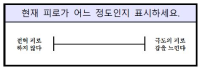
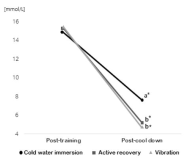
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of recovery methods comparing with change ratio in Lactic acid(LA), Heart rate(HR), VAS(Visual analogue scale) on recovery patterns after field training(FT) in Korea National bobsleigh and skeleton players. [Methods] The tests were conducted for 3 times at a one-week interval as an experimental design within the same subjects(n=9), observed change ratio in LA, HR, VAS through applying Active recovery(AR), Whole body vibration(WBV) & Cold water immersion(CWI) after FT. [Results] The results were summarized as follows: The alteration of ratio in LA, HR, VAS decreased significantly after applying the three recovery patterns(p<.01). The difference between the groups showed that the reduction in lactic acid according to active recovery and whole-body vibration was higher than cold water immersion(p<.01). [Conclusion] In conclusion, although active recovery was more effective than static recovery, there was a significant effect of the three recovery methods in this study on reducing a fatigue in bobsleigh & skeleton players. Therefore, it would be considered to improve the performance of athletes when these methods apply for them depending on situations and environments.

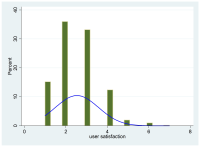
Purpose The study aims to analyze the factors affecting the Residents user satisfaction in order to improve the management of the Open School Sports Center the support facility of the National Sports Promotion Fund. Methods This data is based on Korea Institute of Sports Science(KISS)'s Open School Sports Center Usage Status and Satisfaction Survey (2016) and Open School Sports Center use performance. The analysis model is a regression model (TOBIT) that takes into account the limited characteristics of dependent variables. Results The results are as follows: the satisfaction is negatively related age, number of regulations, weekday opening hours, and usage fees. Conclusion Therefore, in order to increase the satisfaction of Open School Sports Center residents users, various supports are needed. This includes funds for PR, discounts and user-friendliness. It also requires differentiated management of each Center. In the case of regions and facilities, consumer-oriented policies need to be applied instead of collective standards.


Purpose This study was to investigate the systematic application of the life skills program and its effects in a sport setting. Methods Participants were 14 college students(8 males and 6 females) majoring in Taekwondo. Survey tools were utilized to measure items of life skills and journals. Data analyses were conducted by using Excel program and inductive content analysis. Results First, life skills in this study consisted of goal setting, self-talk, imagery, cognitive restructuring. Life skills program has undergone a procedure, such as the introduction, training, development, application, and evaluation. Second, the average scores of life skill variables have been changed according to measured points. Specifically, the average scores of goal setting and self-talk were highly increased over time and the average score of imagery indicated gradual rising line. The average score of negative thought was slightly reduced over time. Third, regarding effects of this program, participants’ responses were categorized into six components; performance enhancement, positive thoughts, chances of change, goal setting, struggling efforts, and motivation formation. Further, participants stated this program was a great opportunity to develop these components. Conclusion The application of life skills program in sport settings will contribute to participants’ life span developmental change in cognitions, emotions, and behavior.




Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of coupled high frequency rTMS and prism illusion in elderly stroke patients, based on the result of previous studies which discovered the effect of bilateral training, mirror rehabilitation treatment, and rTMS. Methods This is a case study of 4 stroke patients who were homogeneous on the basis of selection criteria such as brain injury area, duration of onset, degree of upper limb movement function. A total of 24 rehabilitation sessions were conducted three times a week during the training period, and TMS(transcranial magnetic stimulator), EMG, motion analysis system, and prism optical glasses were used for apparatus. Results The results of the study were as follows: Combined rehabilitation exercises were found to be beneficial to restore upper limb function in stroke patients. Particularly, the maximum speed of stretching and JTT(Jebsen-taylor Test) performance showed improvement after training. The amount of total map volume and MEP(megnetic evoked potential) increased in evaluation of neurophysiology. Conclusion The upper limb dysfunction of stroke patients could be restored by combine rehabilitation exercises.







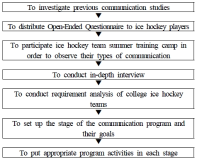
This study was designed to develop a communication training program for college ice hockey teams and examine the effects of this program. College ice hockey players and coaches participated in this study. The various types of data were collected and analyzed to assess the needs of the program and to develop the program with expert meetings. To analyze the effects of the developed program, questionnaires, experience reports, and in-depth interviews were conducted as measures. The results of this study are as follows. First, ice hockey team communication consisted of eight factors (i.e., sympathy, respect, trust, two-way verbal communication, firm expression of opinion, training program communication, developing rapport, and cohesion). Thus, the program developed based on eight factors and consisted of three stages of total 12 sessions which was 90 min to 100 min long. Second, this program increased communication satisfaction, coach-athlete interaction, group cohesion and exercise effectiveness, and these quantitative results were statistically significant. Moreover, qualitative analysis revealed that this program enhanced sympathy, social cohesion, and task cohesion among participants as well as positively changed their communication skills better than before. The communication training program which was developed through this study could provide basic information of a communication training program in the sports domain and positively influence overall sports team effectiveness and performance.


The purpose of this study is to establish the efficient defensive strategy from analyzing the goalkeeper’s gaze behavior and defensive motion in both field hokey penalty corner and penalty stroke. To achieve this goal, 3 national team goalkeepers’ gaze behavior and defensive motions were analyzed, as well as the player’s visual strategies from their interview contents. For the apparatus, multi-channel integrational system were used for analyzing goalkeeper’s reaction movement and personal visual strategies. The result is as follow: First of all, In the penalty stroke, goalkeepers were tended to focus on the bottom of the shooter’s hokey stick. Second, national hokey players had quicker anticipating saccadic movement. For this reason, their visual fixation locations were arrived in targets earlier than the hockey ball. Lastly, in the interview contents, they were reported to focus just on the ball from not disturbed by other various objects(body, hockey stick). However, they actually observed various body parts of shooters. These results imply that we need to develop an effective perceptual skill training in order to anticipate the shooting performance more accurately and rapidly. These types of perceptual and cognitive skill training should be conducted with information on knowing their specific visual cues in anticipating shooting direction.



This study aimed to explore the types of traumatic event experienced by Volleyball players and then prepare to take-off the serial process of posttraumatic growth to schematize a causal network by organizing the factors for overcoming adversity. Participants experiences were collected by distributing open-ended questionnaires to 77 professional Women's volleyball players in 2013-2014 and collected data was categorized by inductive content analysis. These results were schematized by the causal network. As a result of the study, according to the trauma were categorized into four general areas: member conflict, competence loss, physical injury, and coach conflict and the emotions relative to the trauma were categorized into four general areas: powerlessness, pressure, dejection, and hostility also coping factors were categorized into three general areas: social support, intervention strategies, and psychological control. Finally, positive growth emerged as psychological leap, performance improvement, psychological maturity, and emotional stability. And as a result of the categorized study, bring about a better understanding to the posttraumatic growth by causal network. Based on the study results, that volleyball players experienced a positive development on themself after overcoming the problem that they had suffered psychological scars from a traumatic event. In doing so, they contributed to the formation of resources that helped them in their positive lives. In this regard, this study expects to provide the players who have been scratched in mind because of the traumatic experience.





This study aims to suggest the guide line for weight category sports(Taekwondo, Judo, Wrestling, Weightlifting, and Boxing) who have to lose weight to pass weigh-in before games. Reference data was collected from RISS, Medline, PubMed, SciELO and effects of short term weight loss on physiological variables(body composition, physical fitness, blood components, oxidative stress and hormone, immune function) were analyzed. Also, weight loss procedures for weight category sports athletes were analyzed in details. The results of the research are as follows: weight category sports athletes prefer short term (3~5 days) weight loss methods (3~5%) with dietary control, sweating and exercise. Physical changes caused by the loss in body weight, fat-free mass, and BMI, however, do not affect body fat percentage. Different changes of physical strength element depend on weight reduction period. In short term weight loss method, anaerobic exercise capacity, muscular strength, and reaction time partially decrease and affect staying power. In contrast, long term weight loss method do not affect aerobic and anaerobic exercise capacity. Furthermore, most of previous studies show that blood component change has negative effect on body water balance, stress-related hormone, and immune function. In conclusion, short term weight loss method negatively affects athletic performance of weight class competition athletic. Therefore, careful long term weight loss methods are recommended with dietetic consideration to prevent dehydration during weight loss period. Excessive weight loss on lightweight athlete should be prevented by institutional basis as well.

The purpose of this study was (1) to develop a archery lesson using forced connection method-sportcasting for cultivating collaborative problem-solving competencies, and (2) to apply and to examine the responses of students after physical education(PE) lesson. A archery lesson of Understanding-Performance-Appreciation step was developed according to LfPE(Lee, 2014) using backward curriculum design. Participants were tenth grade students (N=148) in a high school. Open-ended question used to collect the data. The analysis of data indicates that students expressed features in lessons. Six features are (a) 朋友信之, (b) 君子不器, (c) 能竭其力, (d) 觀其所由, (e) 溫故知新, (f) 思而不學. In-depth interviewers were carried out for further analysis of the answers to the questionnaires. The results are as follows. First, 朋友信之 means lesson cultivating collaborative problem solving competencies. Second, 君子不器 means pleasant and funny lesson. Third, 能竭其力 means lesson cultivating self management ability. Fourth, 觀其所由 means lesson cultivating appreciativeness for archery. Fifth, 溫故知新 means lesson improving the status of PE teacher and school. This study concluded that a archery lesson generated fun and interest for students. Implication for developing lesson using LfPE, utilize and transform forced connection method-sportcasting in PE were discussed.


This study aims to provide an in-depth study on K-League players' perception and preparation process on retirement. In order to achieve the purpose, data collection was conducted in two major ways; face-to-face interviews and questionnaires from 10 currently working players. The result of study is based on inductive analysis. First of all, sense of expectation and concern, limited scope of secondary job, and necessity for career education are appeared in terms of players' perception. Second, preparation process on retirement is concluded in two categories; personal development activities(non-professional and inefficiency) and financial preparation. Thirdly, difficulties in the procedures of retirement preparation are categorized into ‘limited time and isolated lifestyle caused by staying in club house ’ and ‘lack of educational programs regarding retirement’. Depending on the results of this study, opportunities confined to retired players are supposed to be enlarged to currently working players. In addition, football club and K-League federation need to support players not only to enhance performance but also to prepare retirement.