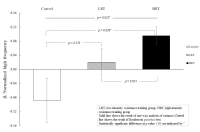
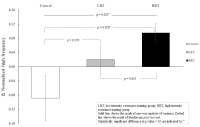
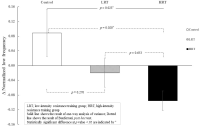
The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of resistance training with different exercise intensities on heart rate variability(HRV) in habitual smokers. Twenty-eight healthy young smokers participated in this study were randomly divided into three groups; CON(control), LRT(low-intensity resistance training; 50% 1RM), and HRT(high-intensity resistance training; 70%1RM), respectively. LRT and HRT groups performed an 8-week resistance training(4 upper- and lower body exercises) using weight training machines, whereas CON group maintained their regular activities. All groups were evaluated basal body composition, hemodynamic parameters, HRV as autonomic nervous function, and muscular strength (1RM and isokinetic test) before and after the 8-week training. To assess the effect of 8-week training with different intensities on autonomic regulation, time and frequency domain indices of HRV were calculated from 5min R-R interval recording. As results, both LRT and HRT groups increased baseline 1RM and isokinetic strength compared to CON group. Meanwhile, high-frequency power reflecting parasympathetic activity was significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. In addition, normalized low frequency power(LF nu) indicating a shift of sympathovagal balance towards sympathetic predominance significantly decreased while normalized high frequency power(HF nu) which reflects vagal predominance significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. Furthermore, improved cardiac autonomic regulation and parasympathetic activation had significant association with increased muscular strength. Overall, the 8-week training has enhanced muscular strength in both training groups, particularly autonomic balance improved in young habitual smokers with high intensity resistance training.


The primary purpose of the study was to identify the characteristics of Korean national youth soccer players’ functional movements. The secondary purpose was to examine whether certain tests of Functional Movement Screen (FMS) meaningfully achieve goodness-of-fit for the soccer-specific movements. Korean national youth soccer players (30 male players, 18.37 ± 0.67 yrs, 178.7±7.09 cm, 70.2±6.46 kg), performed FMS tests [deep squat (DS), hurdle step (HS), in-line lunge (IL), shoulder mobility (SM), active straight leg raise (ASLR), trunk stability push-up (TSP), and rotary stability (RS)]. The mean (±SD) FMS composite score and each test score were calculated. Rasch analysis, which was used to determine the goodness-of-fit for the tests, was applied to examine the item difficulty of the FMS tests. The mean FMS composite score was 10.2± 1.79; the mean DS, HS, IL, SM, ASLR, TSP, and RS score were 1.13±0.35, 1.27±0.45, 1.4±0.56, 1.6±0.77, 2.07±0.69, 1.43±0.82, and 1.3±0.47 respectively. According to the results of Rasch analysis, 4 tests (DS, IL, ASLR, and RS) were shown to be within the acceptable range (infit & outfit > 0.5 ~ < 1.5). The other 3 tests (HS, SM, and TSP) were shown to be out of acceptable range. The additional analysis revealed the DS (logit = 2.08) as the most difficult test and ASLR (logit = -3.16) the least. The results of the study showed that the players’ FMS composite score was lower (< 14) than the cut-off points used by previous studies for different athletes. The further study is warranted to examine the relationships between the scores of the tests appeared to be soccer-specific in the present study and the level of performance variables.


Based on the expanding concept of public value in most of areas as well as in public administration, the purpose of this study is to explore the meaning and functions of public value in sport pedagogy in Korea. For doing this, this paper has classified the concept of public value into classical and modern concepts and re-conceptualized it throughout diverse concepts implemented in several areas (e.g., social welfare, media, & culture-arts). Thus, this paper has explored the meaning of public value in sport pedagogy for analyzing the common element among the public values of sport, education, and scholarship. The public value of sport pedagogy is conceptualized as ‘the discipline that has inquired the public knowledge and also that has been served the instrumental role for making better society’. In addition, this paper has suggested the conceptual framework to extend the areas that can be applied the public value of sport pedagogy inside and outside in Kinesiology with reflection about academic and practical activity of Sport Pedagogy. Lastly, this paper has searched the multiple functions of public value in Sport Pedagogy such as educational, cultural, integrative, and global functions that could connect the academic and professional activity of Sport Pedagogy into making the public value of Sport Pedagogy.


PURPOSE This study explores the impact of visual shape and exercise involvement on consumers' evaluation and happiness with healthy functional foods, specifically protein cookies. METHODS Using a one-factor design with two levels (pretty vs. ugly shape) and one measured variable (exercise involvement), we uncover interesting insights. RESULTS Consumers highly engaged in exercise show a greater purchase intention for ugly-shaped healthy functional foods compared to pretty-shaped ones. Conversely, consumers with low exercise involvement express a higher purchase intention and happiness when it comes to pretty-shaped healthy functional foods compared to their ugly counterparts. CONCLUSIONS These findings contribute to the sports management and sports science literature by shedding light on how visual shape influences the evaluation of healthy functional foods by sport consumers. Furthermore, this research offers valuable practical implications for designing the shape of such foods to cater to the preferences of sports enthusiasts.
PURPOSE The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of 12-week instrumental pilates exercise on isokinetic muscle function and body composition of healthy college women. METHODS Twenty-four college women (aged 21.6±1.3yrs) were recruited to the study. The participants were divided into two groups, as the instrumental pilates group (IPG, n=12) and the control group (CG, n=12). The springboard pilates exercise was conducted 3 times a week for 40~60 minutes during 12 weeks. RESULTS There was significant interaction effects in the right knee and left · right elbow extensor muscles (60°/sec) and left knee flexor and right elbow extensor · flexor muscles (180°/sec)(p<.05, p<.01). There was no significant interaction effects in the muscle mass of the total body, trunk, arms, and legs (NS) and also in the serum growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-I and 25(OH)Vitamin D (NS). Serum creatine kinase was significantly increased (p<.05). There was also no significant interaction effects in weight, body fat, serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, low & high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (NS). CONCLUSIONS These results suggest that although prolonged instrumental pilates exercise of healthy college women might be improving isokinetic muscle function, there is no increasing effect of muscle mass.

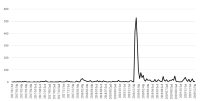
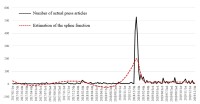
Purpose The purpose of this study is to analyze issues of sexual violence case in sports field reported in the press by using spline function model and text mining. In specific, spline function model is used to measure social interest level based on issue attention cycle theory and figure out the flow of issues by applying text mining. Methods Study material is 2,660 news articles reported from January 1, 2017 to December 31, 2019 and press DB(Big Kinds) of Korea Press Foundation is used to collect study material. Results Social interest level on sexual violence case in sports field is dramatically increased due to disclosure of Sim player starting from Me Too movement started from the culture and art world. Because of this, as structural problem in sports field arises, social interest level comes to a climax, and then it was founded that the government’s countermeasures establishment and special audits by the Ministry of Education were in progress. From the perspective of the issue attention cycle, it has the stages of latent-occurrence-rising-decision-decay-disappearance, but the period from rising to declining is short, so it corresponds to a breaking issue attention cycle. Conclusion This study examines the progress of sexual violence case in sports field from rising to disappearance in the perspective of the issue attention cycle. With this incident, the world of sports is establishing sports ethics center and proceeding policies such as Basic Sports Act, and the future studies need to review the effectiveness of this policy.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the effect of a power-specific weight training program in order to improve the muscle strength of Korean national team’s freestyle wrestlers. Methods Participants were 13 male athletes in the national freestyle wrestling team. The period of the program was 6 weeks. Muscle strength, muscular endurance, muscle power, flexibility, agility, cardiorespiratory endurance, anaerobic power and isokinetic muscle function were measured. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). Paired t-test was conducted for comparison between pre-test and post-test score. Results There were significant difference and tendency in the leg isokinetic power and trunk isokinetic flexion strength. However, there was no significant difference in muscle strength, muscular endurance, muscle power, flexibility, agility and cardiorespiratory endurance. Conclusion The 6-week program focusing on the power-specific weight training indicated a significant difference not in every variable but in isokinetic muscle power, speed power and core strength. It is suggested that the training program was applied to the athletes less continuously and not in the long term because of frequent international games abroad and the need for losing weight. Consequently, a year-long training program with personalized methods should be developed to bring about more significant outcomes.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of training methods on body composition, isokinetic strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function, and anaerobic power in female judo players. Methods Subjects performed weight training (n=10) and circuit weight training (n=10) consisting of 10 sports items for 12 weeks. In order to analyze the effects of training, body composition, isokinetic strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function, and anaerobic power were measured and the effect of training was verified. Results First, the comparison of body composition between WT and CWT groups showed that significant interaction effect between group and period was found in all variables (weight: F=1082.694, p=.001, body fat mass F=199.999, p=.001; skeletal muscle mass F=2481.698, p=.001, and percentage body fat: F=496.246, p=.001). Second, there was a significant interaction effect between group and duration in shoulder muscle strength and knee endurance (EPTL: F=6.598, p=.019; EAPL: F=12.860, p=.002). Conclusions The result of this study showed that the interaction effect between period and group was not significant according to the training method but the overall effect of the circuit weight training group was more positive than the weight training group. Therefore, it can be concluded that the 12 weeks circuit weight training can contribute to improve the performance of female Judo players by improving body composition, strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function and anaerobic power.
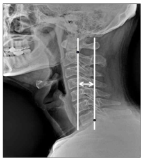
This study was designed to investigate the effects of combined treatment of chiropractic and PNF exercise on musculoskeletal function in forward head posture patients. Thirty patients volunteered to participate in the study as subjects, and they were divided into one of three groups, i.e., chiropractic group (n=10), PNF exercise group (n=10), and combined treatment of chiropractic and PNF exercise group (C+P group; n=10). Subjects in three groups went through each program for 25 min/session, three times/wk for eight weeks. Cervical alignment, cervical muscular strength and endurance, and cervical range of motion were measured and compared among groups and between pre- and post-test utilizing two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables regarding cervical alignment increased significantly in all three groups. The changes in C+P group were more significant than other two groups. 2) All variables regarding cervical muscular strength and endurance increased significantly in all three groups. 3) All variables regarding cervical range of motion increased significantly in all three groups. The changes in ROM regarding flexion and extension in C+P group were more significant than other two groups. It was concluded that all three treatments applied in this study would be effective for functional recovery of the musculoskeletal function in forward head posture patients. Especially, combination of chiropractic and PNF pattern exercise would be the most effective intervention for the patients.


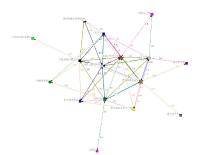
The purpose of this study was to investigate structural characteristics and participants` roles & functions of sport policy network in Korea, by social network analysis on structural characteristics of sport policy network and AHP analysis on participants` roles and functions. For that, 21 executive officers from 19 organizations and agencies related to sports policy were selected as study subjects, and, the materials collected from whole twice surveys on them were analysed by Ucinet 6 and Expert Choice 2000 program. As the results, the governmental organizations like the Blue House and Ministry of CultureㆍSports and Tourism composed the central position group of sport policy network of Korea, and took the main functions of planing and arrangement within their main roles of policy agenda formation and policy decision, so, sport policy network of Korea could be called centralized network by government. And, in cases of private agencies, Korea Sports Council composed the central position group only in policy network of professional sport, Korea Council of Sport for All of sport for all, and Korea Sports Association for the Disabled of disability sport, and, each of them took the main roles and functions of policy execution in their fields, so, it was obvious that the private agencies were divided into their own sport policy areas.