Purpose This study seeks to explore the process where drop-out elite athletes collect their life skills obtained during their sports career and transfer them to their daily lives. Methods An open-ended questionnaire survey was conducted on a total of ninety retired elite athletes and the responses were analyzed. Based on the results of inductive analysis, five subjects were selected for a follow-up in-depth interview. The responses to the open-ended questionnaire were analyzed by the inductive content analysis method and the results from in-depth interviews by the deductive content analysis method. Results A total of 478 life skills were collected from the drop-out elite athletes and structuralized into four general categories: psychological skill, social skill, self-management skill, and goal-setting skill. The results of this study have revealed that life skills positively transferred to their future courses of lives and daily lives. Conclusion It is believed that the results of this study will be helpful to understanding the concept of sports life skills, studying the possibility of transfer, and provide the basic data for helping drop-out elite athletes with re-socialization and positive adaptation.

The purpose of this study was to verify the effect on elementary school students in the exercise start stage by performing a sport psychological skill training to improvement of psychological skill and life skill. Participants were eight elementary school boys volleyball player. The program consisted of psychological skills and life skills in educational counseling model of Visek et al(2009). It was conducted 40-50 minutes a session in total for 22 sessions. Data was collected through a psychological test, worksheet and participant observation, in-depth interviews. The collected data was analyzed to verify difference by paird t-test after pre-middle-post test and to extract meaningful data category. Quantity analysis showed that a result of sport psychological skill test proved a significant difference in willingness to overcome, confidence, concentration, anxiety regulation. Life skill test were no significant differences in all factors. However, the rise of scores was observed on result of the pre-middle paired t-test of life skill during season. Quality analysis showed possibility of goal setting, concentration on the routine, decrease of competitive anxiety, increase of positive thinking, self-understanding and understanding of others, promotion of communication among team members. This sport psychology skill training had a significant effect on the psychological skills of elementary players change. But it seems to be necessary life skills in a more through review of the information.



PURPOSE This study aimed to prove the mediator effect of skill level on participation frequency and injury level of leisure sports players with the highest injury rate. METHODS Raw data of the “2019 Sports Safety accident data” conducted by the Korea Sports Safety Foundation were used for this study. We analyzed 857 leisure sports players participating in events with the top four highest injury rates (Basketball, Soccer, Baseball/Softball, Foot Volleyball). Frequency, descriptive statistics, and correlation analyses using SPSS version 27.0 and Process macro model 4 were employed for analysis. RESULTS The results regarding participation frequency, injury severity, and skill level among recreational athletes are as follows. First, a positive correlation was established between the participation frequency of recreational athletes and their skill levels. Second, the correlation between participation frequency and injury severity was observed only in soccer and basketball. Third, skill level plays a mediating role in the relationship between participation frequency and injury level. The results indicate that as the participation frequency among leisure sports players who participate in ball sports with a high injury rate increases, this affects the degree of injury. CONCLUSIONS Skill level appears to play a mediating role in the relationship between participation frequency and injury level. Based on the results, we recommend safety education not only on the relationship between participation frequency and injury level, but also the intermediary role of skill level.

Purpose This study tells about my life about the past time when I studied for the teacher certification examination, using autoethnography. Methods It primarily used personal memories and diaries. The collected data was analyzed by applying longitudinal coding method through technical categories. Results The finding of this study is described in a chronological order as follows. The first part is about my unstable ego formed in my puberty period just like riding a roller coaster. It mainly features the process of choosing a career path when I was in school and the important starting point that made me today. The second part describes about my life after entering the department of physical education. I joined the military only to flee from a fruitless college life where I was wearing an unbefitting mask to hide myself from the world that is completely beyond my control. In the military, I was lucky to realize how to apply my major to set up my career path by coincidence. The third part is about the process of finding a genuine meaning of being a physical education teacher through a transitional period experienced after returning to school and form a stable self. Lastly, passing teacher certification examination with undaunted struggles boosted my self-esteem and self-efficacy and solidified my self-identity in the end. In addition, it is possible to get a glimpse of the attitudes that teachers need to have for a teaching career in the last part. Conclusions What I want to say throughout my descriptive story is that preparing for the teacher certification examination itself is a great challenge as well as a courageous decision for the candidates, but it is an attainable goal if they try with all their heart.


The purpose of this study was to examine psychological capital acquisition through Asian Games Participation. 17 of national women football players were completed Psychological Capitals Questionnair. The psychological capital consists of optimism, psychological skills, self-management, collective efficacy, and performance perception was investigated after the team call-ups and before the team-release. The data was analyzed by paired t-test. As results, Korean women football players’ collective efficient and performance perception showed a statistical significance at the beginning of the team call-ups but optimism, psychological skills, and self-direction did not show statistic significances. The team-harmony, interpersonal-management, team-power, sufficient training, trust in coach, efficient communication, and psychological football factors, which were subfactor of football players’ psychological capital, showed statistical significances. However, confidence, concentration, goal-setting, imagery, willpower, anxiety-control, mental-management, life-management, training-management, innate-behavior management, physical-management, football skills, mediative skills, and football intelligence factors did not have statistic significances. These results demonstrate that effects of mega sporting events-like experiences and psychological factors’ variability and inflexibility according to weather changes should be considered when it comes to discussion of psychological factors regarding players’ performance. It is expected that this study would be a fundamental resource for understanding of psychological influences through participations in mega sporting events and discussions about further psychological interventions for teams with environmental consideration as well as methodological developments which could measure effects of the psychological interventions.

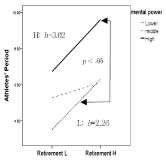
Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the differences between the three simple control models of Hayes (2012) and to determine whether there were Moderating Effects depending on the level of self-esteem, willpower and belief that are psychological factors in the relationship between athlete's retirement and Athlete's period. Methods To achieve this objective, a total of 259 retirees were collected from data on retirement and psychological factors. The data processing method presented the reliability and feasibility of the measuring instrument through technical statistics, frequency analysis, confirmation factor analysis, and reliability analysis. In addition, we conducted a hierarchical regression analysis using the PROCESS command statement in IBM 20 to examine the regulatory effects. Results The results of the study are as follows: The first was the significant model of Hayes (2012)'s three simple control models. It is up to the researcher to choose which model to choose, but when selecting the model, the justification of the variables must be established on the basis of theoretical basis, and the reliability of the variables must be put in to produce reliable and reasonable results. The second was to verify that the relationship between the retirement factor(10) and the Athlete's period has an adjustment effect based on self-esteem, willpower and belief. Among the psychological factors, the Moderating Effects was greatest in the influence of belief on the Athletes' period, and the more reasons for retirement, the longer the Athletes' period than the weaker. The combined mental strength of all three psychological factors combined shows that the combined effect of control also significantly increases the player's ability to survive by combining with the retirement factor. In particular, sportsmanship has resulted in a better mix of retirement factors than the sense of Self-esteem and will, resulting in a longer increase in the capacity. Conclusions Therefore, players who long for a player always keep their dreams of becoming a big star in mind, and ask me to always keep the belief in hope that I will enjoy my career for a long time.






This study examined the association between physical activity (PA) and the prevalence of chronic disease and chronic depression. Additionally, the relationships between PA and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among general population, categorized by healthy, chronic disease and depression were investigated. Cross-sectional data includes 9,739 participants (4,351 males, 5,659 females, over 19 years old) who completed physical activity, chronic disease and HRQoL questionnaires from The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Complex samples frequency, descriptive, cross-tab and logistic analysis were used. Estimated prevalence of chronic disease and depression were significantly different between PA levels and frequency. Based on odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI), participating in lower levels of daily PA including less resistance and flexibility exercise were associated with an increased likelihood of chronic disease. Less frequency of resistance PA was also associated with an increased likelihood of depression. Estimated prevalence of HRQoL was different according to PA in the healthy and chronic disease populations. Adjusted OR and confidence intervals represented through lower levels of daily PA and less frequency of resistance PA were associated with an increased likelihood of poor HRQoL in the chronic disease population. No significant OR between PA and HRQoL in the depression population was observed.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to analyze the level and characteristics of physical activity (sedentary, light, and MVPA) of high school students according to physical education (PE) class (DWPE: days with PE class, DNPE: days with no PE class) and sex. METHODS Data were collected on 147 students (65 male and 82 female) from four high schools in Seoul city, and physical activity was measured using a three-dimensional accelerometer. The collected physical activity data were input into SPSS 25.0, and the descriptive analysis and two-way ANOVA according to PE class and sex were performed. RESULTS The descriptive statistical analysis showed that 31% (40.7% male and 23.4% female) of participants met the recommended physical activity durations (MVPA of 60 min/day). In the two-way ANOVA, sedentary activity, light activity, and MVPA showed statistically significant main and interaction effects according to PE class and sex. According to the results of the interaction effect analysis, the gap in physical activity between DWPE and DNPE was large in male students. For male students, light activity and MVPA significantly increased on the day of the PE class, and sedentary activity significantly decreased. However, for female students, DWPE and DNPE did not differ significantly in all levels of physical activity. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, the level of physical activity of Korean high school students was relatively low, and the effect of daily-life physical activity in the PE class was limited to male students. Accordingly, an alternative should be introduced to increase the physical activity of female high-school students through PE classes.
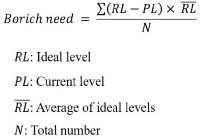
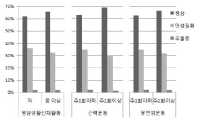
Purpose This study was designed to develop a curriculum for pre-service golf coaches at universities to enhance the coaches’ competencies to counsel athletes on the field. Methods This study was conducted in accordance with the revised and supplemented procedures for the national competency standard (NCS) based curriculum development outline under the level of application of individual instruction-level classes among the types of curriculum development. Results The results were as follows: First, the elements of the counseling competence were guided by conflict resolution counseling, psychological skills training, guidance counseling, coordination and Intervention, and relationship formation. Second, the curriculum was adopted as a curriculum for sports psychology, theory and practice of counseling, counseling practice and super-vision, and psychological skills training, and non-disciplinary activities were participation in group and personal counseling, and an open counseling case study. Third, the feasibility of the curriculum was calculated in the range of 0.8 to 1.0 for all areas to be reasonable. Conclusions The results of this study have structured the counseling competencies required for pre-service golf coaches. Based on this, the results of the study suggest counseling courses in the curriculum of university. This is expected to ultimately seek to improve the coaching field by enhancing the capacity of the coaches.
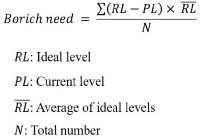


When the long-awaited KSME in PESS was established in 1998, KSME faced a turning point in its growth. Following the changes in both quality and quantity of the society's researches since its establishment and seeking for future themes is important for the society. This research analyzed the society's research trend using mainly the Korean Journal of ME in PESS. Then, by examining the physical fitness test, it proposed possible future themes for the KSME. This research also looked into the American Kinesmetrics’ contribution to Kinesiology, its research trend and future researches The KSME's recent researches show refined quality, diversified themes and reinforcements in practical researches. Regarding the themes, the reliability and validity of tests became predominant, sports analysis and physical activity emerged, and interest in measurement and evaluation in school PE was low. Possible research themes in the future are measurement and evaluation in school PE, game analysis and sport big data. The recent interest of the American Kinesmetrics was the cross validation of criterion-referenced physical fitness cut-off score, the validation of the guideline for physical activity, and the relationship between sedentary behavior and health. Possible future research themes of the American Kinesmetrics were the refinement of test methods, the effectiveness of the physical fitness test award system, and the application of the ubiquitous wearable technology.