PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the association of physical activity level with insomnia severity (Normal, Subthreshold, Moderate and Severe) in adolescents and to use it as a basis for insomnia prevention. METHODS This study was conducted on a cohort of 50 adolescents under the age of 20 (19 males, 31 females) recruited from Hospital N in Incheon, Korea. Participants were categorized into groups according to the severity of insomnia in both males and females using the Korean version of the Insomnia Severity Index-Korean (ISI-K). The Korean version of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire was also used to calculate participants’ weekly moderate and vigorous physical activity. RESULTS The participants’ characteristics did not differ by insomnia severity in males, but there were significant differences in weight (p=.008), BMI (p=.019), SBP (p=.004), and DBP (p=.019) in females by insomnia severity. In male adolescents, there was no significant difference in the amount of physical activity by insomnia severity, but there was a trend toward decreased amount of physical activity with increasing severity. Among female adolescents, there were significant differences in the amount of physical activity by insomnia severity: moderate (p<.05), high (p<.05), and moderate-high (p<.05). In the unadjusted model, adolescents who did not meet the recommended amount of physical activity (150 minutes per week) were more likely to have insomnia (OR=4.67, 95% CI=1.34–16.24) than those who met the recommended amount of physical activity. The model after adjusting for covariates (gender and body mass index) also showed an association between the recommended amount of physical activity and insomnia (OR=3.94, 95% CI=1.17–13.28). Negatice correlations was found between insomnia index and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (r=–.357, p=.013). CONCLUSIONS Adolescents are approximately 4.67 times more likely to suffer from insomnia if they do not meet physical activity recommendations, and there was a negative correlation between the insomnia index and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, suggesting that physical activity should be increased to reduce the insomnia index.

The purpose of this study was to analyze and confirm whether the items used in final paper and pencil test was determined to DIF when school sports clubs in each school operated by discriminatory curriculum in accordance with gender. Participants were 8th middle school students(male=135, female=141). They joined in school sports club every week from freshman to sophomore 1st semester. At that time, boys of them participated in soccer and basketball, and girls played dodge ball. They studied soccer unit at sophomore 1st semester, and had a final examination consisting of 5 soccer items. Using the data, differentially functioning item by the population difference between male and female were analysed quantitatively and qualitatively. The results showed that Mantel-Haenszel method(using classical test theory), comparison of item characteristic curve and likelihood ratio test(using IRT) determined item number 4 and 5 to differentially functioning item. Finally, item number 4 were identified differentially functioning item in favor of male students in intensive qualitative analyses. That item have low content validity and application-level of cognitive behavior classification. The result provides that application-level item can be functioning differentially to female students with little sports experience than male students in paper and pencil test of PE.





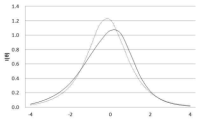
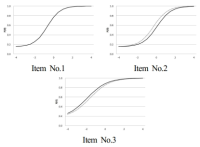
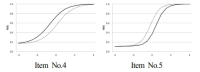
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of perceived organizational support of high school football players on innovative performance. Of particular note, we focused on examining the mediation effect of self-management between perceived organizational support and innovative performance. METHODS A total of surveys returned was 137 and the data used for the final analysis was 130. The data was processed using SPSS 21.0 statistical program and Lisrel 9.2 for confirmatory factor analysis. RESULTS The results of the analysis were as follows: first, perceived organizational support of high school football players had a positive effect on players’ self-management. Second, players’ self-management had a positive effect on players’ innovative performance. Third, players’ self-management fully mediated between perceived organizational support and players’ innovative performance. CONCLUSIONS The study concluded that maximizing both perceived organizational support and self-management of the high school football players are necessary in order for the organization to achieve high level of innovative performance.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore environmental constraints that hindered the physical activity of female students in daily life, and then to provide alternatives to improve the problems based on the social ecological model. Methods Research participants were twelve female students to be selected in two schools(Norang, Parang middle school), the process of data collection(orientation, photovoice implementation, focus group interview) and analysis(choosing a photo, contextualizing, subjecting) were conducted according to the Photo-voice. Results The constraints of physical activity in daily life were categorized on ‘playground as like a desert’(leisure domain), ‘space of recess and in-active play’(family domain), ‘transportation replaced by mom and dad car’(transportation domain), ‘space of the only exercise as well as reproduction of gender discrimination’(school domain). Conclusions The environmental constraints were analyzed as academic, physical, daily living, socio-cultural environment. Lastly, alternatives for promoting physical activity of female student were proposed in the level of organization, community, public policy based on the social ecological model.














The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship of obesity index, fitness and cardiovascular risk index in middle and high school students. Obesity index, fitness score and cardiovascular risk index were measured from 1,044 middle and high school students. The results of relation between obesity index and fitness showed that the higher obesity index had significantly lower fitness score for both boys and girls (boys: p<0.001, girl: p<0.05) The results of relation between obesity index and cardiovascular risk index indicated that the higher obesity index had significantly higher cardiovascular risk index for both boys and girls (boys: p<0.001, girl: p<0.001). Moreover, The lower fitness index showed significantly higher cardiovascular risk index regardless of gender in middle school students (boys: p<0.001, girl: p<0.01). Therefore, the results of this study indicated that obese adolescents had the lower fitness level and high possibility of cardiovascular risk.

Recently, there have been diverse types of physical activities supported by government policy in S. Korea. However, these activities may not be effective if they do not reach to moderate to vigorous level. This study designed school physical education system based on SPARK program, which include traditional physical education, sports club based physical activity, after school physical activity, and Saturday physical activity, to evaluate its effectiveness associated with physical fitness and empirical meanings of physical activity. This study employed a mixed method research paradigm for better understanding. Among various mixed method paradigm stances, this study employed "blending strategy" for complementary analysis. First of all, the effectiveness in health condition was evaluated by quantitative data. Specifically, physical fitness and lifestyle were analyzed by Helmas, IPAQ, and Accelerometer respectively. Second, empirical meanings of physical activity were analyzed by both Photovoice and in-depth interview which are qualitative research method. The result of this study first showed that a specially designed school physical activity program based on the SPARK contributed to improve students' physical fitness and lifestyle as well, however, there were important differences between male and female students. Second, physical achievement, alteration of spatiotemporal meaning, and change of societal relationship emerged as important themes. Further, these themes showed that they played an important role to maintain students' motivation in physical activity and consequently physical activity promotion was invigorated in school. Based on these results, we synthesized investment factors and process factors and outcome factors respectively. Finally, we suggested alternative teaching methods and suggestions for following research to overcome gender issues.










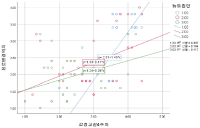
Purpose This study has four objectives. First, the study attempted to see if trainee teachers in PE experienced a higher level of burnout as their experience as trainee teacher accumulated. Second, the current study explored whether female trainee teachers experienced a higher level of burnout than their male counterpart. Third, the study examined whether self-efficacy of trainee teachers had a significant causal relationship on the level of burnout. Forth, the study looked into the possible moderating effect of motivation in the relationship between burnout and intention to change their career path. Methods The data for the study were collected from 112 trainee PE teachers of middle and high schools in Seoul and its vicinity. The data were analyzed with the SPSS statistical package. Results First, the trainee teachers’ level of burnout increased between 2nd week and 4th week and the increase was statistically significant except in the sub-dimension of depersonalization. Second, female trainee teachers showed a higher level of emotional exhaustion than their male counterpart. However, male trainee teachers showed a higher level of diminished personal accomplishment than their female counterpart. Depersonalization did not show any statistical mean difference between male and female groups. Among the four teacher self-efficacy sub-dimensions, only teaching competence showed statistically significant negative influence on emotional exhaustion. Lastly, trainee teachers’ level of motivation worked as a significant moderator in the relationship between emotional exhaustion and intention to change their career path.

PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze physical activity (sedentary, light, moderate to vigorous physical activity [MVPA]) characteristics of middle school students based on region (urban and rural) and sex. METHODS Data were collected from 216 students across 6 middle schools located in medium-sized urban (3 schools) and rural areas (3 schools), and the relevant physical activity was measured using a three-dimensional accelerometer (GT3X model). The collected data were inputted into the SPSS 20.0, and descriptive analysis and two-way ANOVA based on region and gender were performed (<.05). RESULTS The descriptive statistical analysis resulted in the following achievement rate of the physical activity standard (MVPA 60 minutes/day): 9.4%. The two-way ANOVA showed that the main effect according to gender was found in sedentary activity (F=5.258), light activity (F=6.790), and MVPA (F=32.274); furthermore, the main effect according to region was found in light activity (F=10.888) and MVPA (F=7.876). Interaction effect according to region and gender was found at all intensities, and the gap between rural and urban in male students was larger compared to that of female students. CONCLUSIONS After COVID-19, the level of physical activity among adolescents has worsened; this study found the problem of "decrease in physical activity; increase in sedentary activity" to be more serious among male students in urban areas.
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop a team building program for a middle school soccer team in order to verify its effects. METHODS A total of 50 middle school soccer players participated in the needs analysis, and 10 middle school soccer players participated the preliminary program. In addition, a total of 37 ‘S’ middle school soccer players and 2 coaches participated the final team building program to identify its effects. The team building program was developed through the following sequence: program goal setting, organization of program activities, and the pretest. Three types of questionnaires and a self-report were utilized to verify the effects of the team building program. RESULTS The team building program was developed based on interpersonal relationships, goal setting, and communication. The level of team cohesion, team communication, and coach-athletes interaction significantly increased through this program. Furthermore, the effects of stress relief and self-improvement were revealed through the self-report. CONCLUSIONS The team building program was determined to be effective and has various benefits. It is expected to contribute to the growth of middle school soccer players if coaches actively participate in the program with their athletes.
The purpose of the study is to find the impact of social and economic factors in physical activity of children and youth. This study utilized the data from 4th Korean Children and Youth Panel Study(KCYPS), and the analysis were carried out based on the starting sample of 2,009 from ‘the elementary 4 panel’ and 1,978 from the ‘middle school 1 panel’ and 1,984 from the ‘high school 1 panel’, 5,971 full data were used in the final analysis. Data were processed using hierarchical regression analysis and it was statistically validated at the significance level of 0.05. First, Pearson r and Spearman ρ showed that all variables are statistically significant correlations. Second, among the first factors of personal and family characteristics, household income level(B=.113), family composition(B=-.049) and parental education (B=.060) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, parental education (B=.027) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Third, among the second factors of community-level characteristics, Gini coefficient (B=-.810), wealth concentrating (B=.120) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, the Gini coefficient (B=-0.315) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Additional factors that determine the coefficient of variation in the level 2 were found to be 0.623 and 0.001 respectively. Therefore, second factors of community-level characteristics are added such as Gini coefficient, wealth concentrating were explained to children and youth exercise time during physical activity 62.3%(p<.01) and subjective evaluation of physical education in grades 0.1%(p<.01). predictive power to