PURPOSE This study aimed to develop a model for life skills transfer in sport. METHODS A literature review of research on life skills transfer was conducted. The prior representative studies on sport life skills and transfer models were selected and discussed to improve the validity of this study. RESULTS First, based on the basic psychological needs of the internalization and generalization of life skills, the model for life skills transfer should consider the influence of the explicit and implicit climate and environment. Furthermore, access to cognitive processes is required based on the conceptualization and integration of transfer. Second, the concept of a transfer was defined, and key issues of the cognitive processes that support the connection between the sport domain and out of the sport domain were discussed. Third, the model for life skills transfer in sport was presented. In this model, life skills transfer occur through sport context, cognitive process, promoting factors, and out of sport context. CONCLUSIONS Since the 2000s, research on life skills and transfer in sport has developed quantitatively based on positive youth development theory. Unfortunately, research on this area in South Korea is very insufficient. This study suggests a model for life skills transfer in sport based on an extensive and systematic analysis of the prior research, and this model can be used for future research.
Purpose This study seeks to explore the process where drop-out elite athletes collect their life skills obtained during their sports career and transfer them to their daily lives. Methods An open-ended questionnaire survey was conducted on a total of ninety retired elite athletes and the responses were analyzed. Based on the results of inductive analysis, five subjects were selected for a follow-up in-depth interview. The responses to the open-ended questionnaire were analyzed by the inductive content analysis method and the results from in-depth interviews by the deductive content analysis method. Results A total of 478 life skills were collected from the drop-out elite athletes and structuralized into four general categories: psychological skill, social skill, self-management skill, and goal-setting skill. The results of this study have revealed that life skills positively transferred to their future courses of lives and daily lives. Conclusion It is believed that the results of this study will be helpful to understanding the concept of sports life skills, studying the possibility of transfer, and provide the basic data for helping drop-out elite athletes with re-socialization and positive adaptation.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to verify their effectiveness as we develop and apply worksheets for improving life skills and resilience of collegiate Taekwondo athletes. Methods The study went through three stages: developing, applying, and evaluating. In the developing stage, literature review, expert meeting, and pilot test (n=25) were conducted to develop the worksheets. In the applying stage, 37 athletes participated in life skills program using the worksheets. Data were collected by survey and in-depth interview. In the evaluating stage, paired t-test, word cloud analysis, and inductive content analysis used to identify the effect of worksheets. Results First, the worksheets were composed of 3 stages (plan, acquisition, implementation) and 15 sessions including 12 factors of life skills. Second, the worksheets were applied in each phases such as planning, acquiring, and implementing. In the planning phase, they understood life skills knowledge and set goals. In the acquisition phase, students learned specific life skills’ strategies. In the practice phase, the acquired life skills were applied and practiced in real life and relationships. Third, the result of paired t-test showed that all the factors of life skills and 6 factors of resilience were significantly improved. In addition, word cloud and in-depth interviews revealed that the participants' cognitive and psychological changes were most prominent. Conclusions The life skills worksheets consists of 12 factors in 15 sessions and can be considered as an effective intervention tool for improving the resilience and life skills of collegiate Taekwondo athletes.

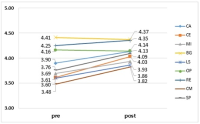









Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a Korean Life Skills Scale for Sports (KLSSS) that original version is the LSSS developed by Cronin and Allen (2017). Methods The subjects were 899 middle school and high school students. The measurement tool was used with LSSS. The validation of KLSSS followed a three-stage of validation procedure; substantive stage, structural stage, and external stage. The result is as follows. Results First, In the substantive stage, KLSSS consisted of 47 items with 8 factors. As a result of the item clarity test, it was confirmed that all the items were appropriate. Second, in the structural stage, KLSSS was explored and confirmed as 5 factors and 18 items. Third, in the external stage, KLSSS showed discrimination and convergent validity. Conclusions KLSSS is composed of 5 factors and 18 items. The factors are teamwork (TW), goal setting (GS), time management (TM), social skills (SS), and leadership (LD). This scale can be used to obtain information on life skills in school physical education or sports.

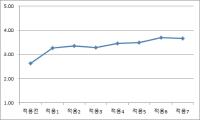
Purpose This study was to investigate the systematic application of the life skills program and its effects in a sport setting. Methods Participants were 14 college students(8 males and 6 females) majoring in Taekwondo. Survey tools were utilized to measure items of life skills and journals. Data analyses were conducted by using Excel program and inductive content analysis. Results First, life skills in this study consisted of goal setting, self-talk, imagery, cognitive restructuring. Life skills program has undergone a procedure, such as the introduction, training, development, application, and evaluation. Second, the average scores of life skill variables have been changed according to measured points. Specifically, the average scores of goal setting and self-talk were highly increased over time and the average score of imagery indicated gradual rising line. The average score of negative thought was slightly reduced over time. Third, regarding effects of this program, participants’ responses were categorized into six components; performance enhancement, positive thoughts, chances of change, goal setting, struggling efforts, and motivation formation. Further, participants stated this program was a great opportunity to develop these components. Conclusion The application of life skills program in sport settings will contribute to participants’ life span developmental change in cognitions, emotions, and behavior.




The purpose of this study was to verify the effect on elementary school students in the exercise start stage by performing a sport psychological skill training to improvement of psychological skill and life skill. Participants were eight elementary school boys volleyball player. The program consisted of psychological skills and life skills in educational counseling model of Visek et al(2009). It was conducted 40-50 minutes a session in total for 22 sessions. Data was collected through a psychological test, worksheet and participant observation, in-depth interviews. The collected data was analyzed to verify difference by paird t-test after pre-middle-post test and to extract meaningful data category. Quantity analysis showed that a result of sport psychological skill test proved a significant difference in willingness to overcome, confidence, concentration, anxiety regulation. Life skill test were no significant differences in all factors. However, the rise of scores was observed on result of the pre-middle paired t-test of life skill during season. Quality analysis showed possibility of goal setting, concentration on the routine, decrease of competitive anxiety, increase of positive thinking, self-understanding and understanding of others, promotion of communication among team members. This sport psychology skill training had a significant effect on the psychological skills of elementary players change. But it seems to be necessary life skills in a more through review of the information.



PURPOSE This study examined the effect of sports life skills and life skills transfer of student-athletes and coaches, applying Actor-Partner Interdependence Model (APIM). METHODS Korean student-athletes and coaches from middle and high school sports teams participated in this study. There were 300 student-athletes (Mage=15.44, SD=1.64; male=218, female=82), with an average of 5.46 (SD=2.40) years of athletic career. Meanwhile, 33 coaches were (Mage=39.70, SD=8.36; male=26, female=7), with an average of 13.52 years of coaching career (SD=10.01). Measures included the Life Skills Scale for Student-Athletes (LSSSA; Jang et al., 2020) and Korean Life Skills Transfer Survey (KLSTS; Lim et al., 2018). Descriptive analysis, correlation, and APIM were undertaken by using the SPSS and AMOS programs. RESULTS First, the correlation between athletes’ and coaches’ life skills was not significant. Second, athletes’ life skills significantly affected their life skills transfer, similar to coaches’ life skills significantly affecting their life skills transfer. Fourth, coaches’ life skills did not significantly influence athletes’ life skills transfer, and the converse was not true either. CONCLUSIONS This study verified the effect of life skills development for two groups of athletes and coaches, on transfer in sports, and attempted statistical verification of whether it affects sports life skills and transfer between athletes and coaches. Although no statistically significant results were found in the partner effect, it is meaningful in that, it provided important implications for conducting a follow-up study on the relationship between athletes and coaches. In other words, it is expected to be a cornerstone for research on building a new model, along with investigating the interactive relations between athletes and coaches on life skills in the sports field.
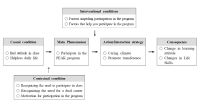
Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the process of participation in the PEAK program of collegiate athletes based on grounded theory. Methods In-depth interviews were conducted with 12 athletes from Y University who were registered in Korea Taekwondo Association. The collected data were analyzed by using the open coding, axis coding, and selective coding of the grounded theory, completed the paradigm model among the extracted concepts, and extracted the core categories through the story outline. Results As the result of data analysis, 'participating in the PEAK program' was found as the central phenomenon, and the causal situation was 'bad attitude in class' and 'helpless daily life'. The contextual conditions were 'recognition of the need for class participation and dual career' and 'motivation to participate in the program', and the intervening conditions were 'factors that hinder participation in the program' and 'factors that help program participation'. The action/interaction strategies were ‘caring climate’ and ‘promoting transfer’, and depending on the consequence, ‘learning attitude change’ and ‘life skill change’ appeared. Conclusion Participants improved their learning attitude through the PEAK program and confirmed the possibility of life skills transfer. It is hoped that this study can lead to implementation of various studies and discussions about life skills and transfer.

PURPOSE This study aimed to apply a capacity building program to sport life skill leaders and to provide cases of this process. METHODS The study participants included four leaders (male=2, female= 2, Mage=37.5) who were managing a sport life skills program at a university. They participated in a capacity building program, which consisted of (a) understanding (leader seminar), (b) application (managing the sport life skills program), and (c) evaluation (leader’s self-reflection), which were conducted in eight sessions. Four leaders conducted self-evaluations using program quality assessment (PQA) during every session, and quantitative and qualitative data were collected. Qualitative data were derived using a cross-case analysis, and quantitative data were used for calculating the effect size after performing the paired t-test. RESULTS Analyzing the reported cases of sport life skill leaders, the use value of the capacity building program was identified. Furthermore, the cases reported by the four leaders enabled observation of how the leader’s capabilities were strengthened. In the paired t-test, the effect size of physical and psychological safety, appropriate structure, supportive relationship, opportunities to belong, support for efficacy mattering, opportunities for life skill building, excluding integration of family, school, and community effort, were all significant. All effect sizes were found to have “very large effects.” CONCLUSIONS The capacity building program played a positive role in strengthening the leaders’ life skill coaching capabilities. These findings have practical implications—chiefly, it is important to strengthen leaders’ or coaches’ capabilities in order to foster life skill development and transfer of student-athletes.
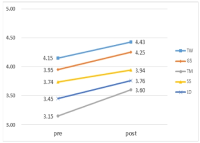
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to apply a life skills program to student-athletes and statistically verify the changes in life skills of the experimental and control group. METHODS Participants were 34 high school Taekwondo athletes (Mage=17.71). They were divided into 18 in the experimental group and 16 in the control group. For eight weeks, the experimental group participated in the life skills program after training and the control group participated in only training as usual. Data were collected by using Life Skills Scale for Student-Athletes (LSSSA), and the participants of two groups filled out the LSSSA before and after the program application. The collected data were analyzed by using repeated measure analysis of variance (ANOVA), and partial η2 (eta squared) was calculated to present the effect size. RESULTS The interaction between time and group was statistically significant in goal setting, coping with stress, positive thinking, and managing emotion among sub-factors of life skills. Partial η2 was interpreted as having a large effect size as it revealed the range of .22 to .51. Therefore, comparing before and after participating in the program, the life skills score of the experimental group among the two groups was significantly improved. CONCLUSIONS Student-athletes who participated in the program experienced positive changes in life skills than those who did not participate in the program.