Purpose The purpose of this study is to analyze the changes in the game factors since the introduction of the VAR system and discuss the meaning of the changes in the K-League. Methods The game factors related to referee decisions (goal, penalty kick, offside, foul, yellow card, red card, additional time) were divided into home and away team and analyzed by two-way ANOVA for 556 games before and 583 games after the VAR system was implemented. All game factors that occurred during the match and additional time were analyzed as independent t-test before and after the implementation of the VAR system. Results First, there was no statistically significant difference between a goal and a penalty kick. Second, the offside was significantly reduced throughout the home team, away team and the entire game(p<.001). Third, fouls were significantly reduced in home teams, away teams and the entire game (p<.01). Fourth, yellow cards were significantly reduced in both home and away teams and the entire game(p<.001). The red card increased significantly throughout the home team, away team, and the entire game(p<.001). Sixth, the additional time showed no difference the first half and the entire game, and was a little reduced in the second half (p<.05). Conclusions As a result of this study, players should not anticipate offside decision and stop playing in critical situations that may lead to a score or penalty kick, and continue playing until the referee makes a final decision. In addition, all red card situations are review through the VAR system, so excessive foul play or unnecessary behavior should be avoided. K-League referees are required to make a more accurate decision in the red card situation, and the time wasted by the VAR system during the game is not much.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the risk factors for anterior cruciate ligament injury using the Landing Error Scoring System (LESS) and muscle activity during the drop vertical jump for overweight females. METHODS The body mass index was 18.5-22.9 kg/㎡ for normal weight females and 23-24.9 kg/㎡ for overweight females among 10 participants aged 20-30 years classified into groups of participants without any injury history and those who were right-footed. An automatic heigh-tweight machine, body composition analyzer, diagnostic imaging, electromyography with the LESS, and muscle activity analysis were used for measurements. The difference in muscle activity between the normal weight and overweight females was evaluated by independent t-test. RESULTS Overweight females had a smaller angle of knee bending during the drop vertical landing, leading to a smaller knee curve angle. In addition, they landed with an unbalanced foot touch on the ground inclined backward, thereby breaking the whole body balance. Overweight females had an incorrect posture compared with normal weight females, with higher LESS points. The muscle activity of the rectus femoris was higher than that of the biceps femoris, indicating a higher load on the muscle. CONCLUSIONS Overweight females take more load on the knee joint and cannot absorb the impact force properly. These results suggest a higher risk of anterior cruciate ligament injury in overweight females.
PURPOSE This study both validated the Characteristics of Resilience in Sports Teams Inventory (CREST) scale for use in Korean sports and analyzed the impact of team resilience on teamwork and performance. METHODS The study surveyed 462 elite football players by using the CREST scale to measure team resilience in Korean sports. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, exploratory factor analysis (EFA), reliability analysis, correlation analysis, multiple regression analysis, and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). RESULTS First, results confirmed that the CREST scale’s two main factors—resilient characteristics and vulnerabilities under pressure—can be meaningfully applied in the Korean context. Second, resilient characteristics showed positive correlation with life skills, whereas vulnerabilities under pressure showed negative correlation. Third, resilient characteristics positively predicted life skills, whereas vulnerabilities under pressure negatively affected life skills. CONCLUSIONS The CREST scale was found reliable and valid in the Korean sports context, demonstrating that team resilience significantly impacts life skills. Thus, the study contributes to evaluation of resilience in Korean sports teams and provides strategicinsights to improve team performance.

The purpose of this study was to investigate basal physical fitness and smash speed of elite national badminton players. To perform this study, total forty six korea national badminton player were participated : twenty two male players(age : 20.90±2.24years, height : 179.30±5.40cm, weight : 73.80±7.12kg, career : 11.27±1.88years) and twenty four female players(age : 19.45±1.95years, height : 167.83±4.36cm, weight : 61.39±3.60kg, career : 9.50±2.47years). Each subjects performed the 6 basal physical fitness trials : agility, muscular endurance, muscular strength, flexibility, balance and cardiorespiratory endurance. And the speed of badminton smash were analysis by using radar gun when players were standing smash success. To determine the difference between two groups, independent samples test was used. As a result, we found that there was a large difference male players and female players in basal physical fitness and smash speed. First, male players were significantly strong in agility(side step 10%), muscular endurance(repetitional jump 12%), muscular strength(left grasping power 3%, right grasping power 31%) and cardiorespiratory endurance(20m suttle run 31%). On the other hand, female players were relatively strong in flexibility(sit and reach 27%) and balance(standing on one leg with eyes closed 51%). Second, maximum smash speed show that male players were about 57km/h(24%) faster than female players(male : 247.72km/h, female : 190.37km/h). Based on the findings, we shall be applicable training program to improve flexibility, balance of male athletes and agility, muscular endurance, muscular strength, and cardiorespiratory endurance of female athletes. our results will be appliable to improve the athletic performances of national badminton players by the coaches in the future.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop the sport 5C scale of the Korean version. Methods The participants were 772 high school students from 17 to 19 who participated in sport regularly. The validation of Sport K-5C followed a three-step validation procedure through substantive stage, structural stage, and external stage. Results First, In the substantive stage, Sport K-5C consisted of 50 items with 5 factors. Second, in the structural stage, although Sport K-5C was explored as 24 items with 4 factors by EFA, but as a result of CFA, Sport K-5C was confirmed as 24 items with 5 factors. Third, the external stage provided additional validity through correlations of tests with other questionnaires which are similar concept and opposite concept, and group differentiation. Conclusions Sport K-5C is composed of 5 factors and 24 items. The factors are Caring, Character, Confidence, Competence, Connection. This scale can be used to provide an objective evaluation of positive development of youth in sport and physical education context.

PURPOSE This study aimed to identify and establish ESG activity assessment factors tailored for sports brands, offering a foundational framework for fostering sustainability within the sports industry. METHODS A Delphi survey was conducted between December 1, 2022, and January 31, 2023, involving university professors, sports brand executives, ESG researchers, sports marketing majors , a nd sports brand influencers. Data were analyzed using SPSS WIN 24.0 and MS Excel, encompassing research subject classification, consistency verification, and empirical analysis. RESULTS The assessment of ESG activity evaluation factors of sports brands revealed that governance, social, and environmental dimensions ranked in descending order of relative importance. Among specific evaluation criteria, the adoption of employee ethics regulations was deemed paramount in the governance evaluation area, while support for stakeholder welfare and social well-being took precedence in the social evaluation category. In the environmental sector, the production and delivery of eco-friendly, durable products held the highest significance. Further analysis, considering the weighted priorities of all evaluation factors, emphasized the importance of factors, such as the adoption of employee ethics regulations, support for stakeholder welfare, social well-being, and the production and delivery of eco-friendly, durable products. Conversely, disclosure of company information and issues, support for the underprivileged, and general shareholders' meeting or agenda for the protection of shareholders' rights and interests ranked lower. CONCLUSIONS In summary, this study validates the role of governance (G) aspects within ESG activities for sports brands, alongside environmental and social dimensions. It highlights the importance of a balanced ESG framework, particularly in an era marked by heightened social responsibility awareness among consumers. Prioritizing governance in marketing strategies not only distinguishes sports brands but also necessitates impactful promotion and advertising efforts.
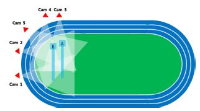
The purpose of the study was to investigate the relationship between the different kinematical variables with respect to the records and techniques performed by the participants during the 2011 Daegu IAAF World Championships Men's Pole Vault Event. Subjects chosen for the study were 8 male athletes who were selected for men's pole vault finals (highly skilled group) and 7 athletes who scored lowest record (skilled group) from the men's pole vault qualifying round. Personal best record of the each subjects were chosen to perform two dimensional (2D) and three dimensional (3D) video analyses. The data were obtained at 60 Hz with the use of five video cameras and digitizing was performed. Kinematical variables were calculated after smoothing the data using 2nd order Low-Pass Butterworth filter at cut-off frequency of 10 Hz and Independent samples t-test was performed to test any differences between two subject groups. The results: during the run-up stage, the horizontal velocity rate of the number of steps and run-up phase was obtained higher in highly skilled group than skilled group. During the take-off phase, deceleration in the horizontal velocity rate was observed in highly skilled group than skilled group. Distinct technical characteristics of distant and lower take-off of the take-off angle (angle of pole support) were also observed in highly skilled group than skilled group. During the pole bending and releasing phase, horizontal velocity was generally higher in highly skilled group than skilled group. It is considered that highly skilled group was able to jump higher as the vertical velocity during the pole bending as well as release phase was much higher in comparison to the skilled group.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to validate the Korean version of Coaching Life Skills in Sport Questionnaire (KCLSS-Q). METHODS Substantive, structural, and external stages were undertaken to address the purpose of this study. At the substantive stage, the scale was translated by discussing with an expert panel and testing item clarity. Ten coaches (9 males, Mage=33.80, SD=4.21) participated in the item clarity test. At the structural stage, descriptive statistics, exploratory factor analysis (EFA), and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) were conducted. A total of 249 (214 male, Mage=34.18, SD=6.82) and 232 coaches (186 male, Mage=34.26, SD=7.69) participated in the EFA and CFA, respectively. At the external stage, correlation analysis using other scales (emotional intelligence in sport coaching, EISSC) was conducted to examine concurrent validation. A total of 130 copies of the CFA data were randomly extracted and used for this stage. RESULTS For the EFA, the scale extracted five factors with 27 items. In the CFA, however, five factors with 26 items were identified as an appropriate structure. Finally, the relationships of all sub-factors between KCLSS-Q and EISSC were statistically significant in the correlation analysis. CONCLUSIONS KCLSS-Q should reasonably consists of nine items on structuring and facilitating a positive sport climate, five on understanding life skills, four on practicing life skills, five on understanding life skills transfer, and three on practicing life skills transfer. KCLSS-Q can be used as a valid measure to evaluate the coaching life skills of Korean coaches.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop the Emotional Intelligence Scale in Sport Coaching(EISSC) based on the emotional intelligence trait model. Methods The participants were 236 professional sports coaches by the purposive sampling methods via e-mails. 48 preliminary items were developed by literature review among expert panels. Then, a total of 40 items were selected after the item-analysis. Exploratory factor analysis was conducted for construct validity and criterion validity was evaluated by Person’s correlation with coaching efficacy scale and general emotional intelligence scale. An internal consistency, Cronbach's alpha coefficient, was used to see the reliability. Results The results of exploratory factor analysis presented a six sub-structure factors (Self-awareness, Awareness of others, Optimism, Utilization of emotion, Emotion regulation, Social skills) with 20 items, which explained 68.49% of the total variance. Criterion-related validity was supported by correlations with in coaching efficacy(r=.713) and general emotional intelligence(r=.647). Reliabilities were secured with Cronbach’s alpha coefficient .854 for the total 20 items. Conclusions The EISSC can be used to provide an valid measure of emotional ability of coaches in sport.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a comprehensive model for facilitating and hindering factors about girls' participation in physical activities. Methods Based on systematic analysis, 26 foreign journals published from 2005 to 2016 were comprehensively analyzed. The journals were directed to facilitating and hindering factors of girls' physical activities. A model was developed by categorizing various factors in the previous studies, and by conceptualizing those categories, and by creating visualization of relations between the categories. Results Seven facilitating factors are referred to as 'SPORTS', including ‘Self-recognition’, ‘Physical environment’, ‘Opportunities’, ‘Relationship’, ‘Treatment’, and ‘Social supports’. In contrast, nine hindering factors are conceptualized as 'INCAPABLE' which includes 'Internalized gazes’, ‘Negative feedback’, ‘Competitiveness’, ‘Alternativeness’, ‘Perceived danger’, ‘Appearance’, ‘Bad feeling’, ‘Lack of opportunities’, and ‘Effeminate norms'. Conclusions It is suggested that the girls' physical activity patterns vary depending on whether the girls subjectively interpret the physical activity or girls are being objectified by other's evaluation. And those individual, relational, and environmental levels are needed to strengthen the subjectification of girls.

