Purpose This study focuses on accessibility to sports facilities that can be classified into structural leisure constraints. The purpose of this study is to explore exploratory analysis of the types of reservation methods and payment methods, which are the initial stages of consuming sports facilities, and to explore inconveniences that consumers feel when making reservations. Methods A quantitative research method was used to derive the results, and data were collected through a questionnaire survey method. The collected data were analyzed by technical statistics focusing on the reservation method, payment method, and inconvenience during reservation. Results As a result, it was found that the main types of reservation methods and payment methods were homepage, homepage/telephone, telephone, homepage/app, and account transfer and card payment, respectively. In the case of inconvenience, the procedure was complicated, address and location, and reservation method were identified as the main matters. Conclusions Efforts must be made to secure both the convenience and publicity of accessibility at an early stage, such as reservation methods and payment methods for sports facilities.

Purpose This study attempted to investigate the difference on job satisfaction and service quality between non-regular and regular workers in commercial sports facilities. Methods With the purpose of the study, the purposive sampling as the non-probability sampling method was used to intentionally select the representative cases. We conducted through utilizing in-depth interviews with 6 non-regular and regular workers, respectively, who have worked for more than a year at total commercial sports facilities holding more than 3 programs with more than 500 memberships. This study aimed to explain real phenomena as much as possible by utilizing NVivo 11, one of qualitative research method programs, on the basis of raw data. Results In conclusion, non-regular and regular employment types in commercial sports facilities did not affect service quality provided for customers. However, it was derived that there was a slight difference between regular and non-regular workers on job satisfaction. Conclusion It is necessary to improve the wage and compensation system for regular workers as well as the labor policy to improve treatment of the wage according to the qualification of non-regular workers in commercial sports facilities. In spite of the instability of non-regular workers, the effort of converting into regular workers would evoke organizational commitment, loyalty, and attachment of non-regular workers, when properly acknowledged.






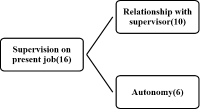
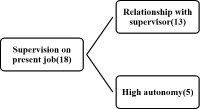





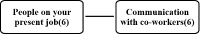








Purpose The purpose of this study is to examine the elite sport system in Germany by selecting six keyword. Methods In order to review the literature, we reviewed the reports of sports organizations such as the Ministry of the Interior, the Olympic Games of Germany, the Sports Council of Germany, and the German sports policy, history, business, programs and financial status. Conclusion In Germany, athletic associations were created in the 40s and 50s and strengthened infrastructure, projects, and workforce infrastructure by the 60s and 90s. Through its long history and tradition, Germany is at the forefront of both the Winter and Sommer Olympics. Among them, the German Olympic Sports Federation, researchers Institute, Olympic training centers, Sports School, Kader-systems and federal police·military·customs are the main keyword of elite sports. In order to support the national players in Germany, the regional Olympic training center supports sports science, sports gymnasium, sports athletic high school, sports elite school, athletes' house are operated for selection and training of excellent athletes. And all the players are in the carder system and there is a system that allows them to enter the federal police, soldiers and customs so that they can support the human resources, facilities and programs as well as train and work at the same time.
Based on public sports facilities’ census data, this study attempts to empirically analyze to the factors affecting the operating balance and use of public sports facilities(PSF). Analysis was carried out through multiple regression analysis using SPSS and location characteristics analysis using GIS. The total floor area and population was confirmed to influence operating balance and use(DV). Management body influence differed for DV (use and operating balance of PSF) by type of PSF. Consequently, this requires diversification of the management body. The size of facilities and location characteristics(population and zoning) are positive effect on the operating balance and Use of PSF. In order to solve the problem of location restriction and security of marketability, it is possible to take into account the integrated management and sports club’s use of large-scale sports facilities.

PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the difficult realities, unresolved problems, and policy proposals of disability sports in Korea through the disability sports movies <Mal-aton> and <Glove>. METHODS We conducted a textual analysis from the perspective of critical theory. RESULTS The problems of Korean disabled sports revealed in the films <Mal-aton> and <Glove> could be cattegorized into three major issues: 'incorrect prejudice and indifference' of non-disabled people that disabled people will not be able to enjoy sports; 'sports facilities' where non-disabled people are prioritized and disabled people are marginalized, and the 'absence of sports facilities' specialized for disabled people; and the 'lack of leaders' who correctly understand the characteristics of the disabled. These have been pointed out as causes that keep them away from the natural right to enjoy sports. CONCLUSIONS The films <Mal-aton> (2005) and <Glove> (2011) were made based on true stories, and despite the fact that more than 10 years have passed since they were made, it remains a sad reality that the problems of Korean disabled sports shown in the films remain unresolved. Improvement measures in various aspects are required to promote sports for the disabled from the perspective of lifelong and adapted sports, such as media education and publicity that can eliminate misunderstanding and prejudice against people with disabilities, building sports facilities tailored to the disabled, and improving the treatment of sports instructors for the disabled.
PURPOSE This study was to examine safety awareness of sports among university students. METHODS Total 1950 university students of 9 regions responded to questionnaires on safety awareness of sports with using simple random sampling. The date were analyzed by frequency analysis and Two-way ANOVA. RESULTS The results of this study werew as follows: Fistly, male students were experienced safety awareness education more than female students. In addition, the education of safety awareness of sports took place in sports field, but most of students did not aware of safety personnel. Secondly, university students thought that sports was not safe because sports facilities and equipments were not managed and they were worn out. Thirdly, they perceived sports safety was managed generally normal. Furthermore, they perceived the aging of facilities and equipments at sports sites was major factor in the occurrence of safety accidents. In order to reduce sports safety accidents, it is necessary to facilitate safety education of sports at government. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study will be used as fundamental information to raise safety awareness in university students and to establish safe sports culture.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to find effective skin scuba activation factors and to provide basic data that extend the scope of research related to skin scuba. Methods Delphi method was used and the experts were categorized by experts to analyze the results. The questionnaires collected through the 2nd and 3rd delphi surveys were SPSS win ver. 22.0 and Microsoft Office Excel 2013 to calculate mean, standard deviation, median, and coefficient of variation. The concrete conclusions are as follows. Conclusions First, in terms of organization sub-factor, fostering sports-for-all participants and college club came out to be very effective and followed by cooperation system with Ministry of Public Safety and Security and Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, strengthening cooperation and exchange with other education organizations, initializing new scuba diving education organization management and inspection institution and establishing scuba diving education organization. Second, in terms of facility/equipment sub-factor, factors that cause most effectiveness came out as expanding scuba-diving installation, developing connection system with medical department, enlarging indoor-diving education facilities, improving scuba diving equipment, consecutively. Third, in terms of leader sub-factor, training instructor through leader personality education and verification came out to be the most effective, followed by objectifying professional education institution leader training system, improving leader treatment. Fourth, in terms of program sub-factor, it is found that safety education program as the most effective factor, coming next with environment education/professional manpower training program, developing various programs, lastly, inventing insurance product. Fifth, in terms of advertisement sub-factor, as in order of guiding publics to change their view towards scuba-diving, expanding scuba-diving related events and establishing advertisement system had its effectiveness. Sixth, in terms of policy sub-factor, establishing cooperation system among administration departments came out to be most effective and then improving related law-system.
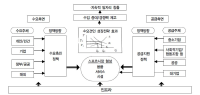
This paper focuses on the analysis of growth policies in the sport industry and the suggestions of the owned demand-pull growth model. The Korean government have enforced the supply-oriented growth policy in the sport industry. However, when the demand for sport is low and inelastic, the supply-oriented growth policy could be less effective. When the supply-oriented growth policy is based on the demand-pull growth policy, the growth policy in the sport industry could be more effective. Concretely, if the government carries out the introduction of sport voucher system, the enlargement of public and private sport facility use, the development of fused policies linked with sport-health-welfare, etc., the sport industry will be advanced more rapidly.

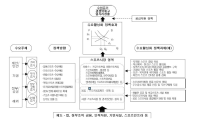
PURPOSE This study explores injury attributions accepted by serious football participants, specifically intermediate and advanced players. METHODS Utilizing Q methodology, 25 Q-samples and 33 P-samples were selected, and Q-classification was conducted. Principal component factor analysis through the PQ method (vers. 2.35) was employed for data analysis, and types were interpreted and named based on the Q-sample with a Z-score of ±1.0 or higher. RESULTS Results categorized injury attributions accepted by the participants into four types: 'Type I: Facility/ Human Resource Responsibility Type,” 'Type II: Luck/Other Responsibility Type,” 'Type III: Self Responsibility Type,” and 'Type IV: Insufficient Safety Education.” This study provided academic and policy discussions by reclassifying four types according to their internal and external location and controllability. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, this study emphasizes the relevance of all four types of injury attribution to policy considerations. Ensuring participants' right to participate in safe and enjoyable sports requires addressing facilities/human resources, education, and insurance as major policy components of sports safety.
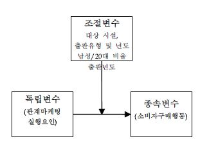
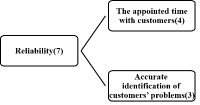
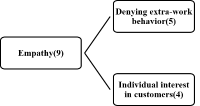
The current study aimed to investigate the impact of relationship marketing on sport consumer behaviors using meta-analytic techniques. Findings from 18 dissertations and 17 journal articles were used to test the relationship marketing and various sport consumer behaviors via the comprehensive meta analysis (CMA) program. Results showed that consumer orientation positively affected purchasing behavior of consumer. On the other hand, sport consumer behavior was not influenced by price. The relationship marketing factors had a most positive effect on, in order of, preference, reliability, and satisfaction. Results didn't find significant moderating evidence for sport facility types, publication types, publication year, the ratio of male and respondents'age.