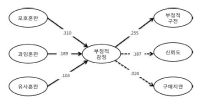
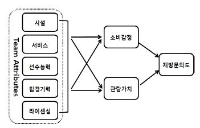
The ever-increasing golf club market made difficult and brought confusion to most of amateur golfers to differentiate and choose suitable clubs for them. Therefore, the purpose of study was to examine how consumer confusion proneness affects consumer’s negative emotion, negative word of mouth, trust and decision postponement, during the process of purchasing golf clubs. 450 questionnaires were distributed to recreational golfers in 6 different golf-driving rages and 4 golf courses located in Seoul, Gyeonggi and Gangwon area with a return rate of 98.4% (n=443). Total of 432 questionnaires were used for data analyses with PASW 18.0 and AMOS 18.0. The results of the study are as follow. First, all of the subordinate factors of consumer confusion proneness had a significant effect on the consumer’s negative emotion. Second, consumer’s negative emotion had a significant effect on negative word of mouth. Third, consumer’s negative emotion had a significant effect on trust. Fourth, consumer’s negative emotion had no significant effect on purchase postponement.

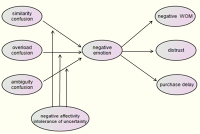
Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify how the three variables of consumer confusion proneness affect consumers' negative emotion, word of mouth, trust and decision postponement during the process of purchasing golf club. Futhermore, this study looked through the moderating effect of the personal characteristics in the relation between consumer confusion proneness and negative emotion. Method A total of 850 questionnaires were used for data analyses(i.e., frequency analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, structural equation modeling) with PASW 18.0 and AMOS 18.0. The results of the study are as follow. Results First, all of the subordinate factors of consumer confusion proneness had a significant effect on the consumer's negative emotion. Second, consumer's negative emotion had a significant effect on negative WOM. Third, consumer's negative emotion had no significant effect on distrust. Fourth, consumer's negative emotion had a significant effect on decision postponement. Fifth, the moderating role of negative effectivity partially had a significant influence in a relation ship between confusion proneness and negative emotion. Sixth, the moderating role of intolerance of uncertainty had a significant influence in a relation ship between confusion proneness and negative emotion. Conclusion The results of this study contributed to provide fundamental information on over all golf industry as in service providing point of view as well as development and application relate to it.

PURPOSE This study aimed to explore methods for stimulating consumer purchasing behavior in the sportswear market, where gaining a competitive edge through traditional means has become increasingly challenging, by focusing on the recently highlighted environmental, social, and governance (ESG) management practices. The objective was to present strategic alternatives for sportswear brands grounded in sustainable management and value creation. METHODS The research employed SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 for frequency analysis, reliability and validity analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, structural equation modeling, and mediation effect analysis. RESULTS First, among the sportswear brand‘s ESG message trust and ESG authenticity, only ESG authenticity positively impacted consumer behavior. Second, both the sportswear brand‘s ESG message trust and ESG authenticity were found to positively influence ESG congruence. Third, ESG message trust and ESG authenticity negatively affected ESG skepticism. Fourth, ESG congruence positively impacted consumer behavior. Fifth, ESG skepticism was found to negatively influence consumer behavior. The mediation effect analysis yielded the following results: First, the direct effect of ESG message trust on consumer behavior was not statistically significant; however, a full mediation effect was observed through ESG congruence and skepticism. Second, the direct effect of ESG authenticity on consumer behavior was statistically significant, with a partial mediation effect through ESG congruence and skepticism. CONCLUSIONS For sportswear brands to achieve sustainable management and profit generation, it is essential to explore methods for stimulating consumer purchasing behavior based on trust and authenticity in ESG messages.
Purpose Sport has become a popular platform for corporate social responsibility (CSR) campaigns. Growing numbers of athletes, teams, and organizations are engaging in CSR campaigns to promote awareness and behaviors to support CSR campaigns addressing pressing social issues (e.g., disease prevention, health promotion, etc.). However, much of the previous work has focused on whether such initiatives benefit the organization, but not the community. The present paper provides theoretical explanations on the psychological mechanism that can demonstrate how consumers respond to CSR campaigns initiated by a sport organization. Method In particular, existing literatures in moral psychology and CSR have been reviewed to identify an explanatory mechanism that promote prosocial behavior among sport consumers. Results The present paper posits that moral emotion is a central processing mechanism explaining the link between CSR and socially responsible behaviors in consumers. The paper also provides a theoretical account to explain how moral emotions are evoked in the CSR context and how they can prompt prosocial behaviors. Conclusion This paper adds to the literature by answering the call for the need to understand underlying mechanisms linking CSR with positive social outcomes (cf. Aguinis & Glavas, 2012).
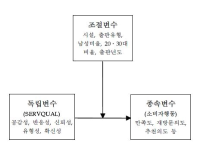
The current study aimed to investigate the impact of SERVQUAL on sport consumer behaviors using meta-analytic techniques. Findings from 25 dissertations and 26 journal articles were used to test of a model of the SERVQUAL on various sport consumer behaviors via the comprehensive meta analysis (CMA) program. Results showed that SERVQUAL has a large effect on sport consumer behaviors, with a fixed effect size of .383. In terms of the relative importance of the SERVQUAL sub-factors, sport consumer behaviors were influenced most by empathy, followed by reliability and tangibles. In predicting sport consumer behaviors, SERVQUAL had a most positive effect on, in order of, loyalty, customer orientation, and commitment. Results also found significant moderating evidence for sport facility types, publication types, publication year, the ratio of male and respondents' age.





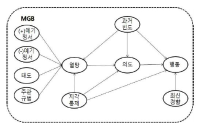
The purpose of this study was to provide managers and owners of Korea professional baseball teams with the necessary information for improving managerial performance by fan acquisition and retention. This paper chose LG, Nexen, and SK fans over the age of 17 as population of this study who visited at least twice home games held in the Jamsil, Mokdong, and Munhak baseball stadium. For the analysis of data, 413 questionnaires were used using SPSS 15.0 Windows and Amos 7.0. To examine respondents demographics traits, frequency analysis was processed and reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis and correlation analysis for relationship among the variables were conducted. Also, convergent validity analysis and discriminant validity analysis were made. Finally, path analysis was made for the verification of model suitability and of research hypotheses through structure equation modeling. The research results are as per the below. First, team attributes like physical facilities, team performance and licensing had significantly positive influence on consumption emotion. Second, team attributes like service and team performance significantly positive impact on viewing value. Third, consumption emotion had significantly positive impact on revisit intention. Fourth, viewing value had significantly positive impact on revisit intention.


PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the underlying dimensions of brand (professional sport team) authenticity and to develop a valid, reliable scale to measure these dimensions. METHODS A pool of 67 potential items was drawn through a literature review, content analysis, qualitative research (n=43), and an expert evaluation. The identified items were subjected to exploratory factor analysis (n=248) and confirmatory factor analysis (n=285). In addition, multiple regressions were conducted to examine the criterion validity of the scale. RESULTS The results showed that the brand authenticity scale for professional sport teams consists of 42 items representing 8 dimensions: continuity, originality, quality commitment, heritage, symbolism, credibility, stakeholder-related integrity, and consumer-related integrity. The study has proven evidences of internal consistency and convergent, discriminant, and criterion validity of the scale. CONCLUSIONS The findings suggest that the scale developed in this study offers a vital foundation to understand the structure of brand authenticity in the context of sport fans and its impact on sport consumer behavior.
The current study aimed to investigate the impact of relationship marketing on sport consumer behaviors using meta-analytic techniques. Findings from 18 dissertations and 17 journal articles were used to test the relationship marketing and various sport consumer behaviors via the comprehensive meta analysis (CMA) program. Results showed that consumer orientation positively affected purchasing behavior of consumer. On the other hand, sport consumer behavior was not influenced by price. The relationship marketing factors had a most positive effect on, in order of, preference, reliability, and satisfaction. Results didn't find significant moderating evidence for sport facility types, publication types, publication year, the ratio of male and respondents'age.





The current study aimed to examine behavioral intentions of online sports products consumers using the Extended Goal-directed Behavior Model. The questionnaires were distributed to consumers who had experience of purchasing sports products online. Data collected from 282 respondents were analyzed mainly using structural equation modeling. The results were as follows: First, attitude and subjective norm had a positive effect on desire. Second, perceived behavior control did not affect desire but had a positive effect on behavior intention. Third, positive anticipated emotions had a positive effect on desire and negative anticipated emotions had a negative effect on desire. Fourth, prior knowledge did not affect desire and behavior intention. Fifth, frequency of past purchase behavior did not affect desire, but had a positive effect on behavior intention. Lastly, desire had a positive effect on behavior intention.




[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to examine acceptance intentions of Sports O2O Service Potential consumers using the revised model of goal-directed behavior. [Methods] The 330 surveys were distributed to potential consumers through convenience sampling method for pilot study. Due to the reliability of data, 42 samples were discarded and 288 samples were put to actual analysis. Then data were analyzed for frequency analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis and structural equation modeling technique via SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 22.0. [Results] The results of this study were as follows. First, attitude and subjective norm had a positive effect on desire. Second, perceived behavior control did not affect on desire but had a positive affect on acceptance intention. Third, positive anticipated emotions had a positive effect on desire but negative anticipated emotions did not effect on desire. Fourth, desire had a effect on acceptance intention. [Conclusions] According to the result, sports O2O service operators should do best to improve consumers positive attitude. Especially, they have to establish marketing strategies of introducing strong aspects of sports O2O services. Also, providing easy processes and intuitive interface are needed to consumers. To promote sports O2O services to potential consumers which is unfamiliar to that services, it is important to induce easy ways for potential consumers to experience sports O2O services.


