This study aims to suggest the guide line for weight category sports(Taekwondo, Judo, Wrestling, Weightlifting, and Boxing) who have to lose weight to pass weigh-in before games. Reference data was collected from RISS, Medline, PubMed, SciELO and effects of short term weight loss on physiological variables(body composition, physical fitness, blood components, oxidative stress and hormone, immune function) were analyzed. Also, weight loss procedures for weight category sports athletes were analyzed in details. The results of the research are as follows: weight category sports athletes prefer short term (3~5 days) weight loss methods (3~5%) with dietary control, sweating and exercise. Physical changes caused by the loss in body weight, fat-free mass, and BMI, however, do not affect body fat percentage. Different changes of physical strength element depend on weight reduction period. In short term weight loss method, anaerobic exercise capacity, muscular strength, and reaction time partially decrease and affect staying power. In contrast, long term weight loss method do not affect aerobic and anaerobic exercise capacity. Furthermore, most of previous studies show that blood component change has negative effect on body water balance, stress-related hormone, and immune function. In conclusion, short term weight loss method negatively affects athletic performance of weight class competition athletic. Therefore, careful long term weight loss methods are recommended with dietetic consideration to prevent dehydration during weight loss period. Excessive weight loss on lightweight athlete should be prevented by institutional basis as well.
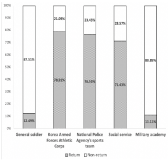
Purpose The purpose of this study is to identify the negative effects of long-term exercise (training and competition) suspension of male elite athletes due to compulsory military service on athletic performance, and to provide a basis for enhancing the importance of providing support systems and social conditions for maintaining athletic performance. Methods In this study, 17,418 male athletes aged 18 to 21 who were registered as athletes for the Korean Sports & Olympic Committee from 2003 to 2005 were enrolled. The athlete registration data includes information about the athlete's gender, age, sport and affiliation. According to the continuity of registration and belonging information, the compulsory military service type was classified into a manipulator. According to the form of Compulsory military service performed by male elite athletes, the return rate was confirmed and the career (year) was calculated. Results As a result of the survey, 12.49% of the athletes who served as general soldiers returned to the athletes after compulsory military service, showing a relatively low return rate compared to 78.91% of the Korea Armed Forces Athletic Corps, 76.55% of the National Police Agency's sports team, and 71.43% of the social service. Also, Athletes who served as general soldiers had a career of 2.46 years (± 1.94), while the Korea Armed Forces Athletic Corps was 10.21 years (± 3.58), the National Police Agency's sports team was 9.45 years (± 3.26), and the social service was 5.86 years (± 4.06), The exemption was 11.08 years (± 2.27), and the compulsory military service exception was 9.79 years (± 5.55). Conclusions Male elite athletes' decrease in athletic performance after compulsory military service is a natural result, as confirmed through the results of this study, and it is necessary to seek a support system between compulsory military service to maintain athletic performance.

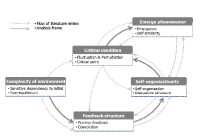
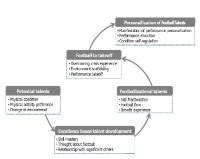
Purpose This study was aimed at interpreting the football talent development stages based on complexity theory. Methods The data for this study was gathered through literature review and in-depth interviews that were analyzed by thematic analysis. Literature review of the studies regarding complexity theory revealed the features of complexity theory and five football players participating in the K-league were interviewed. Gathered materials were analyzed by the thematic analysis. Initial codes and potential themes of football talent development stages, the conception and potential themes of the complexity theory were interpreted by metaphorical analysis. Results Results of literature review were as follows: analysis frame of complexity theory were organized environment of complexity, feedback structure, self-organization, critical condition and emergent phenomenon. The football talent development stages, interpreted as a result of literature review, were divided into Potential Talents, Excellence based Talents Development, Footballizational Talents, Football to Takeoff and Personalization of Football Talents. The stages were specifically materialized as follows: Potential Talents was materialized into physical condition, physical activity preference and change of environment. Excellence based Talent Development was materialized into skill mastery, thoughts about football and relationship with significant others. Footballizational Talents was materilized into skill fractionation, football flow and growth experience. Football to Takeoff was materialized into overcoming crisis experience, performance scaffolding and performance takeoff. Personalization of Football Talents was materialized into manifestation of performance personalization, performance evolution, condition maintenance. Conclusion Football talent development stages, interpreted by means of complexity theory, were divided into Potential Talents stage, Excellence based Talent Development stage, Footballizational Talents stage, Football to Takeoff stage and Personalization of Football Talents stage. Utilization of this study as a fundamental resource of football talents development programs and as a means to understanding football talents development is looked forward to.


[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to investigate the process of Jang Changsun’s winning gold medal in the 1966 Toledo World Amateur Wrestling Championship and its meaning. [Methods] Jang Changsun and Katsumura Yasuo who had competed with Jang Changsun for the gold medal were selected as participants, a player and an executive who had participated in the Championship were selected as informants. Data had been collected by in-depth interview were analyzed firstly by using the Patton(1991)’s data analysis method, and the following conclusions were obtained by comparing with preceding studies, press releases, reports etc. [Results] Jang Changsun won a gold medal through the three stages of desperate struggles. The first struggle was to loose weight. Jang Changsun lost three times more weight than other players through fasting treatment, intensive training and dehydration in order to secure an advantageous position in the competition. His second struggle was the sparring itself. He made his mind to win gold medal 2 years before the Championship and started to strengthen his physical fitness and polish up his techniques to fight with strong players from powerful nation of wrestling. He finished the sparring by winning 4 games and tieing 2 games resulting in the same deduction points with Katsumura. It was inevitable for him to fight desperately to lose weight again to get gold medal. He eventually won the gold medal by losing his weight until he fainted because of injuries and serious dehydration. [Conclusion] The first gold medalist Jang Changsun contributed a lot to development of Korean sports by offering chance to consider significance of improving elite player’s exercising environment, scientific coaching, gaining self-confidence to win medal, and realizing the importance of sports informations.


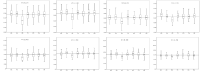
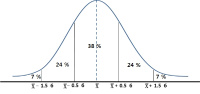
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the physical performance and develop the criteria of 4243 middle and high school students across 5 provinces (Busan, Gwangju, Daejeon, Gyeongi and Jeonbuk) in Korea that took part in the talent development project. The data was collected between 2011 and 2014. The criteria was divided by gender and age across different grades, and the mean, standard deviation and 5 evaluation levels were calculated and analyzed.

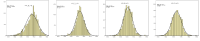
PURPOSE Using GPS data from actual field hockey matches, this study examined the effects of position and substitution time on the physical performance of elite female players. METHODS From 25 matches played in 2023, data involving 26 players were collected. Players’ positions were classified as forwards (FW), midfielders (MF), and defenders (DF). Substitution times were segmented into 5, 10, and 15 minutes, respectively. A two-way ANOVA was employed to analyze movement patterns across different exercise intensities as influenced by player position and substitution time, followed by Bonferroni post-hoc tests for further detailed analysis. RESULTS Analysis revealed that both position and substitution time significantly affected exercise intensity. Notably, at a substitution time of 5 minutes, substantial differences were observed in high-intensity movements, including the distance covered at high-intensity and the frequency of high-intensity efforts. Furthermore, the substitution time’s impact was particularly pronounced among forwards and midfielders. CONCLUSIONS Findings suggest that shorter substitution times can enhance players’ active movement, thereby supporting maintenance of tactical adjustments and positively influencing overall performance. Implementing shorter substitution times could be particularly beneficial for optimizing team performance, especially for players in forward positions.
PURPOSE This study aims to help improve performance by comparing and analyzing the kinematic variables for each upper and lower extremities segment when two groups of players attack the national women’s fencing players in a match situation. METHODS This study divided the movement time, movement time ratio, Fente step length change, angle factor at each event, and velocity factor of the fencing point of a sword at each event into the Olympic medalists’ group (Group A) and the international competition winners group (Group B) during the fencing Marche Fente. An independent t-test was performed for each factor, and the results were compared. RESULTS As a result, the difference between the two groups in movement time was statistically significant in the front of the foot in the velocity factor. However, no statistical significance was found between the two groups in the front angle of the trunk, the elbow angle, and the knee angle. CONCLUSIONS This indicates that group A and group B are both outstanding players with the best performance, so they are similar in the details of the movements except for the very slight difference in time and velocity. Therefore, the average of the result values of the joint angle will be a feedback index for fencing beginners or education subjects who are now starting to fencing.
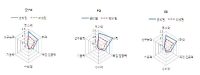
This study has been conducted to develop methods and techniques for the analysis of data related to baseball performance using the winning and losing games. The purposes of the study were to examine differences of athlete performance for semi playoff, playoff, and Korean professional baseball series and to develop optimal forecasting model for the short term series. Data used in the study were taken from Korean professional baseball association. Three data sets including semi play off from 1982 to 2012, play off from 1989 to 2012, and Korean series from 1982 to 2012 were used. To compare athlete performance by winning and losing games for short-term series t-test was applied. This study created new parameters by weighted value through the equalization process to calculate skill related variables as a predicted variable. Three predicted models such as discriminant, binary logistic regression and artificial neural network models were developed to clarify the suggested models. The results showed that the number of significant parameters increased as the series continued. In particular, a variable related to error was added as a significant variable at the Korean Series. A third base hit in the play-off and a second base hit were also added as significant parameters in the play-off and the Korean series, respectively. In addition, W/L a major variables affecting a given technology area, the pitching PO, PO, the inertia, KS, the pitching, respectively. An artificial neural network model was finally selected with the highest accuracy and lowest input of estimated parameters in the semi play-off. In the play-off, artificial neural network model that applied technical area parameters by specialist criteria had better accuracy rate than two others. In the Korean series, artificial neural network model that created estimation parameters by applying all parameters was chosen as the final model. When the overall accuracy level of semi-play off, play off and Korean series was figured out, binary logistic regression model had higher accuracy of classification than discriminant model, but artificial neural network model had the higher accuracy of classification than binary logistic regression model.



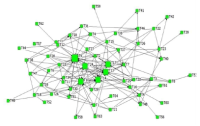
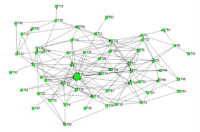
Previous work has shown that coaches sought information from several sources; however, there was a strong reliance on learning from other coaches within their social networks. There has been limited research examining the nature of these social networks with other coaches (Trudel and Gilbert 2004). Thus the purpose of this study was to examine the structures of coaches’ social networks of Korean rhythmic gymnasts. Research questions were: (1) What are the network structures of Korean rhythmic gymnasts’ coaches? (2) What structural parameters contribute to coaches’ network structures, and (3) Is there an association between coaches’ network and flow of information in their networks? A total of 37 coaches of youth rhythmic gymnasts (6-18 years old) participated in this study. Each of those coaches was asked to complete a Name Generator Questionnaire (i.e., list four names that you have a close relationship with) and general socio-demographic survey. Data were analyzed using social network analysis tools such as UCINET, p-net, and Quadratic Assignment Procedure. Analysis of network centrality, density, and strong components showed that (1) homophily was identified in the structure of coaches’ social networks (2) homophily (e.g., by gymnasts’ ranking, mentor coaches) contributed to the total social network of coaches, and (3) interacting only with close coaches in the network, coaches received information about coaches/coaching from the strong ties rather than weak ties (Granovetter, 1973). This study also has strong links to Wenger’s (1998) community of practice which posited that groups of people share a common characteristic in practice.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to examine the goalkeeper’s area of defense and how the range varies depending on the relative position of the goal, goalkeeper, and ball in a 9-meter jump shot during handball matches. METHODS Data was collected from seven qualifying divisions in mens handball from the 99th National Sports Festival in Korea. A total of 231, 9-meter jump shots were analyzed with the goalkeeper‘s area of defense measured from the point the ball left the shooter’s hand and calculated based on the relative position of the goal, goalkeeper, and ball. Video analysis was conducted using the Kwon3D 3.01 program and three-dimensional coordinates calculated using the DLT method. RESULTS First, dimension of handball goals measure 3m wide and 2m high, however, results show that goalkeeper’s actual area of defense was narrower than the width of the goal posts, while vertically, area exceeded the height of the cross bar. Second, if the goalkeeper defended the striker’s shot from the side rather than from the front, the goalkeeper’s defense range was higher for the opposite side of the goal post than the near side of the goal post. CONCLUSIONS Key factors influencing goalkeeper’s area of defense include height of shot and position of goalkeeper. Results also indicate that vertical movements are more important than horizontal movements for goalkeepers in handball thus such implementation in training may lead to performance enhancement.