PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to develop the estimating equations for 4 types of Wingate Anaerobic test setting. METHODS 80 male elite athletes performed 4 trials of the Wingate Anaerobic test by each type. Subjects were conducted the retest one week later. Data collected from the Wingate Anaerobic test included mean power, peak power, and power drop for 30s were measured. Coefficient of correlation was used for validity of type 1(DOS version) and the other types(ver. 2.24, 3.3.0, and 3.2.1). Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to examine the reliability of test and retest. Simple regression analysis was used for calculating the estimating equation. RESULTS There was significant correlation for absolute value(Watt, p<.01) and relative value(Watt/kg, p<.01) of mean power, absolute value(W, p<.01), relative value(Watt/kg, p<.05), and power drop rate(%, p<.01). Test and retest reliability was excellent for all test variables(p<.01). CONCLUSIONS From the all results, the estimating equation was calculated to convert all outputs from each type to the other types of the Wingate Anaerobic test setting. These findings suggest that the estimating equations are compatiable to 4 types of Wingate Anaerobic test setting.
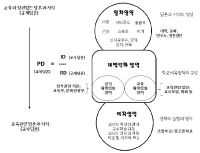
Drawing on Bernstein theory (1990, 1996) of pedagogic discourse, this study is aimed at exploring the construction of pedagogical meaning in physical education policy in Korea and providing critical implications for the development of policies for physical education and school sport. Both open-ended questionnaires (n=22) and in-depth interviews (n=9) were conducted. The collected data was commissioned by an inductive data analysis to look at patterns of regulative discourses embedded with physical education policy influencing on teachers’ educational practice. This study identified three main discourses constructing and constituting policies; sport, moral, and health. Sport discourse was the most dominant through the policy, in which two sub-discourses were central: ‘competition’ and ‘exclusion.’ Moral discourse had a strong connection with ‘crime reduction’ and ‘academic achievement.’ The structure of health discourse alleged increase in youth physical inactivity associated with sedentary living leads to an obesity epidemic. This study argued that there were significant dangers which dominant regulative discourses created a limited universe of possibilities for physical education. Therefore, we must not lose sight of the powerful discourses produced in the primary field, which have an impact on shaping forms of policy and practice in physical education. Furthermore, we need to examine in detail forms of physical education practice in order to achieve alignment in the school practice with current dominant discourses.

PURPOSE This study investigated the correlation between anaerobic power and maximum muscle strength in relation to core muscle strength among Korean national golfers. METHODS A total of 96 national golfers (53 females and 43 males) participated in the study. Body composition was assessed using multi-frequency impedance devices, while core and lower extremity muscle strength (extension, flexion, flex/ex ratio) was measured using isokinetic strength tests. Anaerobic power was evaluated through peak power, average power, and power drop rate tests conducted on bicycle ergometers, along with one-repetition maximum (1RM) tests for squats and bench presses. Mean and standard deviation values were calculated for all variables, and linear regression analysis was performed to verify correlations, with statistical significance set at α=.05. RESULTS The comparison of physical characteristics between male and female national golfers revealed significant differences in age, height, body fat percentage, lean body mass, and weight. There was a strong correlation between core muscle strength and isokinetic lower extremity muscle strength. Additionally, a strong correlation was observed between core muscle strength and anaerobic power and between peak power and average power. Furthermore, there was a high correlation between core muscle strength and bench press and squat maximum muscle strength. CONCLUSIONS This study highlights the correlation between various professional physical fitness variables of Korean national golfers over the past decade. The findings are expected to provide valuable insights for coaches and players in developing future training programs.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to find out the physical characteristics of Wushu athletes by comparing the differences on the results of physical fitness between the male athletes of the Wushu national team Taolu and the Sanda group. Methods Measurement of basic and professional fitness based on muscle function, targeting 37 men Wushu national team players (24 taolu, 13 Sanda) in the selection and evaluation contests twice in 2018 and 2019. Body composition, isometric muscle strength, flexibility and equilibrium, anaerobic power, and isokinetic muscle strength. The fitness factors were divided into two groups, Taolu and Sanda. Results First, body fat rate of the Sanda athlete group was significantly lower than that of the taolu athlete group (p<.01). Second, in the isometric muscle strength category(back muscle strength, grip strength), the Sanda athlete group had higher muscle strength than Taolu athlete group, but there was a statistically significant difference only in the left grip strength (p<.01). Third, in terms of flexibility and equilibrium, the taolu players were significantly higher in all items(p<.001). Fourth, in the anaerobic power, the taolu athlete group had higher both the peak power and the mean power, and there were a significant differences(peak power: p<.01, mean power: p<.001). Fifth, isokinetic muscle strength was significantly higher in the right knee flexion of the taolu athlete group (p<.01), and lumbar extensor muscle was significantly higher in the Sanda athlete group (p<.05). Sixth, in the isokinetic strength ratio, the knee flexion ratio of the Sanda athlete group were significantly higher on the left and right knee flexion and extensor ratios (p<.05). In addition, in the lumbar flexor and extensor ratios, the group of Sanda athlete group were significantly higher on the lumbar extensor(p<.05). Seventh, there was no significant difference between two groups in isokinetic muscle power. Conclusions The results of this study can be used as basic data to improve the efficiency of technical and physical training through the analysis of the characteristics of Taolu and Sanda. The effectiveness of this training will help to improve the performance.
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect on Electro-chemical screen and anaerobic exercise capacity caused by short-term weight loss in amateur boxing players. Subjects of this study were 10 male university boxing player who conducted to weight loss methods. In 1st weight loss, boxing players took rapid weight loss during 5-7days, In 2nd weight loss, boxing players took weight loss 3kg during 2 weeks. The change of ECS and anaerobic exercise capacity were measured before and after weight loss period. Anaerobic exercise capacity was measured by 1RM of bench press and squat. In addition, using the wing-gate test muscle power and power endurance was evaluated. To find out the changes in ECS, urine and saliva was collected after waking up were analyzed. The results were as follow. First, 1RM of squat(p=.003), peak power(p=.023) and mean power(p=.015) showed significant decrease after 1st weight loss method. However in 2nd weight loss method, no factor of ECS and anaerobic exercise capacity were significantly decreased. Second, total urea(p=.015), urine rH2(p=.017), urine conductivity(p=.003), and utilization of vitamin(p=.005) showed significant decrease after 1st weight loss method. However in 2nd weight loss method, urine conductivity(p=.038) and saliva rH2(p=.028) showed significant increase after weight loss. In conclusion, amateur boxing players need a systematic weight loss to maintain optimal conditioning.

[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to investigate the process of Jang Changsun’s winning gold medal in the 1966 Toledo World Amateur Wrestling Championship and its meaning. [Methods] Jang Changsun and Katsumura Yasuo who had competed with Jang Changsun for the gold medal were selected as participants, a player and an executive who had participated in the Championship were selected as informants. Data had been collected by in-depth interview were analyzed firstly by using the Patton(1991)’s data analysis method, and the following conclusions were obtained by comparing with preceding studies, press releases, reports etc. [Results] Jang Changsun won a gold medal through the three stages of desperate struggles. The first struggle was to loose weight. Jang Changsun lost three times more weight than other players through fasting treatment, intensive training and dehydration in order to secure an advantageous position in the competition. His second struggle was the sparring itself. He made his mind to win gold medal 2 years before the Championship and started to strengthen his physical fitness and polish up his techniques to fight with strong players from powerful nation of wrestling. He finished the sparring by winning 4 games and tieing 2 games resulting in the same deduction points with Katsumura. It was inevitable for him to fight desperately to lose weight again to get gold medal. He eventually won the gold medal by losing his weight until he fainted because of injuries and serious dehydration. [Conclusion] The first gold medalist Jang Changsun contributed a lot to development of Korean sports by offering chance to consider significance of improving elite player’s exercising environment, scientific coaching, gaining self-confidence to win medal, and realizing the importance of sports informations.

