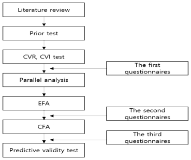
The purpose of this study was to develop an instrument that measures participantsʼ satisfaction in sports instructor training programs. The instrument development process includes focus group interviews, parallel analysis, and validity and reliability tests. Data were collected from 897 participants from three regular training sessions and were analyzed primarily using SPSS and MPlus software. The results indicated that the service satisfaction of sport instructor programs has an underlying three sub-factors, including ʻadministrative supportʼ, ʻcurriculum contentsʼ, and ʻlearning environmentʼ. This study can provide helpful information to managers in improving their respective sport instructor training programs.


PURPOSE This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the effectiveness of exercise programs in improving physical fitness among middle-aged adults in Korea. METHODS A literature search was conducted using KCI-registered databases on DBpia, RISS, and KISS up to September 21, 2023. The review followed the PICOSD framework (population: middle-aged adults; intervention: exercise program; comparison: did not participate in exercise program; outcome: physical fitness; study design: randomized controlled trials). Two researchers independently evaluated bias using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2). The data was synthesized using the CMA 3.0 program, applying a random effects model to estimate the overall effect size using Hedges’g. RESULTS Out of 914 screened documents, 15 studies were selected, comprising 405 participants. The overall effect size for improving physical fitness was significant (g=0.994, 95% CI: 0.712–1.276). Sub-analysis indicated significant improvements in various components, including muscle strength (g=1.295, 95% CI: 0.909-1.682), muscular endurance (g=0.972, 95% CI: 0.637-1.308), cardiorespiratory endurance (g=1.092, 95% CI: 0.453–1.731), flexibility (g=0.883, 95% CI: 0.555–1.210), muscle power (g=1.421, 95% CI: 0.656– 2.186), and agility (g=1.854, 95% CI: 0.347–3.361) compared to the control group. An additional analysis focusing solely on women revealed a slight increase in effect size, although the order of effect sizes remained consistent across fitness components. CONCLUSIONS This meta-analysis confirms the effectiveness of exercise programs in enhancing physical fitness in middle-aged adults. The systematic review also highlights key considerations for designing exercise programs for this demographic. Future studies should aim to minimize bias and enhance the quality of reporting to ensure more robust results.
[Purpose] The present study attempted to verify the effectiveness of an early childhood physical health improvement program (subsequently in the present study, KICCE Early Childhood Health Improvement Program) developed in Korea by modifying and improving the Mission-X: Train Like an Astronaut program developed by NASA to be suitable for children of ages 4 and 5. [Methods] The subjects in the study were 679 children at 7 facilities in Seongnam city, Osan city, and Yongin city, of which 4 were daycares and 3 were kindergartens. The participant group consisted of 339 children, and the control group consisted of 340 children. The program consisted of total 24 activities 3 times a week over 8 weeks, of which 8 activities were related to nutrition and 16 activities were related to physical activity, and in the 9th and 10th weeks, the 16 physical activities were reconfigured and performed 3 times a week. Physical parameters and related fitness parameters were measured before and after the program, and an ANCOVA analysis was performed in which descriptive statistics and scores before the program were the covariate variables. [Results] The results show that first, growth statuses of participant children were in the upper middle section of the distribution, and second, of the 6 fitness developments, flexibility, balance, and quickness were improved, and in most areas, boys and below-normal-BMI group showed beneficial effects. [Conclusion] Thus, KICCE Early Childhood Health Improvement Program is conclusively proven to be effective for early-childhood physical development.
PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the factors influencing the success of the sports entertainment program “A Clean Sweep” using big data analysis. METHODS Text mining, sentiment analysis, TF-IDF, connection centrality, and semantic network analysis were conducted using the social big data analysis program Textom and social network analysis program Ucinet6. The research period was limited from June 6, 2022 to November 30, 2023. RESULTS The factors determining success were entertainment programs, Monday, OTT, and independent league. The events and marketing factors were extracted, and A Clean Sweep X Kelly, A Clean Sweep X Mom love, cheering song, uniforms, and direct viewing day influenced success. The new hire factors were rookie draft, Young-Mook Hwang, Sung-Joon Won, and Hyun-Soo Jeong. Positive (such as good, fun, looking forward to, best, and funny) and negative (such as esoteric, regrettable, shocking, dislike, and uncomfortable) emotional factors were also extracted. The extracted star marketing factors were directors (Seung-Yup Lee, Sung-Geun Kim) and players (Dae-Ho Lee, Geun-Woo Jung, Hee-Kwan Yoo, Moon-Ho Kim, Yong-Taek Park, Taek-Geun Lee). CONCLUSIONS We were able to identify the success factors of “A Clean Sweep”, which we hope will contribute to the revitalization of professional baseball as well as sports entertainment programs.
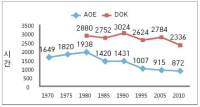
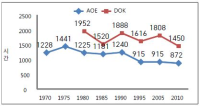
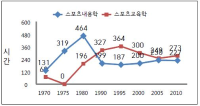
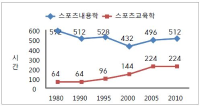
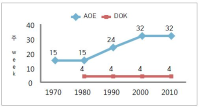
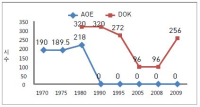
The aim of this study is to examine the directions of Physical Education Teacher Education (PETE) programs in Korea through the historical changes of each one PETE institute in England and Korea from the 1970s to 2010s based on academicisation. Document analysis and grounded theory were used to analyse historical sources and interviews. I identify four findings. First, the amounts of hours in curricula in both PETE courses have been reduced. Second, discipline knowledge in England was a first priority in the 1970s but has urgently reduced since the 1980s because of the growth and adoption of sport pedagogy. In Korea, discipline knowledge has still kept as a first priority for 40 years. However, professional knowledge in Korea has increased to enhance PETE since the middle of 2000s. Third, teaching experiences in England has increased by nearly double from 15 weeks to 32 weeks. In Korea, student have, and continue to participate in only four weeks of teaching experience. Fourth, education studies in England abolished in the 1990s. In Korea, they urgently increased in 2009. I conclude by confirming the need to study a structure and content of units of discipline knowledge and professional knowledge. I propose a system for selection of majors in the Department of Physical Education.


Researchers and teachers in physical education have emphasized sportsmenship in sport education setting. However, how to teach sportsmenship in physical education is not proposed yet. The purpose of this study was (1) to develop an instructional program for teaching and learning sportsmanship and (2) to examine its effects on sportsmenship. Participants were 7th middle school students(N=95). Data were collected using Sportsmanship Test(Park, 2014), open-ended questionnaire and in-depth interviews with students. The data were analyzed through paired samples t-test and qualitative content analysis. Results showed that significant difference was observed in students' sportsmanship test scores after instruction. Analysis of interview data showed that students experience the value of utmost effort, respect for opponents, respect for teammates, acknowledging results, respect for judgment, and valuable lessons related to character education. Implications for sportsmanship education using instructional program were discussed.



PURPOSE This study developed and applied a group counseling program for university athletes’ career development. METHODS Following Kim’s (2002) procedure for developing group counseling, this program was based on social cognitive career theory and finalized by using two preliminary studies and expert validation evaluation. Afterward, Taekwondo players from University A in Chungcheongnam-do and University B in Seoul were assigned to experimental and control groups, respectively, and then a nonequivalent control group design was conducted. The experimental group was provided with a six-step career group counseling program, including introduction, understanding personal and distal context, enhancing self-efficacy and outcome expectations, developing career interest, deciding on a career, and closing, for ten 45-minute sessions, twice a week. RESULTS First, results of two-way repeated measures ANOVA showed statistically significant changes in career decision self-efficacy (self-appraisal, occupational information, goal selection, planning, and problem-solving) and career attitude maturity (determination, certainty, and independence). Second, analysis of the outcome assessment by session showed the following positive results: consideration about the future after sports retirement, self-understanding, identification of jobs that fit aptitude, improvement of self-efficacy, having a positive mindset when switching careers, confidence in one’s preferred career, exploration into solutions to career barriers, understanding of preferred career, setting specific career goals, and deeper understanding of careers. CONCLUSIONS In sum, these findings indicate that the career counseling program had a positive effect on university athletes’ career development. We hope this study will serve as a catalyst to expand the discussion on retirement from sports and career development.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to explore the effects of the student-athlete and student peer mentoring program as a collegiate class. METHODS The peer mentoring program, conducted at A University in the first semester of the 2023 school year, was evaluated using practical action research (Zuber-Skeritt, 1996). RESULTS In the introduction stage, ‘relative and absolute evaluation’, ‘member ratio’, and ‘definition of professor role’ were categorized as challenge issues. In the progress stage, ‘de-formalized lecture method’, ‘student athlete’s coaching experience’, and ‘student’s experience of football culture’ were discovered as possibilities, while ‘vacancy and absence of mentor-mentee’, ‘limited group activities and limitations of team sports’, and ‘lack of objective evaluation’ required improvement. At the end stage, student-athletes experienced changes in values such as self-identity, football, and human relationships, as well as quantitative and qualitative changes in sports participation. CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the potential of the peer mentoring program as a collegiate class as well as its practical significance for guaranteeing student-athletes' learning rights and for forming sports culture on collegiate campuses.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to develop a non-face-to-face self-regulation training program for middle and high school student-athletes through the conduct of a group online video counseling session, as well as to verify the effectiveness of such a tool. METHODS Based on the models of Zimmerman(2000) and Han Si-wan (2008), the 12-session non-face-to-face self-regulation training program consisting of interactions involving cognitive, emotional, and behavioral factors was developed and used on a 16-member experimental group. Additionally, self-regulation and mental toughness questionnaires were given to each member before and after the program, and the results were compared with the results of a 17-member control group. Since a qualitative evaluation was conducted, recorded training contents were organized into a text file; after which, a step-by-step coding procedure was performed, and then meanings and themes were identified and categorized. RESULTS Quantitative analysis found that the volitional inhibition mode of the control group decreased significantly; this was in comparison to the increase in the self-regulation mode of the experimental group. In addition, among the seven sub-factors of the mental strength test of the experimental group, a significant increase was found in the post-test of self-belief, attention control, emotional regulation, resilience, and optimism factors. As a result of qualitative data analysis, they complained of difficulties in the early stages of participation, but gradually recognized their problems and searched for changes, showed changes in cognition, emotion, and behavior as they approached the end of the study period. CONCLUSIONS It can be said that the non-face-to-face self-regulation training program helped student athletes improve their school life and performance by driving positive cognitive, emotional, and behavioral changes.
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop a positive psychological intervention program for a college ice hockey team and test its effects based on application to the team. METHODS The demands of 78 college ice hockey players were asked through open questionnaires. Collected results underwent integrated analysis to develop the desired program through the participants who were also observers of the team. The objectives of the program were established, and an appropriate program was developed based on the analyzed data, expert opinion, and precedent research. The developed program was applied to 26 players of a college ice hockey team to verify its effects. Tasks included writing experience reports and in-depth interviews. The Happiness Measures 1, Strength Knowledge, and Team Interaction Questionnaires were also administered. Collected qualitative data were categorized to follow inductive analysis procedures, while paired t-tests were performed for quantitative data using SPSS 25.0. RESULTS To improve the application of the program in real situations and maintain credibility and validity, the program was developed based on analyses of individual and team demands, methods of the participant as an observer, expert opinion, and other considerations. Statistically meaningful differences in positive psychological mind, happiness, recognition and utilization of strengths, team interactions, team cohesion, and so on were found using paired t-tests comparing data before and after the developed positive psychological intervention program. CONCLUSIONS Providing opportunities to recognize individual and team strengths and have valuable experiences for each player could enhance interactions between teammates and create a favorable team environment.