
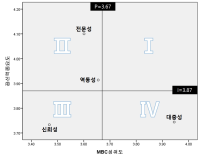
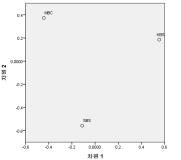
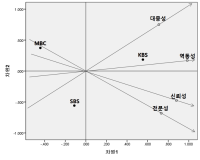
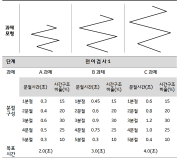
The purpose of this study was to evaluate sports commentators’ public confidence by the difference between media recipients’ expected level on the public confidence and their perceived outcomes, and to investigate how such characteristics are perceived by media recipients. The questionnaires were given out to people in Seoul and Gyeonggi province, who have experience of having watched the 2014 FIFA World Cup Brazil. The samples were collected by snowball sampling method and a total of 218 questionnaires were chosen as final validity sample. For data analysis, frequency analysis, exploratory factor analysis, paired t-test, importance-performance analysis (IPA), PROXSCAL analysis, and a multiple regression analysis were done by using PASW 21.0. The derived results are as follows: First, according to results from IPA analysis, the Quadrant I is a status-quo area, which is inclusive of the professionalism of KBS and SBS commentators. The Quadrant Ⅱ is a concentrated effort-oriented area, which includes dynamics of KBS and SBS commentators, and professionalism and dynamics of MBS commentators. The Quadrant Ⅲ is an inferiority ranking area, which contains popularity of KBS and SBS commentators, and reliability of MBC commentators. The Quadrant Ⅳ is a rejection of overexertion area, which incorporates reliability of KBS and SBS commentators and popularity of MBC commentators. Second, according to results from MDS analysis in terms of the characteristics of public confidence, an order of KBS>SBS>MBC appeared in the fields of professionalism, reliability and dynamics, and an order of KBS>MBC>SBS appeared in popularity.




This study was to verify the structure of efficacy related to performance perceived by short-track athletes when playing a match. Therefore, 50 players answered open questionnaires and 200 players participated in construct validity verification, a total of 250 players of short-track members of national, business and university team were sampled during the research phase. The data was analyzed through the study procedures. The results were as follows: First, efficacy structure of players during the match were categorized into three groups as game managing strategy(including course management, race control, match management and selective attention ability), psychological control ability(including positive imagery, match competition, competitive spirit, ability to handle hardship, anxiety control, and patience), and physical usage of ability(including physique, endurance, and quickness). Second, the result of the first construct validity verification through exploratory factor analysis showed 7 factors in 29 items as game management, course management, psychological control, physical use, coping with hardship, speed control and psychological stability. Finally, as a result of confirmatory factor analysis, short-track self-efficacy showed the 5 factor in 15 items except for coping with hardship and psychological stability.

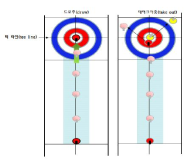
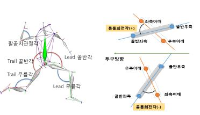
In this paper, we tried to find out the difference of CoM displacement, CoM velocity and Foot-pressure between draw motion and takeout motion in curling’s delivery motion. To do this, we experimented for 10 female athletes of curling national team(all athletes are in her 20th~30th ages) to carry out draw motion and takeout motion from backline to near hogline in state of speed limit. The limited speed was 3.80~3.90 sec for draw and 2.97~3.07 sec for takeout. From the experiments, we obtained the result like followings. 1. Draw motion is more increase than takeout motion in displacement of horizontal direction of CoM displacement. 2. Takeout motion is more increase than draw motion in displacement of vertical direction of CoM displacement. 3. Takeout motion is faster than draw motion in both of horizontal and vertical direction of CoM max. velocity. 4. Takeout motion is higher than draw motion in pressure of fore-foot and mid-foot of foot-pressure 5. Draw motion is higher than takeout motion in pressure of fore-foot and mid-foot of foot-pressure These result means that the characteristics of techniques for draw motion and takeout motion is differ from each other and it is necessary to take different training protocol individually to enhance athletes’s performance. And further research will contains another things like that the pursuit of curling stone’s rut by various delivery techniques






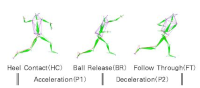
The purpose of this study was to classify high school baseball players as superior or inferior group by Functional Movement Screen(FMS) and to provide basic information for finding great pitcher and improving exercise performance by comparing and analyzing the pitching motion. The results of this study are as follows. The inferior group’s center of mass(COM) moved significant on the left side than superior group at heel contact(HC), ball release(BR), and follow throw(FT)(p<.05). There were no significant difference in linear velocity of shoulder, elbow and wrist between two groups, but inferior groups showed large difference in each joint. The superior group controled rotation of pelvis at HC and showed significant higher knee extension at BR and FT than inferior group(p<.05). The angular velocity of superior group’s throwing arm were higher in acceleration period(p<.05). Taken together based on the results, the players who have higher muscle function showed great pitching motion, so we can conclude that FMS could be useful for evaluating the potential of pitcher.


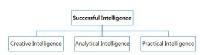
This study was to analyze the hierarchical importance of successful intelligence in Football coaches and players. In order to explore the hierarchical importance of successful intelligence 24 football coaches(under AFC A course) and 20 Korea Football Association U15 Players were responded to analytic hierarchy process questionnaires. In the Analytic Hierarchy Process, football coaches and players completed the AHP Questionnaire with creative intelligence, analytical intelligence and practical intelligence. The hierarchical importance order of successful intelligence for coach and player were analytical intelligence, practical intelligence, and creative intelligence respectively. Evaluation of hierarchical importance of successful intelligence for coach is analytical intelligence(.542), practical intelligence(.278), creative intelligence(.181) in order. Evaluation of hierarchical importance of successful intelligence for coach was analytical intelligence(.684), practical intelligence(.161), creative intelligence(.155) in order. The hierarchical importance of successful intelligence for coach and player were similar each other. Analytical intelligence, was evaluated most important factor for coach and player in successful intelligence. Successful intelligence is important issue for sport performance. More consider needs to Successful intelligence for sport psychology researchers.




PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze the dynamic posture stabilization and kinematic variables between visual feedback and Y-balance training groups during jump-landing. METHODS Thirty-eight male players (age: 22.6 ± 1.12 years, height: 175 ± 3.54 cm, weight: 65.5 ± 5.11 kg) were included in this study, and chronic ankle instability was checked using Cumberland Ankle Instability Tool (CAIT) and Balance Error Scoring System (BESS). They were randomly assigned to the Visual biofeedback (Training group: TG, n = 19) and Y-balance groups (Control group: CG, n = 19) for four weeks. TG performed balance training using the Biodex balance system (BBS) and CG performed training using the Y-balance system. During jump landing, time to stabilization (TTS), force plate (COP, GRF); joint angle and moment were collected and analyzed. All analyses were performed with SPSS 21.0, and Bonferroni was used for repeated measured ANOVA and post-hoc. RESULTS The results indicated that there was an interaction between TG and CG in terms of AP and ML directions of TTS (p < 0.05). AP/ML TTS of the TG for the post-test was smaller than that for CG (AP: p = 0.000; ML: p = 0.046). ML TTS of the TG for post-test was smaller than at pre-test (p = 0.041), and AP TTS of the CG for ankle joint moment (p < 0.05). There was an interaction between TG and CG in terms of dorsiflexion (DF) and plantarflexion (PF) of joint moment (p < 0.05). Ankle moment of the CG for post-test decreased than at pre-test (DF: p = 0.040, PF: p = 0.032), and ankle dorsiflexion moment of the CG for post-test was decreased than at pre-test (p = 0.046). CONCLUSIONS Balance ability was achieved more effectively through visual biofeedback training than Y-balance training. Therefore, we recommend balanced training with visual feedback on chronic ankle instability.
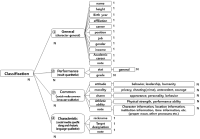
Purpose Soccer-related social media BigData includes complex information related to soccer players and is continuously and instantly generated. Text mining research is actively carried out for this kind of social media contents analysis, but it tends to be analyzed with limited linguistic characteristics such as understanding of language complexity and context, ambiguous terms, rhetoric, and new terms. This can be attributed to the fact that the tools commonly used for text mining use universal terminology dictionaries and packages that exclude the peculiarities of the analysis themes. The purpose of this study is to develop an Ontology model, which are representative tools for defining semantic ambiguity and relationships and systems between terms of text data. Methods In order to achieve the research objectives, we applied the 7-step development method of ‘Ontology Development 101: A Guide to Creating Your First Ontology’, which is useful for ontology development. Each step includes 1) Determine the domain and scope of the ontology 2) Consider reusing existing ontology 3) Enumerate important terms in the ontology 4) Define the classes and the class hierarchy 5) Define the properties of classes-slots 6) Define the facts of the slots 7) Create instances. In particular, the 3rd-step of this study, the glossary stage, is to extract core terms that make up he ontology, but since the goal of this study is to develop the ontology that can be used in social media contents analysis of soccer players, we conducted a social media text analysis related to actual soccer players and selected 484 core terms. Results The ontology which was developed in this research for social media contents analysis of soccer players consisted largely of four parts(General terms, performance results terms, common terms, and Characteristic term) and classified according to the content characteristics of the term. Conclusion Developed ontology in this study is object-oriented that defining classes and objects to define divisions and relationships between terms and also means a social media contents knowledge system of soccer players. In addition, it performs a function as a secondary tool which can be utilized for atypical data analysis.

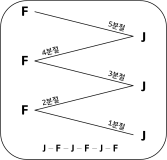
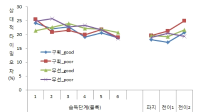
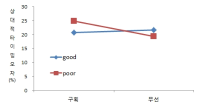
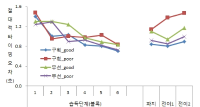
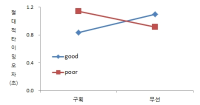
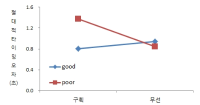
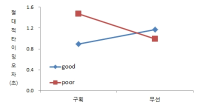
The present study was conducted to determine the effect of contextual interference (CI) and motivational properties (MP) of Knowledge of Result (KR) in learning on relative and absolute timing. Participants (N=48) were randomly assigned to one of four practice groups, which differed in practice structure on CI (blocked, random) and KR on MP (good trial, poor trial). They performed temporal timing tasks in pre-exercise and acquisition phase and went through a retention test and 2 transfer tests after approximately 24 hours. The main findings showed that first, for the relative timing error there was no significant main effect of CI and MP in the acquisition phase, retention, transfer1, and 2 test. However, there was a significant interaction effect between CI and MP in the transfer 2 test. Second, for the absolute timing error there was no significant main effect of CI and MP in the acquisition phase, retention, and transfer test 2 while there was in the transfer test 1. Moreover, there was a significant main effect between CI and MP in the retention, transfer 1, and 2 test. The findings indicated that 1) there was a significant learning effect of absolute timing between KR_good group and KR_poor group on blocked practice in the retention test, 2) random practice schedule and KR_good condition resulted in enhanced absolute timing performance relative to blocked practice and KR_poor respectively at transfer test 1, 3) there was a significant learning effect of absolute timing between KR_good group and KR_poor group on blocked practice at transfer test, 4) KR_good condition could be an useful relative timing learning strategy relative to KR_poor on blocked practice schedule at transfer test 2, effector transfer test. KR-good condition resulted in learning superior to KR_poor group on blocked practice schedule as well. However, there was no significant difference between two conditions on random practice, and 5) there was no difference in the learning effect of absolute timing error between KR_good and KR-poor group in the blocked practice, while there was not in the random practice. It indicated that motivational properties would influence the learning effect of timing in the blocked practice.

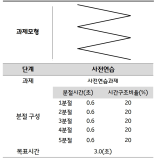
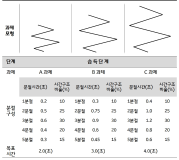

The primary purpose of the study was to identify the characteristics of Korean national youth soccer players’ functional movements. The secondary purpose was to examine whether certain tests of Functional Movement Screen (FMS) meaningfully achieve goodness-of-fit for the soccer-specific movements. Korean national youth soccer players (30 male players, 18.37 ± 0.67 yrs, 178.7±7.09 cm, 70.2±6.46 kg), performed FMS tests [deep squat (DS), hurdle step (HS), in-line lunge (IL), shoulder mobility (SM), active straight leg raise (ASLR), trunk stability push-up (TSP), and rotary stability (RS)]. The mean (±SD) FMS composite score and each test score were calculated. Rasch analysis, which was used to determine the goodness-of-fit for the tests, was applied to examine the item difficulty of the FMS tests. The mean FMS composite score was 10.2± 1.79; the mean DS, HS, IL, SM, ASLR, TSP, and RS score were 1.13±0.35, 1.27±0.45, 1.4±0.56, 1.6±0.77, 2.07±0.69, 1.43±0.82, and 1.3±0.47 respectively. According to the results of Rasch analysis, 4 tests (DS, IL, ASLR, and RS) were shown to be within the acceptable range (infit & outfit > 0.5 ~ < 1.5). The other 3 tests (HS, SM, and TSP) were shown to be out of acceptable range. The additional analysis revealed the DS (logit = 2.08) as the most difficult test and ASLR (logit = -3.16) the least. The results of the study showed that the players’ FMS composite score was lower (< 14) than the cut-off points used by previous studies for different athletes. The further study is warranted to examine the relationships between the scores of the tests appeared to be soccer-specific in the present study and the level of performance variables.

Purpose The valuable impacts of exercise-intervention in diverse type of cancer patients were rationally well-prescribed, though many experimental and review researches already performed in this fields. Generally, cancer-related fatigue and pain remains one of the most prevalent problems for cancer populations. Therefore, exercise has become increasingly significant in cancer prevention and progression. The purpose of this recent study was to analyze the combined exercise program on cancer-related fatigue, pain, quality of life and cancer prognosis in diverse type of cancer patients. This study analyses the safety and feasibility of exercise intervention in diverse stages of cancer patients such as early stage, advanced stage and even metastatic periods in cancer populations. we also wanted to know the impacts of dose-response trial of aerobic and resistance exercise on quality of life in cancer survivors. Methods we conducted a comprehensive PubMed/MEDILINE electronic database from Jan 2015 to August 2020. The reference lists of eligible experimental research articles and relevant systemic review articles were checked. Inclusion criteria were adult cancer survivors from randomized controlled trials performing well-tailored exercise intervention programs to diverse type of cancer patients, Using predefined search items ‘exercise-intervention, cancer & immunology’. Based on reference search, more than 100 articles were identified whereas 30 research papers met the inclusion criteria and were well connected with exercise-intervention and cancer progression. we analyzed the connections between physical exercise and cancer intervention in the main text. Results Moderate to vigorous exercise (aerobic and resistance exercise) revealed to decreased level of cancer-related fatigue, pain, and cancer-related symptoms, however increased level of sleep quality, activities of daily living, exercise performance and health- related quality of life. Exercise intervention reduced pro-inflammatory markers and oxidative stress as well as insomnia, fatigue, pain symptoms whereas it enhanced the antioxidant systems and immune functions. In addition, home-based aerobic physical exercise might enhance muscular strength and quality of life in many types of cancer survivors. Psychological intervention also effective for reducing cancer-related fatigue and pain during and after cancer treatment. they might be the much better intervention than available pharmaceutical options. we believe that it is the related mechanisms of immune cell mobilization and activation such as NK cells which is induced by the activation of sympathetic system during and after physical exercise. Conclusion According to the aforementioned results, it was concluded that implementation of exercise intervention appear to be the best non-pharmaceutical interventions for cancer populations, and also revealed to be safe and feasible in early and advanced stages, although not in the metastatic periods. Sometimes, psychological intervention such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) might be useful in reducing anxiety, depression, fatigue, pain and enhancing quality of life, quality of sleep for cancer populations. we can conclude, exercise-intervention might not just be prevention effect but might be therapeutics, however more studies are urgently needed to confirm the exercise intervention on the NK-receptors activation and immune connection of cancer populations.