PURPOSE The outdoor camping market size is expected to hit a new high in 2021 as the popularity of outdoor activities surges due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The purpose of this study was to investigate the structural relationships among servicescape, perceived value, flow and behavioral intention, focusing on participants of international outdoor camping exhibition. METHODS Demographic analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation modeling analysis were perfomed. RESULTS The findings suggest that (1) all servicescape factors (attractiveness, cleanliness, accessibility and responsiveness) have a positive effect on perceived value, (2) attractiveness, cleanliness and responsiveness are significant predictors of flow, (3) perceived value affects both flow and behavioral intention, and (4) flow also significantly impacts behavioral intention. CONCLUSIONS These findings highlight that high quality servicescape can result in enhancing a positive perceived value and flow, and in turn leading to behavioral intention of consumers. Hence, it is recommended for practitioners and staff of the exhibitions to considering the strategies for improving servicescape factors in order to achieve their goal.

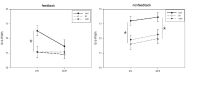
[Purpose] Perception plays an important role in understanding the environment or related objects in order for humans to perform physical movements more effectively. Sometimes they create different movements with different perceptions. Especially, visual perception errors that occur in sports situations can have a considerable effect on performance. Accurate knowledge of the environment in this process of perception is important in performing movements or actions. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of learning formation on perception using Muller-Liar illusion diagrams. To measure this, we compared the feedback group that induced knowledge learning and the control group that did not provide knowledge To see if there is a difference. Therefore, in this study, we have provided a visual feedback that can establish the cognitive awareness of the actual stimuli length to subjects, and investigated the changes in their matching action responses. [Methods] A total of 32 young and healthy subjects were randomly divided into two groups (Feedback and Non-Feedback groups). Subjects were asked to match the stimulus size with their index fingers and thumbs. Initially (pre-test), three different visual stimuli (inward, outward, and no arrows) were randomly presented 60 times (20 times each) and the grip sizes were recorded using the Liberty Motion Analysis System (Polhemus Co., America). Then, video clips of two lines merging each other were presented as feedbacks. Post-test protocol was identical to the pre-test protocol. The data were analyzed using the 3-way ANOVA with one RM factor (2 x 3 x 2). [Results] Results showed a significant 2-way interaction effect. Post-hoc results showed significant interaction between stimulus shape and pre/post-tests only in the experimental group. There was a significant decrease in the grip size after feedback in the OUT condition of experimental group. However, in the control group, there was no interaction between stimulus shape and pre/post-tests. [Conclusion] Overall, current results indicates that, while visual illusion can affect the action, the provision of visual feedback can establish the awareness of actual stimulus size and suppress the influence of illusion on action.

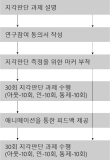

Purpose This study was designed to develop a team building program that helps freshmen student-athletes to adapt to college life and enhance team function and process and to examine the effects of this program. It could provide basic information of a team building program that effectively accelerates team function in the college team sports domain. Methods The program was developed through this process. First, an open-ended questionnaire was utilized to discover the needs of the program. Second, the results of needs of the program and important factors of team-building program were taken into consideration. Third, expert meetings were conducted. Consequently, the program consisted of three stages of total 10 sessions which was 90 min long. The questionnaires(Group Cohesion Questionnaire and Coach-Athlete Relationship Questionnaire), experience report, and program evaluation form were used as measures to identify the effects of the developed program. SPSS version 24.0 and inductive analysis were used to analyze the data. Results The results of this study are as follows. First, there was no statistically significant influence between developed program and the level of group cohesion. In contrast, the level of coach-athlete interaction was significantly increased. Second, the analysis of experience report revealed that this program reduced interpersonal conflict between team members and formed positive interpersonal relationship by mind of respect and consideration. Conclusion In conclusion, the hierarchical culture was strongly formed and team member suffered from the dual role of athlete and student in Korean college team sports. Thus, these should be resolved in order to enhance team function and process. As a results, this process could increase team performance as well as offer psychological stability to college student-athletes.


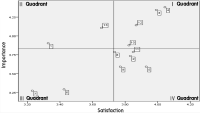
Purpose The purpose of this study is to grasp consumers' perception of badminton racket brand image using MDS and ISA. Methods To do this, we conducted questionnaires on those who participated in badminton and had experience of participating for 6 months or more in Seoul and Gyeonggi province from April 12 to 28, 2017, selected and analyzed a total of 313 copies as valid samples of this study. Results The results of study are as follows. First, as a result of MDS analysis, it showed that only the price of brand image attributes were in order of Trion > Joobong > Lining > Victor > Yonex, and the other attributes(Design, Functionality, Quality, Awareness, Advertising image, Event, Color, Popularity, Sophistication, Originality, Trust, Service) were in order of Yonex > Victor > Lining > Joobong > Trion. Second, as a result of ISA analysis, in I quadrant, Yonex showed functionality, quality, sophistication, and trust and Trion showed price, design, functionality and quality, Victor showed price, design, functionality, quality, color, sophistication, trust, service, and Joobong showed price, functionality, quality, and trust in this area. In quadrant Ⅱ as concentrated area, Yonex showed price and service, Trion showed color, trust, service, Victor showed price, Lining showed trust and service, and Joobong showed service in this area. In quadrant Ⅲ as low rank, Yonex showed advertising image, event, Trion showed awareness, advertising image, event, popularity, sophistication, originality, Victor showed advertising image, event, popularity, originality, Lining showed awareness, advertising image, event, popularity, originality, and Joobong showed design, advertising image, color, popularity, sophistication in this area. In quadrant IV as excess avoidance, Yonex showed design, awareness, color, popularity, originality, Victor showed awareness, Joobong showed awareness, event, originality in this area.








The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of running economy and energy return in lower extremities according to the increase of bending stiffness of the shoes, furthermore to investigate the relationship between running economy and energy return for the improvement of sports performance. Subjects employed for this study were 10 healthy male college students who have not had the experiences in lower extremities injuries. Four different kinds of shoes in bending stiffness as with 0.56 N/mm, 0.74 N/mm, 0.96 N/mm, 1.21N/mm were used respectively. 3-D cinematography and pulmonary gas analyzer were utilized for energy return and energy consumption data during running according to the increase of bending stiffness of the shoes to obtain the following results. As the bending stiffness of running shoes increased, the statistical significance were not founded, however, the tendency of decrease in max. flexion moment and power, increase in max. extension moment and power in lower extremity joint were showed. Joints energy showed no statistical significance in phase 1, however, the tendency of lesser absorbtion as the bending stiffness of running shoes increased were showed. More energy were generated as the bending stiffness of running shoes increased in phase 2 with no statistical significance. Energy economy increased according to the increase of bending stiffness of running shoes. Negative correlation were showed between flexion moment of hip joint and energy consumption(p<0.05). Slightly higher degree of correlation between max. flexion power of hip and ankle joint and energy consumption were showed without statistical significance. Negative correlation were showed between joints energy and energy consumption for ankle joint in phase 1(p<0.05).


PURPOSE This study theoretically explains the relationship between Keirin players’ core competencies and their performances. It also analyzes the impact of interaction between objectively identifiable core competencies and players’ efficiency toward their results, that is, the ability to convert their resources into performance. METHODS Using Python 3.11.1, 20,185 race records were collected of cyclists who competed at Gwangmyeong Velodrome in 2022 and 2023, and player efficiency was estimated using the R 4.3.1 package. Subsequently, the impact of players’ physical abilities (200 m records) on performance and player efficiency’s influence on the relationship between physical ability and performance were analyzed using Model 1 of PROCESS 4.1 Macro installed in SPSS 26.0. RESULTS First, players’ physical ability had a statistically significant impact on their performance. Specifically, the 200 m record significantly influenced the likelihood of finishing in the top 1 (coef = –.68 , p<.01 ), top 2 (coef = –.56, p<.01), and top 3 (coef = –.46, p<.01). Second, player efficiency moderated the relationship between players’ 200 m record and the likelihood of finishing within the top ranks. Specifically, the interaction term’s influence was empirically demonstrated between 200 m records and player efficiency on the likelihood of finishing within the top 1 (coef = –.47, p<.05), top 2 (coef = –.28, p<.05), and top 3 (coef = –.28, p<.05) for players with similar speeds, in that it significantly increased. CONCLUSIONS This study pioneers research that explains the relationship between players’ key competencies and performance based on resource-based theory, and it empirically demonstrates that player efficiency serves as a moderating variable in the relationship between key competencies and performance.

Purpose The present study explores educational values of professional coaches from perspectives as educators while they are giving the players sports coaching. Since free agent system was introduced in 1999 at Korean Baseball Organization(KBO) league, the socio-economical differences between players and coaches are getting bigger and bigger. In this situation, professional coaches tend to have more difficulties in interacting with the players. The study focuses on looking into professional coaches' educational agony and reward. Also, it highlights their educational values as educators rather than coaches. Methods Two professional baseball coaches and a TV commentator participated in the study: all past professional players, and professional coaches for more than 10 years. The researchers collected data through semi-structured in-depth interviews; each participant was interviewed three times. The researchers recorded and transcribed all of the interviews; then, the researchers reread the interview transcripts and inductively produced codes for themes whenever emergent codes appeared. Verbatim quotations from the interviews are excerpted in the present research report. Results The findings indicate that, first, the participants are all highly motivated in giving lessons to the players. They all helped the players overcome the difficulties and be good players. They emphasized the importances of endeavors and attitudes during their lessons to be well-received by the players. Second, the participants agreed that good coaches should have the ability to find the potentials of the players and have personality to gain the players' trust. They always have to work and study hard to keep expertises. Conclusions This study argues that the participants are playing their roles in a sport coaching area not only as coaches, but also as educators.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the technique and power of the Korean national athletes and international athletes in the start phase of the 500 m speed skating to improve the performance and to understand the relationship between the biomechanical variables affecting the record. Method The subjects were 8 Korean national athletes (Korean athletes) and 6 international athletes (international athletes). For the three dimensional motion analysis, 5 high-speed cameras were used to capture the 40 m start phase of the athletes participating in the international competition. The variables selected for analysis were the kinematic chain, 100 m net time, time to 9 strokes, horizontal position of center of mass after 2.5 sec, range of motion of trunk, knee, push-off angle, net power output, total power loss. Results The correct kinematic chain ratio of Korean athletes was 61.2%, which was lower than 76.0% of international athletes. The time to 9 strokes was 2.82±0.25 sec for Korean athletes, which was significantly lower than 2.53±0.11 sec for international athletes (p=.001). The range of motion of the push-off angle was 60.15±2.75° for Korean athletes, which was significantly lower than 64.76±2.55° for international athletes (p=.001). The net power output was 887.2±269.9 W for Korean players and 1103±264.1 W for international players (p=.021). The variables related to the 100 m net time were the horizontal position of center of mass after 2.5 sec (r=-.956, p=.001), the net power output (r=-.931, p=.001), and the total power loss (r=-.904, p=.001). Conclusion In order to improve the start performance of Korean athletes, it is necessary to maximize the efficiency of skating through skill training to use the correct kinematic chain. Also power enhancement training is needed to improve leg power because the net power output related with 100 m net time.


PURPOSE This study assessed elite Taekwondo athletes’ physical fitness and developed reference standards for both their basic and specialized physical fitness. METHODS Data for analysis were collected from 870 athletes: from national teams, 123 elite Taekwondo athletes from the Performance Analysis and Assessment System (PAAS) administrator website (1999–2020); from regional sports centers, 731 collegiate and general division elite Taekwondo athletes (2015–2019); and from Y University, 16 elite Taekwondo athletes. Through measurement items’ selection and categorization, 20 physical fitness items were selected for the reference standards’ development, including 9 for basic fitness and 11 for specialized fitness. Taekwondo weight classes were divided into two: light + middle (fin, fly, bantam, feather) and middle + heavy (light, welter, middle, heavy). RESULTS Descriptive statistics for basic and specialized physical fitness items were categorized by gender and athletes’ fitness level. The reference standards’ development was aligned with existing standards, integrating the Cajori physical fitness 5-levels. It also introduced minimum physical fitness reference standards and target achievement reference standards for evaluating elite Taekwondo athletes’ physical fitness. CONCLUSIONS The reference standards proposed here can serve as objective indicators in selection of national representative athletes and also provide foundational data to establish fitness goals and evaluate future elite athletes’ physical fitness.
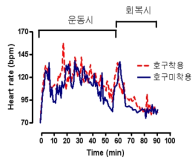
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of wearing of safeguard devices on various blood ions (i.e., Na+, K+, Ca2+) concentrations, gas parameters (PO2, PCO2, hematocrit [Hct], hemoglobin [Hb], Saturated [Sat] O2), and energy substrates (i.e., glucose, free fatty acid [FFA], lactate) concentrations during Kumdo training. Research scope extended to examine the heart rate changes during each exercise sessions. In order to achieve the research goal, 10 male elite Kumdo players, who play for G city in Gyeongsangbuk-do, were participated, and their mean maximum oxygen uptake level was 51.2(±6.1)mL· kg-1min-1. All subjects undertook Kumdo training sessions twice, which carefully pre-planned and consisted of routinely carrying out exercise program. Training period for each session was 80 min long including 10 min each for warm-up and warm-down period, but the conditions with wearing body protection devices were different following either with wearing complete set of safeguard devices or without wearing any safeguard devices except general training cloth. Heart rate was measured by every minute interval. K+ and Ca2+ showed interaction effect between the conditions with wearing safeguard devices and conditions with time of Kumdo training. Hct and Hb level significantly increased after 60 min Kumdo exercise regardless of wearing safeguard devices. Kumdo training induced dropping of blood pH independently with wearing safeguard device conditions, however the values and/or concentrations of PO2, Na+, glucose, lactate, Sat O2were significantly increased. Heart rate was maintained marginally higher values throughout exercise period when safeguard devices were worn. Based on these results, it was concluded that wearing the safeguard devices could possibly be causing a physiological metabolic changes, and this may be drawn by increased body fluid loss and energy expenditure. Further study should be undertaken to examine the effects of wearing safeguard devices on hitting intensity and hormone secretion and concentrations, that closely associated with body fluid and ion balance during Kumdo exercise and/or training.
