PURPOSE This study investigated the effects of 12 weeks of clubbell and stepbox training on physical fitness, badminton skills, and fatigue in male badminton, grade A (top grade) club members aged 20–30s, with over 5 years’ experience. METHODS Participants in a training group (TR: n=15) engaged in 12 weeks of clubbell and stepbox circuit training involving maximum 8–12 reps of clubbell exercises and stepbox exercises at over 77% of HRmax for 50–55 min/sessions three times a week. Participants in a control group (CON: n=15) maintained their normal lifestyle pattern during the same intervention period. Dependent variables were measured and compared using repeated measures two-way ANOVA. RESULTS The main results were as follows: 1) The groups showed no significant differences in body composition. 2) Regarding physical fitness, VO2max, relative peak power, relative average power, grip strength, push ups, repeated jump squats, SSPT (seated single-arm shot-put test), 10 m sprint, and hexagon agility increased significantly in the TR, while push ups decreased significantly in the CON. 3) As for badminton skills, forehand clear accuracy, badminton agility, badminton endurance, and smash speed increased significantly in the TR. Forehand clear accuracy decreased significantly in the CON, but badminton agility and smash speed increased significantly. 4) The groups showed no significant differences in fatigue. CONCLUSIONS In male badminton club members aged 20–30s, 12 weeks of clubbell and stepbox circuit training effectively improved physical fitness and badminton skills. However, lack of any improvement in body composition and fatigue warranted further research in these areas.
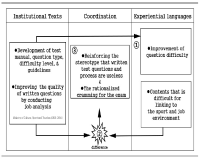
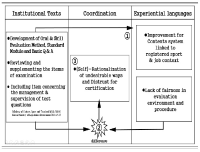
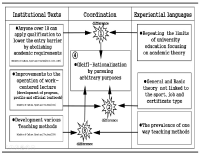
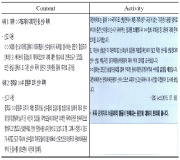
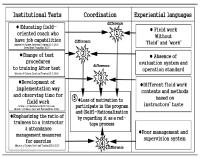
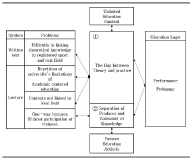
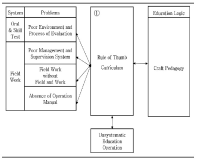
Purpose There are two purposes of this study; First is to investigate the reality of curriculum in the qualification system through the coordination process between participants’ experiences and institutional texts. Second is to identify the light and shade of the educational logics underlying the certificate courses of Level 2-sport-for-all-coach. Methods By relying on the institutional ethnography approach(Smith, 2005), the data were collected through on-site materials and semi-structural interviews with seven coaches who participated in the qualification programmes after 2015 system revision. The data were analyzed by mapping the social organization. Results The analysis shows two key findings. First, participants faced inconsistencies with institutional texts in the subcategories of qualification system and experienced (self-)rationalization process including doubt, complaint, acceptance and compromise toward the system. Second, Performance pedagogy and Craft pedagogy were operating at the root of the current qualification system, and the two logics led to the fundamental limitations(unlinked educational content, passive educational activity, and unsystematic educational operation) for the improvement of system. Conclusion The activation of the retrospective approach to distinguish the pros and cons of various educational logics was suggested. These findings are expected to provide useful implications for building the future framework to educate sport-coaches more systematically.

The purpose of this study was to examine psychological capital acquisition through Asian Games Participation. 17 of national women football players were completed Psychological Capitals Questionnair. The psychological capital consists of optimism, psychological skills, self-management, collective efficacy, and performance perception was investigated after the team call-ups and before the team-release. The data was analyzed by paired t-test. As results, Korean women football players’ collective efficient and performance perception showed a statistical significance at the beginning of the team call-ups but optimism, psychological skills, and self-direction did not show statistic significances. The team-harmony, interpersonal-management, team-power, sufficient training, trust in coach, efficient communication, and psychological football factors, which were subfactor of football players’ psychological capital, showed statistical significances. However, confidence, concentration, goal-setting, imagery, willpower, anxiety-control, mental-management, life-management, training-management, innate-behavior management, physical-management, football skills, mediative skills, and football intelligence factors did not have statistic significances. These results demonstrate that effects of mega sporting events-like experiences and psychological factors’ variability and inflexibility according to weather changes should be considered when it comes to discussion of psychological factors regarding players’ performance. It is expected that this study would be a fundamental resource for understanding of psychological influences through participations in mega sporting events and discussions about further psychological interventions for teams with environmental consideration as well as methodological developments which could measure effects of the psychological interventions.
PURPOSE This study aims to provide empirical foundational data for the development of a new profit model in Korean professional baseball. It does so by examining the influence of professional baseball NFT product attributes on customer perceptions of value, satisfaction, and purchase intention. METHODS Data were collected from consumers who have experience purchasing KBOLLECT. A total of 363 samples were collected for analysis. Surveys were utilized for data collection, encompassing 39 items that measured product characteristics, perceived value, satisfaction, purchase intention, and demographic information. Using the collected data, various statistical analyses were conducted including descriptive statistics, exploratory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis and multiple regression using SPSS version 21. The ensuing results from the correlation analysis and multiple regression analysis are as follows. RESULTS Product features, including aesthetics, symbolism, and scarcity, had a positive impact on consumer’s perceived emotional value. Moreover, product features, encompassing aesthetics, symbolism, scarcity, and creativity played a significant role in enhancing consumer’s perceived economic value. Furthermore, product attributes such as aesthetics, symbolism, and creativity positively contributed to consumer’s perceived social value. Similarly, product features comprising aesthetics, scarcity, creativity, and symbolism positively affected consumer’s perceived intellectual value. Additionally, the research revealed that product features related to aesthetics, symbolism, creativity, and scarcity were instrumental in bolstering consumer. Importantly, these very attributes, including aesthetics, symbolism, scarcity, and creativity, exhibited a positive influence on consumers’ purchase intentions. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, this study underscores the substantial impact of professional baseball NFT product characteristics on consumers’ perceptions, satisfaction, and purchase intentions. To maintain enduring relationships with consumers who engage with professional baseball NFT products, it is essential to fortify these product attributes and offer diverse services utilizing them.
This study was to explore the factors influencing Olympic performance positively and negatively. In order to achieve this purpose, 60 athletes, who participated in 2012 London Olympic games, responded on open-ended questionnaire. In addition, 10 athletes, who won medals in London Olympic, responded on in-depth interview. Collected data were analyzed by deductive content analysis. The results of this study were as follows: firstly, the factors influencing Olympic performance positively were psychological preparation, strengthening training, physical conditioning, support from significant others, material support, cheering of Korean people, self respect as a Korean national athlete, different game environment, team cohesion, sharing Olympic experience, and support of sports science. Secondly, the factors influencing Olympic performance negatively were psychological pressure, excessive expectation, negative interpersonal relationship, condition decline, overtraining, unstable environment, insufficient facilitation, decrease in performance level, and especially ineffective village room placement and media management during Olympic period. Thirdly, the differences between Olympic games and other world competitions , perceived by athletes were competition scale, psychological attitude, training support, systematic preparation, and benefits from winning medals. The results of this study will give fundamental information in developing a scale which can measure Olympic preparation level and in developing Olympic preparation guideline. Therefore, it will help athletes ,who participate Olympic for the first time or athletes who did not perform well in pre-participated Olympic games, to understand and apply in training the factors influencing Olympic performance and help them to perform better in Olympic games.

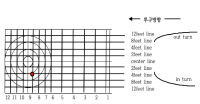
Purpose This is to provide essential data for training necessary for sweeping through the analysis of muscle activity generated at this time and how much sweeping and what trajectory moves the stone when the movement of the stone is controlled through sweeping. Methods To check and record the distance between the stones by checking the stop position of the stone made by sweeping each section, the length (progress distance) and width (progress direction) were recorded using a reference table and a record preparation table. With the EMG attached, a total of 60 sweeps were made 20 times each from the beginning of the section to the end of the section. Sweeping subjects were asked to sweep as much as possible under the same conditions in all three sections. Results As a result of the study, the muscle mobilization patterns of the 1st and 2nd sections of the stone with the faster speed and the 3rd section with the stone's slower speed appeared differently. It was confirmed that the sweeping motion of curling is a motion that is used evenly among the muscles of the upper extremity, and it can be verified that it is a suitable item for the development of upper body muscles. Also, the right deltoid's muscle activity rate during push and the right triceps brachii during pull was high. Conclusion Each section of the stone's sweeping effect is an exercise that has many variables, such as changes in atmospheric temperature and humidity, changes in ice temperature, temperature-size-number of pebbles, and the edge state-resilience of stones, etc. It is judged that experience can cope with these variables and requires training.

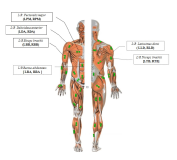
PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to analyze the biomechanical variables involved in ballet dancers’ ankle muscle imbalance when performing relevé movements. METHODS The subjects of this study (n=14, age: 22.29±1.73 years old, height: 161.4±5.06cm, weight: 51.88±7.51kg) were 14 ballet dancers with 9 years of experience. Based on the reciprocal muscle strength ratio, the dancers were divided into the following groups: Close to the normal value (RMIS) and far from the normal value (RMIB) using the maximum values of plantar flexion and dorsiflexion of the ankle joint using an isokinetic measurement equipment (60°/sec). RMIB). The biomechanical variables, namely the ankle joint movement and ground reaction force, were subsequently measured. SPSS 26.0 was used for data analysis and independent t-test was used for statistical verification. RESULTS The ground reaction force in the Z (vertical) direction based on the ankle joint muscle strength imbalance of ballet dancers was significantly lower in the RMIB group. In addition, although it was not a statistically significant difference, the plantar flexion movement was lower in the RMIB group, and there was a significant difference in the generation of ankle joint movement in the Z direction. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, in order for a ballet dancer to efficiently utilize the force generated from the supporting leg when performing a movement, ankle imbalance must be taken into consideration when training.
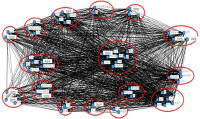
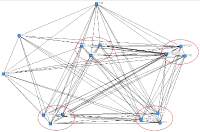
Purpose This study reviewed the seriousness of the Match-fixing through the mixed research methods of the big data analysis (quantitative) and the focus group interview (qualitative) using the keyword, ‘Match-fixing’ and discusses the cautious and comprehensive basic direction for coping with negative issues and preventing recurrence. Methods For the quantitative research method, Naver and Daum were used as the analysis channel and the main keywords selected for the data search were ‘Match-fixing’ and ‘Match-fixing+(measures/eradication/solution)’. The data collection period was limited from January 1, 2010 to December 31, 2016. In addition, for the qualitative research method, 6 homogeneous groups (experience, interest, knowledge) related to the research topic were constructed and interviewed using purposive(intentional) sampling. Results First, five factors (emotion, participant, cause, punishment, countermeasure) were categorized by big data analysis. Second, through Focus Croup interview, additional keywords for three factors (emotion, participant, countermeasure) were derived. Conclusions Therefore, it is required that various preventive measures such as emotional reward for negative emotion, preventive and ethical education, advancement of sports, establishment of Match fixing committee, Expert training are needed.


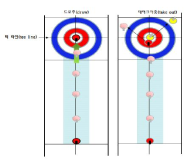
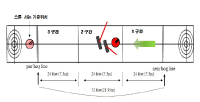
In this paper, we tried to find out the difference of CoM displacement, CoM velocity and Foot-pressure between draw motion and takeout motion in curling’s delivery motion. To do this, we experimented for 10 female athletes of curling national team(all athletes are in her 20th~30th ages) to carry out draw motion and takeout motion from backline to near hogline in state of speed limit. The limited speed was 3.80~3.90 sec for draw and 2.97~3.07 sec for takeout. From the experiments, we obtained the result like followings. 1. Draw motion is more increase than takeout motion in displacement of horizontal direction of CoM displacement. 2. Takeout motion is more increase than draw motion in displacement of vertical direction of CoM displacement. 3. Takeout motion is faster than draw motion in both of horizontal and vertical direction of CoM max. velocity. 4. Takeout motion is higher than draw motion in pressure of fore-foot and mid-foot of foot-pressure 5. Draw motion is higher than takeout motion in pressure of fore-foot and mid-foot of foot-pressure These result means that the characteristics of techniques for draw motion and takeout motion is differ from each other and it is necessary to take different training protocol individually to enhance athletes’s performance. And further research will contains another things like that the pursuit of curling stone’s rut by various delivery techniques






PURPOSE This study compares the effects of video group and metaverse group counseling for student athletes to analyze differences in immersion, sychological skills learning effects, and each approach’s participation experiences. METHODS Twenty-four high school archery students were divided into three groups: a metaverse experimental, a video comparison, and a control group. For the experimental and comparative groups, 10 non-face-to-face psychological skills training sessions were conducted. With the control group, results were compared and analyzed by measuring psychological skills and social presence pre- and post-training. Additionally, analysis of the qualitative effects of psychological skills training was performed. RESULTS The psychological skill test’s quantitative analysis of the video comparison group showed a more significant effect in anxiety control factors than the metaverse experimental and the control groups. Moreover, in the social presence test, both the metaverse and the video groups showed significant differences in social presence and satisfaction; furthermore, Scheff post-verification results showed that the two environments’ satisfaction was significantly higher than that of the control group. Qualitative analysis confirmed that the metaverse and video groups experienced psychological, technical, and relational changes in common. CONCLUSIONS Although the metaverse group using avatars was likely to increase immersion, both the video and the metaverse groups were effective in psychological skills training, suggesting that the training effect may vary depending on the non- face-to-face environment’s stability and participation method. Future studies should examine effects of applying the metaverse platform to sports psychological skills training and various psychological support activities by solving the metaverse environment’s technical limitations.