PURPOSE This study aimed to a) develop suitable screening tools for identifying gambling severity in Korea and b) explore factors that affect the gambling severity index in order to prevent Korean sports betting users from easily falling into gambling addiction, thus providing practical and useful guidelines in this regard. METHODS This study examined Korean sports fans who had experiences of participating in sports betting (Sports Toto), a legal sports betting system in Korea. Toward this end, an online survey was conducted from May 10 to June 25, 2022. A total of 214 questionnaire results, excluding 23 who gave insincere and/or incomplete answers, were analyzed for normal distribution through skewness and kurtosis, and subscale scores were calculated after performing exploratory factor analysis and reliability analysis using Cronbach’s α. RESULTS A psychological gambling severity index and behavioral gambling severity index were developed based on a stepwise regression analysis, which was conducted using the demographic characteristics of domestic sports betting participants and their lifestyle habits (e.g., smoking and drinking, problem gambling severity index, self-control scale, and gambling expectation scale). CONCLUSIONS First, factors affecting the psychological gambling severity index were identified (having a job, job stability, and security) along with lifestyle habits (smoking and drinking). Second, gender, occupational characteristics, full-time employment, confidence in self-control, and desire for self-improvement were indicated as significant factors that influenced the behavioral gambling severity index.

Purpose: This study was to verify the relationship between coaching behavior(autonomy/controlling behavior), self-regulation motivation and performance. Method: 356 athletes (from middle to work and professional team) in individual and team sport completed coaching behavior scale developed by this researchers assessing autonomy and controlling coaching behavior perceived by players, Korea Basic Pyshoclogical Needs Scale (KBPNS) assessing basic psychological needs, Behavioral Regulation in Sport Questionnaire (BRSQ) assessing sports motivation level based on self-determination theory, and sport performance score. To estimate the relationship between coaching behavior, self-regulation motivation and performance, this study employed the structure equation modeling analysis. Results: The relationship between psychological needs, regulation motivation and performance showed that autonomy coaching behavior tend to reinforce competence and autonomy of player. These variables have a positive effect on more inner regulation motivation. Moreover, the intrinsic motivation through stimulation experience was a key factor leading to a positive performance by improving the performance strategy and skill of athletes. Conclusion: These results are meaningful as an empirical evidence that relationship between motivation and performance can be changed according to the type of coaching behavior, and that autonomous coaching behavior play an important role in maximizing the performance of player that provided theoretically form.

The purpose of this study was to develop and validity Competitive State Anxiety Scale for Taekwondo Form athlete(CSATF). The participants were composed of the 48 Taekwondo Form athlete to explore sub-factors of Competitive State Anxiety for Taekwondo Form athlete. The data were collected by an open-ended questionnaire and interview. The participants were composed of 257 national Taekwondo Form athlete to develop Competitive State Anxiety Scale for Taekwondo Form athlete. This 157 athlete data were used for items analysis, reliability analysis and exploratory factor analysis. And 100 athlete data were utilized for confirmatory analysis. Also convergent validity, discriminant validity, predictive validity latent mean analysis of CSATF were performed The results of this study were as follows. Firstly, the results revealed that the four general dimensions were identified such as cognitive anxiety, somatic anxiety, state of confidence, environmental anxiety. Secondly, CSATF comprised cognitive anxiety(5 item), somatic anxiety(5 item), state of confidence(5 item) and environmental anxiety(6 item). Thirdly, convergent validity, discriminant validity and predictive validity, the multi-group analysis according to gender examined validity of CSATF.

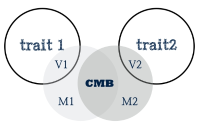
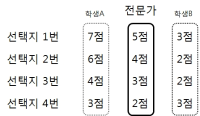
Common Method Biases(CMB) is not the matter of measuring tools but the various errors caused by measurement. One of the procedural remedies to overcome these errors is the separation of measurement. However, according to the analysis of the papers published in sports psychology academic journals during the last ten years, the papers used the separation of measurement were just 24 papers of total 197 papers and most measurement were the questionnaires of Likert scale. So this research introduces the Situational Judgment Test(SJT) which can measure the psychological variables using different method except for the questionnaires of Likert scale and describes the developing process and the existing research results. In addition to this, on the basis of the Situational Judgment Test(SJT) developed in the area of sports, it suggests that the scoring key methods which is applied both the distance score and order score show better the validity compare with methods using only the distance score.

This study was to explore the factors influencing Olympic performance positively and negatively. In order to achieve this purpose, 60 athletes, who participated in 2012 London Olympic games, responded on open-ended questionnaire. In addition, 10 athletes, who won medals in London Olympic, responded on in-depth interview. Collected data were analyzed by deductive content analysis. The results of this study were as follows: firstly, the factors influencing Olympic performance positively were psychological preparation, strengthening training, physical conditioning, support from significant others, material support, cheering of Korean people, self respect as a Korean national athlete, different game environment, team cohesion, sharing Olympic experience, and support of sports science. Secondly, the factors influencing Olympic performance negatively were psychological pressure, excessive expectation, negative interpersonal relationship, condition decline, overtraining, unstable environment, insufficient facilitation, decrease in performance level, and especially ineffective village room placement and media management during Olympic period. Thirdly, the differences between Olympic games and other world competitions , perceived by athletes were competition scale, psychological attitude, training support, systematic preparation, and benefits from winning medals. The results of this study will give fundamental information in developing a scale which can measure Olympic preparation level and in developing Olympic preparation guideline. Therefore, it will help athletes ,who participate Olympic for the first time or athletes who did not perform well in pre-participated Olympic games, to understand and apply in training the factors influencing Olympic performance and help them to perform better in Olympic games.
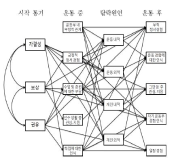
The purpose of this study is to explore the drop-out process of student-athletes and propose valuable policy ideas related to interscholastic sports. For this purpose, we surveyed 560 middle and high school drop-out student athlete's in 13 areas and finally 400 completed surveys were used for the study. To set the scales used for the study and test the reliability and validity of the scales, factor-analyses, Cronbach's alpha, and interfactor correlations were conducted using SPSS. For the main test, the paths analyses were carried out with AMOS program. As a result, we found two paths which had major effects on the drop-out process of student-athletes, self-efficacy path at the point of starting athletic career and negative relation path during athletic experiences. Based on these results, the following policy ideas were proposed. First, student-athletes should be able to join and leave athletic teams voluntarily. Second, the comfortable environments were provided to promote student-athletes' positive emotion toward athletic teams.

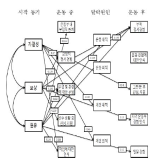



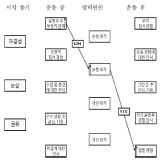
PURPOSE For student-athletes to be able to successfully dedicate themselves to training and competition, the following key factors play an important role: The coach, team climate, and individual motivational characteristics. To test this hypothesis, the structural relationships between having a perceived autonomy support, a caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment were analyzed. METHODS Participants were 297 high school athletes registered with the Korea Olympic Committee (203 males, 94 females, Mage=17.88 years). Data were collected using sports climate questionnaires for autonomy support, caring climate scale, basic psychological needs scale, and sport commitment measurement. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling. RESULTS The model’s fitness was indicated by x2/df=2.797 (x2=106.288, df=38), CFI=.977, TLI=.967, RMSEA=.078 (90% CI=.061, .096). Examining the various path coefficients revealed that coach autonomy support had a positive effect on the athlete’s caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment. The caring climate had a significant effect on basic psychological needs, but did not have a statistically significant effect on sport commitment. Finally, basic psychological needs had a positive effect on sport commitment. CONCLUSIONS Coach autonomy support fosters a caring climate, and athletes who are able to perceive this are able to dedicate themselves to their sport since their basic physiological needs are met. Therefore, coaches should use appropriate coaching strategies to enhance athletes' autonomy and foster a caring climate, as both are essential factors for meeting athletes' psychological needs and promoting sport commitment.
PURPOSE This study aims to provide policy recommendations for the development of women’s football and the enhancement of the Women’s University Football League (WUFL) by examining participant satisfaction and meaningfulness of football. METHODS To achieve this goal, we distributed survey questionnaires, including 5-point Likert scale and open-ended questions, and subsequently analyzed 153 responses using qualitative data analysis software, N-vivo. RESULTS Our findings reveal that female students actively engaged in the WUFL express high overall satisfaction. Furthermore, participants perceive football as a source of happiness, an energy booster, and a platform for new experiences. Their involvement in football goes beyond typical leisure; it is regarded as a form of serious leisure. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS Based on these results, we propose actions such as fostering and elevating amateur women’s competitions, promoting female students’ participation in football, and developing a comprehensive strategy for increasing women’s enjoyment of playing football.
PURPOSE This study developed and tested a theoretical research model delineating the relationships between sports consumers’ team identity and their response to regional identity, sense of community, and community contributions. METHODS To achieve the purpose of this study, a total of 1,196 spectators who attended professional baseball games were surveyed. For the data analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, convergent validity, discriminate validity, and composite reliability were performed to confirm the validity and reliability of the scale through AMOS 24.0. Research model and hypothesis testing were conducted using structural equation modeling, which used data from ten different professional baseball team area contexts. RESULTS The results provide empirical evidence of the positive influence of sports consumers’ regional identity and sense of community on team identity toward community contributions in sporting event area contexts. CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the role of regional identity and sense of community in building professional sports team identities and community contributions.
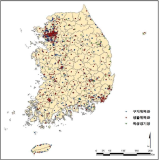
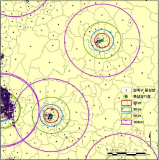
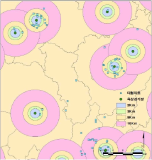
Based on public sports facilities’ census data, this study attempts to empirically analyze to the factors affecting the operating balance and use of public sports facilities(PSF). Analysis was carried out through multiple regression analysis using SPSS and location characteristics analysis using GIS. The total floor area and population was confirmed to influence operating balance and use(DV). Management body influence differed for DV (use and operating balance of PSF) by type of PSF. Consequently, this requires diversification of the management body. The size of facilities and location characteristics(population and zoning) are positive effect on the operating balance and Use of PSF. In order to solve the problem of location restriction and security of marketability, it is possible to take into account the integrated management and sports club’s use of large-scale sports facilities.