PURPOSE This study analyzed the relationship among coaching behaviors, motivational climate, sports competence, effort, and failure tolerance as perceived by high school athletes. Additionally, it examined whether motivational climate, competence, and effort mediate the relationship between coaching behaviors and failure tolerance. METHODS Using questionnaires measuring autonomy-supportive coaching behavior, controlling coaching behavior, motivational climate, sports competence, effort, and failure tolerance, 365 high school athletes were surveyed. Using SPSS 28.0 and Amos 28.0 software, descriptive statistics and structural equation modeling were conducted along with the following types of analyses: reliability, correlation, confirmatory factor, convergent validity, and discriminant. Additionally, the bootstrap method was used to verify serial multiple mediating effects. RESULTS Autonomy-supportive behavior had a significant positive effect 1) on motivational climate, sports competence, and effort and 2) on failure tolerance. 3) Controlling coaching behavior had a significant negative effect on motivational climate and sports competence. 4) Motivational climate and 5) sports competence both had a significant positive effect on effort. 6) Effort had a significant positive effect on failure tolerance. Last, in the relationship between autonomy-supportive behavior and failure tolerance, motivational climate, sports competence, and effort showed partial mediating effects. CONCLUSIONS This study confirms the importance of coaches’ autonomy-supportive behavior in determining failure tolerance among adolescent athletes. Based on this information, counseling (educational) programs aimed at enhancing performance can be developed and provided in sports settings, thus fostering success among athletes.

Purpose: This study was to verify the relationship between coaching behavior(autonomy/controlling behavior), self-regulation motivation and performance. Method: 356 athletes (from middle to work and professional team) in individual and team sport completed coaching behavior scale developed by this researchers assessing autonomy and controlling coaching behavior perceived by players, Korea Basic Pyshoclogical Needs Scale (KBPNS) assessing basic psychological needs, Behavioral Regulation in Sport Questionnaire (BRSQ) assessing sports motivation level based on self-determination theory, and sport performance score. To estimate the relationship between coaching behavior, self-regulation motivation and performance, this study employed the structure equation modeling analysis. Results: The relationship between psychological needs, regulation motivation and performance showed that autonomy coaching behavior tend to reinforce competence and autonomy of player. These variables have a positive effect on more inner regulation motivation. Moreover, the intrinsic motivation through stimulation experience was a key factor leading to a positive performance by improving the performance strategy and skill of athletes. Conclusion: These results are meaningful as an empirical evidence that relationship between motivation and performance can be changed according to the type of coaching behavior, and that autonomous coaching behavior play an important role in maximizing the performance of player that provided theoretically form.


Values, such as development and social responsibilities, are added on victory-oriented Korean sport. Those change of values are along with discussions regarding improvement of players’ training environment, however, discussions on improvement of players’ training environment so far rather focused on ideological concepts, such as players’ holistic human development and human rights, therefore, there was a lack of discussion on practical training methods or teaching methods. This study focused on mental coaching as a specific method for improvement of players’ training environment. Mental coaching provides players with performance enhancement, personal growth, and self-actualization utilizing mental training, consulting, and mentoring in their training processes. This study examined a possibility of introduction of mental coaching as a training camp method for players by creating a training camp reflected on mental coaching perspectives and verifying the program effects of application. First of all, a mental coaching training camp was created through consultations with mental coaches, supervisors, and coaches. Goals of the mental coaching training camp were development of competition-routines, establishment of competition-circumstance coping strategies, comprehension of elite-players’ psychological resources, goal-setting, and motivation and the program consist of badminton competitions, mental education, a special lecture by an Olympic gold medalist, tracking, and sharing. The mental coaching training camp proceeded with middle and highschool badminton players and 31 coaches during three-days and four-nights. As results, the training camp was effective for players’ performance enhancement, personal growth, and self-actualization and team coaches realized a necessity of improvement in terms of their training and teaching behaviors. In other words, mental coaching training camp played a role as a source of long-term change as well as short-term results, thus, this study verified that the mental coaching can be introduced as a training camp method. It is anticipated that this study can provide sport fields and academic sport areas with an opportunity to consider both training contents and methods when it comes to discussion players’ training environment development.



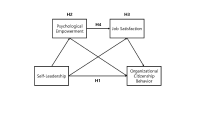
[Purpose] The purpose of this study is to draw practical implications applicable to the field through analysing serial multiple mediator model of self-leadership, psychology empowerment, job satisfaction and organizational citizenship behavior. [Methods] In order to achieve the purpose of this study, we surveyed Korea national league players(187 usable sample). Four hypotheses were tested using frequency analysis, exploratory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis and PROCESS macro through SPSS statistics. [Results] The results are as follows. First, self-leadership has a significant effect on organizational citizenship behavior. Second, mediating effects of psychological empowerment between self-leadership and organizational citizenship behavior were significant. Third, mediating effects of job satisfaction between self-leadership and organizational citizenship behavior were significant. Fourth, serial multiple mediator effects leading to self-leadership→psychological empowerment→job satisfaction→organizational citizenship behavior were significant. [Conclusions] Korea national league players must perform self-leader, goal setting, self-observation, self criticism, constructive thinking strategies, dedication and voluntary attitude for clubs and colleagues. The team’s coaches should strive to praise the athletes for their pride, provide appropriate feedback, prevent job burnout, and the management of front office should make practical efforts such as improving the welfare environment and presenting the future vision of club.


Purpose This study was to explore construct of fear and courage behavior overcoming the fear and relationship between fear and courage in competition. Methods Total 65 national athletes of combat sports(Judo, Boxing, Taekwondo, Fencing) responded to open questionnaire about fear and courage behavior in competition. The data was analyzed by triangle verification and content analysis. Results Firstly, the fear of combat sports athletes consisted of five factors, which were negative consequences, lack of preparation for a game, concerns of performing one’s best, expectation of significant others, and internalized ego threat. Secondly, courage behaviors to overcome fear were self-effort, self-suggestion, self-conviction, selfish self-regulation, social self-control, self-analysis, and acceptance of experience. Finally, there were the relationship between fear and courage in competition. Conclusion These results will contribute to provide useful information for combat sport athletes and coaches in different level to cope with competition fear.

The purpose of this study was to examine psychological capital acquisition through Asian Games Participation. 17 of national women football players were completed Psychological Capitals Questionnair. The psychological capital consists of optimism, psychological skills, self-management, collective efficacy, and performance perception was investigated after the team call-ups and before the team-release. The data was analyzed by paired t-test. As results, Korean women football players’ collective efficient and performance perception showed a statistical significance at the beginning of the team call-ups but optimism, psychological skills, and self-direction did not show statistic significances. The team-harmony, interpersonal-management, team-power, sufficient training, trust in coach, efficient communication, and psychological football factors, which were subfactor of football players’ psychological capital, showed statistical significances. However, confidence, concentration, goal-setting, imagery, willpower, anxiety-control, mental-management, life-management, training-management, innate-behavior management, physical-management, football skills, mediative skills, and football intelligence factors did not have statistic significances. These results demonstrate that effects of mega sporting events-like experiences and psychological factors’ variability and inflexibility according to weather changes should be considered when it comes to discussion of psychological factors regarding players’ performance. It is expected that this study would be a fundamental resource for understanding of psychological influences through participations in mega sporting events and discussions about further psychological interventions for teams with environmental consideration as well as methodological developments which could measure effects of the psychological interventions.