Results The exercise information intervention using SNS during 12 weeks had a positive effect on the stages of physical activity of inactive college students, and there were statistically significant differences. In addition, physical activity, perceived benefits and barriers, self-efficacy, motivation positively improved after the intervention, but there were no statistically significant differences between experimental and control group. Conclusions The present study suggests that psychological strategies using various SNS programs have positive effects for inactive college students to increase physical activity and its related psychological variables.

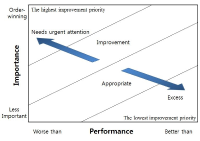
Purpose The purpose of this study was to verify the importance and satisfaction of service quality of visitors to screen baseball using the Importance-Performance Analysis. Methods Selected visitors who participated in screen baseball using convenience sampling of non-probability sample method from January 26 to May 27, 2017, and conducted a questionnaire survey to a total of 213 data were used in this study except 17 data which were untrustworthy responses or non-responses. SPSS 21.0 statistical program were used to exploratory factor analysis, reliability analysis, frequency analysis and IPA. Results The results were as follows. first of all,Ⅰquadrant derives 7 items including modernized facilities and equipments. Next, Ⅱ quadrant, there are 5 credibility of the program and continuous service provision. Also, in the quadrant Ⅲ, the service promised to the customer and the interest and effort of the staff in case of trouble were confirmed.. In the quadrant IV, four items were analyzed such as the interest in the members and the matching of the members' use time. In the analysis of Slack's(1994) diagonal model, twelve kinds of improvements such as costumes, appearance, internal facilities and services promised to customers were derived. In addition, there are 5 appropriately provided properties such as modern facilities and equipment, and facilities suitable for enjoying baseball. Finally, in the attributes that are provided in excess, four attributes are indicated, attention to members and matching of members' use time. Conclusion Based on the results of this study, it is meaningful to be a marketing and management practice data for operating the screen baseball.



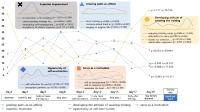
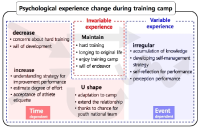
Purpose The current study aimed to identify national youth cyclist`s experience and change tendency of experience during camp training. Methods A total of 35 cyclists who participated in 2017 Korea youth national cycling camp training provided the data. The survey was conducted 9 times during the 20 days of camp training using open-ended questionnaire by diary method. The collected data were analyzed based on inductive categorization and response rates. This study was conducted in the order of formation rapport, data collection, and data analysis. Results Youth cyclists experiences during camp training to growing pains as an athlete, developing the attitude of savoring training, serve as a motivation, expertise formation and opportunity of self-examination. Based on the change in response frequency of the survey data, camp training experience falls into two categories: variable and invariable. Conclusions Youth national cyclist were growing their growth power through various experiences during the training camp, and these experiences changed to specific inflection points from the beginning to the end of the camp. Understanding changes in psychological experience can provide the design of timely psychological support and coaching method. This study will be used as a material for the design of the camp training program for the youth cyclist, as well as an opportunity to increase the interest of continuity reflection on the psychological experience.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between physical activity and depression according to the presence of disease. Methods A survey and basic assessment were conducted for 2,754 (Male=1,025 and Female=1,729) aged 40 and over who participated in the rural-based cohort study. The survey included physical activity, depression scale and disease preservation. The basic assessment measured height, weight, and body fat percentage. The measured data were analyzed by using logistic regression to examine the relationship between physical activity and depression prevalence. Results First, physical activity reduced the prevalence of depression by 33% and 51%, respectively, in the general population and in patients with the disease. Second, physical activity once or twice per week reduced the prevalence of depression in patients with disease by 51%, and at least three physical activities reduced the prevalence of depression by 37% in the general population and 33% of patients with disease. Third, physical activity less than 150 minutes per week reduced the prevalence of depression in patients with disease by 43%, and physical activity of more than 150 minutes and less than 300 minutes per week reduced the prevalence of 43% of the general population and 52% of patients with disease. Physical activity over 300 minutes per week had a 38% reduction in the prevalence of depression in the general population. Conclusions This study suggests that the level of physical activity suggested by the ACSM guidelines is appropriate to reduce the prevalence of depression. In addition, the patients with the disease was found to be effective with less frequency and amount of physical activity than the general person.