This study was to identify the structure of anger behavior that athletes illustrated in competitions. In order to achieve research purpose, 167 high school, college, and professional athletes responded to open questionnaires. Targeting 541 players, the structural validity of psychological measurement was verified. As a result of analyzing the sources of anger behaviors during matches, four factors of anger-out, anger-in, anger control, and anger-helplessness were deduced. Afterwards, the validity of 4 factor-model was verified through correlation analysis with trait anger and verification of group differences. That is, the level of trait anger had a positive relationship with expression of anger-out and anger-helplessness while it had a negative relationship with anger-in and anger-control. Especially, the behavioral aspect such as anger-helplessness is a structure that has not been found in other criteria of anger behavior and it reflects the uniqueness of sports situation. Based on such results, the significance of sport anger behavior and implications were discussed.
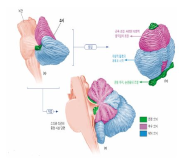
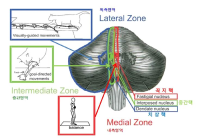
The cerebellum is one of the major parts of the brain involved in the motor control including motor coordination, muscle tone, balance, and the learning of motor skills. The purpose of this review paper was to explore of pathophysiology, anatomical function and neurophysiological mechanism for cerebellum. For this, we sought to examine of previous study related cerebellar disease. Specifically, this paper suggested that motor deficiency of limb movements, coordination, gait/posture balance, adaptation of during movement execution through information proprioception or kinaesthesia, and motor planning and programming of cerebellar patients. We expect that this review will be able to offer the useful information to research. For example, movement scientists will provide an academic information about cerebellar ataxia. Patients and their families will provide relevant information to the daily life (e.g., management and rehabilitation exercise).

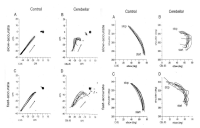



The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of happiness improvement program on psychological variables which were happiness feeling, self-esteem, interpersonal relationship, internal-external locus of control, stress, coping, perceived performance and physiological variables such as cortisol and serotonin of collegiate badminton players. The participants consisted of 10 collegiate badminton players. Happiness improvement program for collegiate badminton players was developed by previous literatures, in-depth-interview, psychological test data, and consultation of happiness improvement experts. The happiness improvement program consisted of 12 intervention program: orientation, rapport development and the understanding happiness, self-esteem enhancement techniques, interpersonal relationship strategies, stress and coping management, peak performance methods, and action plan of happiness improvement program. Each program was applied to participants in about 90-120 minute a session(2-3 times session a week). The instruments of this study were made up of three broad categories: (a) psychological data, b) physiological data, and (c) qualitative data. Firstly, happiness improvement program significantly increased happiness feeling, self-esteem, internal-external locus of control, interpersonal relationship capability, coping skills of collegiate badminton players. Secondly, happiness improvement program significantly decreased stress of collegiate badminton players. Thirdly, participants positively perceived the effects of happiness improvement program on psycho-physiological variables. The limitations of this study and future implications were discussed.
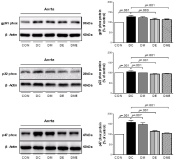
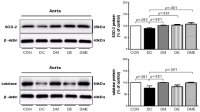
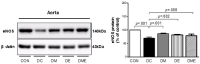
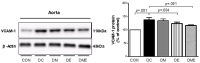
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment on NADPH oxidase, antioxidation and vascular function-related factors in aortic of D-galactose-induced aging rats. Methods To induce the animal model of aging, D-galactose was diluted in saline, and a dose of 100mg /kg was intraperitoneally injected into Sprague-Dawley rats once a day for a total of 10 weeks. Rats were divided into five groups: Control group (CON, n=9), D-galactose control group (DC, n=9), D-galactose+MitoQ group (DM, n=9), D-galactose+Exercise group (DE, n=9), D-galactose+MitoQ + Exercise group(DME, n=9), and treadmill exercise was conducted for 5 days/week during 8 weeks with gradual increase of intensity. MitoQ treatment was intraperitoneally injected at a concentration of 100μM/kg twice a week for 8 weeks during the research period. Results The result showed that treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment decreased the expression of NADPH oxidase level and increased antioxidant enzyme such as SOD-2, catalase. It lead to positive effects such as increasing the level of eNOS, a protein involved in vascular function while decreasing the level of VCAM-1. In addition, as a result, it showed the structurally reduced intima-media thickness. Conclusions It can be concluded that treadmill exercise and MitoQ treatment are effective in ameliorating and treating vascular dysfunction resulting from aging.


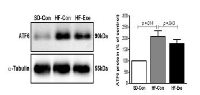
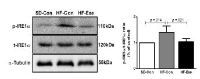
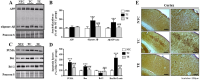
This study was to performed to the effect of 8-week endurance exercise influences on body weight, glucose tolerance and ER-stress in soleus of 16weeks Rats fed High-Fat diet. Rats were randomly assigned to 3 group; (1)Sprague-Dawley Control diet (SD-Con/n=4), (2)High-Fat diet Control (HF-Con/n=4), (3)High-Fat diet Exercise (HF-Exe/n=4). Exercise group ran on the treadmill for 30min/day at the level of 21m/min for 5days/week during 8weeks. Results showed that body weight and glucose tolerance of the HF-Con group was remarkably increased(p<.05) compared to other groups. However, HF-Exe group significantly decreased body weight and glucose tolerance compared to HF-Con group. Moreover, level of GRP78, ATF6, PERK and IER1⍺, which are main proteins of ER-stress were significantly increased in HF-Con group higher than other group, whereas HF-Exe group significantly decreased the expression of GRP78, ATF6, PERK and IER1⍺. Taken together, these finding suggested that the reduction of the body weight, glucose tolerance and unfolded protein response by treadmill exercise may represent a positive adaptation protecting against high-fat diet-induced ER stress.




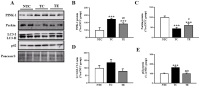
Purpose The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of treadmill exercise on mitochondrial quality control in the APP/sw transgenic mice model of Alzheimer's disease(AD). Methods The experimental mice were divided into non-tg-control (NTC, n=10), tg-control (TC, n=10), and tg-exercise (TE, n=10), and treadmill exercise was conducted for 12 weeks (15m/min, 60min, 5 times/week). And then, we measured the cognitive function using MWM and the brain cortex was evaluated to determine whether any changes in the oligomer Aβ, apoptotic-related factors, mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. Results As a result, treadmill exercise significantly reduced oligomer amyloid and also had a positive effect on proteins (PUMA, Bax, Bcl-2) associated with apoptosis. In addition, through the treadmill exercise, PINK-1 decreased, and increased parkin, showing that active inhibition of mitophagy has been partially relaxed. It has been confirmed that the key autophagy markers LC3 and p62 significantly reduce p62 expression in TE group compared to TC group, and that LC3-II/LC3-I ratio tended to decrease, although not significant, increasing the activity of mitophagy. Next, proteins related to mitochondrial biosynthesis (SIRT-1, PGC-1α, Tfam, and COX-IV) have been identified, and the treadmill exercise has confirmed that the expression of all proteins has increased in part. Finally, cognitive has been shown to improve cognitive by shortening both swimming distance and time through treadmill exercise. Conclusions Thus, our finding suggested treadmill exercise alleviates cognitive dysfunction by improving mitochondrial quality control(mitophagy, mitochondrial biogenesis) and neuronal cell death via reducing amyloid accumulation, which may play a role in a preventive strategy for AD.

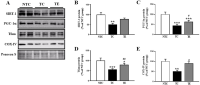
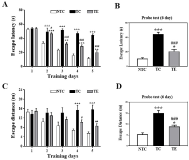
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the mediating effect of psychological needs in the relationship between multiple coaching styles and teamwork among college football players. METHODS This cross-sectional study involved 526 elite football players. Descriptive statistics, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, path analysis, and macroprocess were performed using statistical software to test the mediation effects of the data collected. RESULTS The findings suggested that autonomy-supportive and structure coaching styles positively correlated with and impacted psychological needs satisfaction and teamwork. Conversely, control and chaos coaching styles negatively correlated with and impacted psychological needs satisfaction and teamwork. In addition, autonomysupportive and structure coaching styles negatively correlated with and impacted psychological need frustration, while control and chaos styles positively correlated with and impacted psychological needs frustration. Furthermore, psychological needs satisfaction and frustration were found to partially mediate the relationships between autonomy support and teamwork, structure and teamwork, control styles and teamwork, and chaos styles and teamwork. CONCLUSIONS Autonomysupportive and structure coaching styles positively influenced teamwork by satisfying psychological needs. In contrast, control and chaos coaching styles negatively impacted teamwork by contributing to psychological needs frustration.

The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of the functional movement improvement training program on the score of high-school baseball players’ functional movement screen (FMSTM) test. After 16-weeks treatment period, a significant increase of Deep Squat, Hurdle Step, In-Line Lunge, Shoulder Mobility, Active Straight Leg Raise, Rotary Stability, and total score was found only in treatment group. There was decrease on the number of players in treatment group whose total score is less than 14; the criteria vulnerable being injured. The results of this study suggested that applying functional movement improvement training program on high-school baseball players can be effective to prevent injuries.





















PURPOSE The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of 12-week instrumental pilates exercise on isokinetic muscle function and body composition of healthy college women. METHODS Twenty-four college women (aged 21.6±1.3yrs) were recruited to the study. The participants were divided into two groups, as the instrumental pilates group (IPG, n=12) and the control group (CG, n=12). The springboard pilates exercise was conducted 3 times a week for 40~60 minutes during 12 weeks. RESULTS There was significant interaction effects in the right knee and left · right elbow extensor muscles (60°/sec) and left knee flexor and right elbow extensor · flexor muscles (180°/sec)(p<.05, p<.01). There was no significant interaction effects in the muscle mass of the total body, trunk, arms, and legs (NS) and also in the serum growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-I and 25(OH)Vitamin D (NS). Serum creatine kinase was significantly increased (p<.05). There was also no significant interaction effects in weight, body fat, serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, low & high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (NS). CONCLUSIONS These results suggest that although prolonged instrumental pilates exercise of healthy college women might be improving isokinetic muscle function, there is no increasing effect of muscle mass.
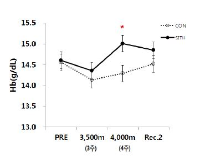
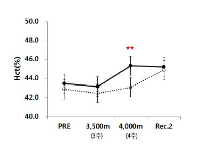
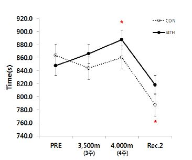
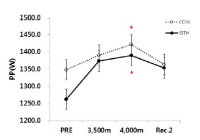
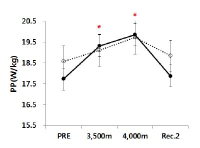
In this study, hypoxic exposure and training with regard to the current progress during the various models 'live and/or sleep high: train high' by way of 4 weeks in elite level tennis players. The experimental group which SITH(SIT with hypoxic) a 2,500m-4,000m to the graded elevation every 500m increased by the week five times a day, two times four weeks treated to a SIT (sprint interval training) and three hours of exposure in hypoxic chamber(simulated normobaric hypoxic). The CON(control) was conducted same period and methods without exposure to hypoxia that a SIT at sea level. As a results, the haematological variables were Hb and Hct compared Pre with the treatment at the end of 4,000 m(at 4 weeks) has been shown to significantly increased in both groups respectively(p<.05, p<.01; vs. Pre). Aerobic exercise capacity related variables that Time was SITH has been shown to significantly increased at 4,000 m(p<.05; vs. Pre). Also, VO2max was SITH has been showed increased in the same period a tendency(p=.072). Anaerobic exercise capacity related variables that PP(W) was both groups increased significantly at 4,000 m(p<.05; vs. Pre), and PP(W/kg) was CON group has been showed increased in the same altitude a tendency, whereas SITH group has been showed increased at 3,500m and 4,000m respectively(p<.05; vs. Pre). Therefore, this study was unlike previous studies with similar positive results as a follow-up study will be contribute to the attainment of a higher value.