PURPOSE This study aimed to develop a positive psychological intervention program for a college ice hockey team and test its effects based on application to the team. METHODS The demands of 78 college ice hockey players were asked through open questionnaires. Collected results underwent integrated analysis to develop the desired program through the participants who were also observers of the team. The objectives of the program were established, and an appropriate program was developed based on the analyzed data, expert opinion, and precedent research. The developed program was applied to 26 players of a college ice hockey team to verify its effects. Tasks included writing experience reports and in-depth interviews. The Happiness Measures 1, Strength Knowledge, and Team Interaction Questionnaires were also administered. Collected qualitative data were categorized to follow inductive analysis procedures, while paired t-tests were performed for quantitative data using SPSS 25.0. RESULTS To improve the application of the program in real situations and maintain credibility and validity, the program was developed based on analyses of individual and team demands, methods of the participant as an observer, expert opinion, and other considerations. Statistically meaningful differences in positive psychological mind, happiness, recognition and utilization of strengths, team interactions, team cohesion, and so on were found using paired t-tests comparing data before and after the developed positive psychological intervention program. CONCLUSIONS Providing opportunities to recognize individual and team strengths and have valuable experiences for each player could enhance interactions between teammates and create a favorable team environment.
Purpose This study aims to explore migration factors of Korean male footballers who have moved from South Korea to Southeast Asian countries. Methods Qualitative case study was conducted with 9 footballers, 4 their agents and 2 K-league staffs as the participant. Results As a result, by regarding their migration as involuntary decision, this study could provide academic and practical discussion on sport labor migration. First of all, this study established theoretical framework for involuntary migration of the participants through ‘Push-Pull Theory’ which focuses on demand and supply on the labor force. Second, this study found that a local rule (FA compensation system) of Korean professional football league (K league) and hierarchical collectivist culture contributed to their migration, which has not been reported by previous studies focused on the voluntary migration of mainstream players and it reflected local context of K league. Conclusions In conclusion, this study confirmed that sport labor migration was also considered as social phenomenon and reflected a cross section of a particular society. Through the migration of athletes, we can provide a variety of viewpoint on economic (market) structure, related policy and system in a particular society, and understand migration motives in terms of agency (subculture).
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop an effective college life adaptation program for freshman student-athletes. Methods A total of 160 student-athletes and 5 experts agreed to participate in this study. Four procedures were followed in this study: the needs assessment, the preliminary program development, and the application of the program. For the needs assessment, in-depth interviews were conducted, and the data were analyzed using an inductive reasoning process. Results The results of the needs investigation showed seven need factors and four interruption factors for college life adaptation. In addition, three need factors based on experience and seven interruption factors based on experience were found. The preliminary program was developed based on the needs assessment through the expert meeting, and the program consisted of four stages. Each stage consisted of three sessions, and each session contained a specific topic. The program was provided to nine freshman student-athletes in two months. As a result, the final program which consisted of four stages and thirteen sessions was developed after the reinforcement process based on evaluation of the preliminary program was conducted. Conclusions It is concluded that, the program is able to be expected to help them to understand their roles, have a better sense of responsibility and improve their self-esteem. Therefore, coaches and mental performance consultants should provide the college life adaptation program for freshman student-athletes to reduce their stress and have a better college life.
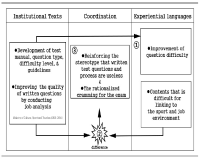
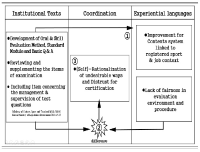
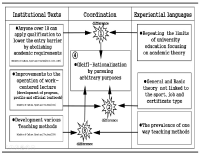
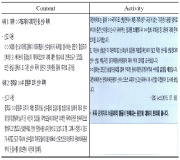
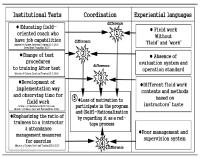
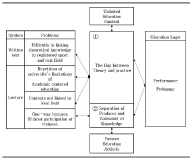
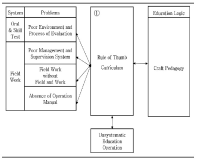
Purpose There are two purposes of this study; First is to investigate the reality of curriculum in the qualification system through the coordination process between participants’ experiences and institutional texts. Second is to identify the light and shade of the educational logics underlying the certificate courses of Level 2-sport-for-all-coach. Methods By relying on the institutional ethnography approach(Smith, 2005), the data were collected through on-site materials and semi-structural interviews with seven coaches who participated in the qualification programmes after 2015 system revision. The data were analyzed by mapping the social organization. Results The analysis shows two key findings. First, participants faced inconsistencies with institutional texts in the subcategories of qualification system and experienced (self-)rationalization process including doubt, complaint, acceptance and compromise toward the system. Second, Performance pedagogy and Craft pedagogy were operating at the root of the current qualification system, and the two logics led to the fundamental limitations(unlinked educational content, passive educational activity, and unsystematic educational operation) for the improvement of system. Conclusion The activation of the retrospective approach to distinguish the pros and cons of various educational logics was suggested. These findings are expected to provide useful implications for building the future framework to educate sport-coaches more systematically.

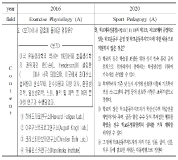

Purpose This study was to investigate the effect of various motor leaning techniques which were applied on the youth soccer training program. Methods 12 elementary soccer players and the director of R youth soccer team have participated in the study. The expertise level of youth soccer team were ranged from beginner to advance. To investigate the effect of new soccer training program we adopted a methodology of action research. We first analyzed the problems of original youth soccer program and reconstructed the training program considering of individualized characteristics. The 3 main problems of original soccer program (1. feedback provisions 2. difficulty of task level 3. time distribution of training) have been reconstructed by four motor learning experts. For the data analysis, several qualitative analyze techniques were conducted to observe player’s improvements. Results First, participants had a better understanding on proper motion of shooting and lifting skills from the guidance techniques. Second, utilizing the personal skills and team cohesion have been improved by the modified rules and space competition. Third, the ability of active problem solving have been improved from the self-learning environment. Forth, the player’s confidence level have been improved by eliminating performance outcome. Conclusions From the aspects of variety circumstances in sport education field, the comprehensive motor learning program should be developed and applied.

Purpose The current study investigated the effects of exercise information using social network service(SNS) to identify changes of physical activity and psychological variables among inactive college students. Methods Inactive college students(30 experimental group, 30 control group) were voluntarily participated in the 12-weeks intervention. During this period, the experimental group received exercise information through SNS. And all study participants’ physical activity, stages of physical activity, self-efficacy, motivation, and perceived benefits and barriers were measured at the pre, mid and post intervention. Frequency analysis, chi-square test, 2-way ANOVA RM were conducted to analyze data obtained in the study. All procedures were performed by using SPSS 23.0. Results The exercise information intervention using SNS during 12 weeks had a positive effect on the stages of physical activity of inactive college students, and there were statistically significant differences. In addition, physical activity, perceived benefits and barriers, self-efficacy, motivation positively improved after the intervention, but there were no statistically significant differences between experimental and control group. Conclusions The present study suggests that psychological strategies using various SNS programs have positive effects for inactive college students to increase physical activity and its related psychological variables.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop the sport 5C scale of the Korean version. Methods The participants were 772 high school students from 17 to 19 who participated in sport regularly. The validation of Sport K-5C followed a three-step validation procedure through substantive stage, structural stage, and external stage. Results First, In the substantive stage, Sport K-5C consisted of 50 items with 5 factors. Second, in the structural stage, although Sport K-5C was explored as 24 items with 4 factors by EFA, but as a result of CFA, Sport K-5C was confirmed as 24 items with 5 factors. Third, the external stage provided additional validity through correlations of tests with other questionnaires which are similar concept and opposite concept, and group differentiation. Conclusions Sport K-5C is composed of 5 factors and 24 items. The factors are Caring, Character, Confidence, Competence, Connection. This scale can be used to provide an objective evaluation of positive development of youth in sport and physical education context.

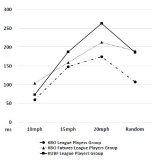
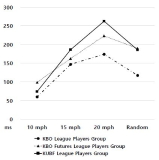
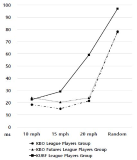
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to investigate effects of baseball expertise and stimulus speeds on coincidence-anticipation timing accuracy of batting. [Methods] Participants were 21 baseball batters, 7 of Korea Baseball Organization(KBO) League, 7 of Korea Baseball Organization Futures League, and 7 of Korea University Baseball Federation(KUBF) League. All of the participants were asked to swing the bat exactly at the time when the light arrived the target point of the runway. The Bassin Anticipation Timer was used to present stimulus with stimulus speed of 10, 15, and 20mph. Participants performed 10, 15, 20mph trials (3 kinds of speed per 5 times) and random trials (3 kinds of speed per 3 times randomly). The timing error of coincidence anticipation task was recorded and raw scores were transformed to constant error(CE), absolute error(AE) and variable error(VE). For data analysis, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures were used. And post-hoc test (Tukey HDS) were conducted. [Results] Results indicated a significant interaction on expertise and stimulus speeds for CE, AE and VE. The KBO League players group showed more accurate and consistent performance than the KBO Futures League players group and the KUBF League players group in baseball batting timing. [Conclusion] This findings revealed that coincidence-anticipation timing accuracy batting in baseball can be used as a factor to distinguish the ability of the other.

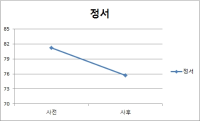
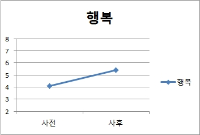
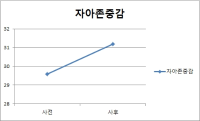
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of positive psychological intervention program on mood state, self-esteem and happiness of university student athletes. Methods The participants were 10 university student athletes. The measures utilized the Profile of Mood States(POMS), self-esteem inventory and happiness questionnaire. Positive psychological intervention program was developed by previous studies, participants interview and expert discussion. The positive psychological intervention program were managing life, self-esteem enhancing program, being optimistic, positive emotion program, gratitude, forgiveness, communication skill training program, habit/routine making program and action strategy development. The data were analyzed by SPSS 20.0. Results These results were as followings. Firstly, positive psychological intervention program decreased total mood disturbance(TMD) of university student athlete. Secondly, positive psychological intervention program improved self-esteem of university student athletes. Lastly, positive psychological intervention program increased happiness level of university student athletes. Conclusion Training and education system should be established in which a positive psychological intervention program can be applied to university student athletes.


Purpose This study aims to find out the attitude changes of consumers on a corporate sponsor in a cause related marketing based on frequency of information exposure and the image of the sponsor. Methods The data were collected from 191 students of C university in Seoul and its vicinity. The data were collected three times from the sample to see the attitude changes over time. The hypotheses of the sutdy were developed based on meaning transfer theory and spreading activation theory. This study hypothesized that the attitude toward a sponsor would change in a positive direction when consumers are exposed to related information and the change would be moderated by the frequency of information exposure. Also, the changes in attitude would be different based on the image of sponsors(i.e., positive image sponsor vs. negative image sponsor). The hypotheses were analyzed using mixed-design ANOVA. Results The results of the analyses indicated that the attitude change was greater when the frequency of information exposure was higher. The attitude change in positive image sponsor was statistically lower than that of negative image sponsor possibly due to ceiling effect.

