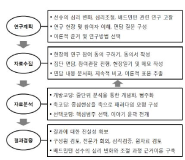
The purpose of this study was to describe psychological changes and variables of injured elite athletes during sport injury rehabilitation. 5 injured elite athletes were selected as participants, and open-ended questionnaires, participant observation, and in-depth interview were used for collecting data. Results from the data were analyzed through transcription, coding, and categorization with inductive method. To validate the results of this study, triangulation, in-depth description, member checks, and peer debriefing were used, and findings of this study were as follow. The participants showed negative psychological state such as fear of return to play and anxiety during the initial rehabilitation program, but their psychological state was changed positively such as recovery of confidence and desire of return to play at the end of program. However, the specific psychological changes of each participant showed several differences according to participant's surrounding environment and situation during the rehabilitation program. All findings have important implications for implementing and developing rehabilitation program, so needs to be investigated further.
This study was purposed to explore psychological change and regulation process during badminton competition. The data were conducted using group interviews and participation observations who 18 K college badminton players. The data were analyzed using open, axial, and selective coding based on grounded theory method (Strauss & Corbin, 1998). The results were as follows: Open coding results, 89 concepts, 44 subcategories, and 18 categories emerged as psychological change and regulation process during badminton competitions. Axial coding results, the categories are showed structural relationships such as performance, score, psychological momentum, the importance of competition, court environment, physical condition, competition strategy, psychological preparation, past experience, outcome expectation, psychological disturbance, psychological skills, game situation-changing strategy, support-seeking strategy, significant others' behavior, the opponents' behavior, psychological resilience, and maintenance psychological disturbance. Selective coding results, core category of this study was revealed to maintain psychological homeostasis. Environmental context during badminton competitions causes specific situations and events that evoke psychological disturbance. In turn, a player seeks mental and behavioral strategies to maintain psychological homeostasis. There is psychological homeostasis mechanism during badminton competitions for peak performance. Development of proper interest for psychological homeostasis will be improved through this research approach in sport psychology.

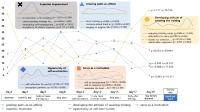
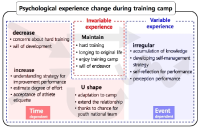
Purpose The current study aimed to identify national youth cyclist`s experience and change tendency of experience during camp training. Methods A total of 35 cyclists who participated in 2017 Korea youth national cycling camp training provided the data. The survey was conducted 9 times during the 20 days of camp training using open-ended questionnaire by diary method. The collected data were analyzed based on inductive categorization and response rates. This study was conducted in the order of formation rapport, data collection, and data analysis. Results Youth cyclists experiences during camp training to growing pains as an athlete, developing the attitude of savoring training, serve as a motivation, expertise formation and opportunity of self-examination. Based on the change in response frequency of the survey data, camp training experience falls into two categories: variable and invariable. Conclusions Youth national cyclist were growing their growth power through various experiences during the training camp, and these experiences changed to specific inflection points from the beginning to the end of the camp. Understanding changes in psychological experience can provide the design of timely psychological support and coaching method. This study will be used as a material for the design of the camp training program for the youth cyclist, as well as an opportunity to increase the interest of continuity reflection on the psychological experience.

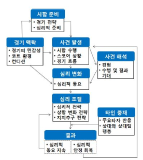
The purpose of this study was to conduct an in-depth exploration of Korean national badminton players’ psychological momentum strategies. Data were collected using an open-ended questionnaire and group interviews of 66 badminton players, including 40 members of the 2018 Korean national badminton team and 22 college and semi-pro badminton players who each had badminton careers of 10 or more years and were registered in the Badminton Korea Association. The data were analyzed using inductive content analysis and the deductive process based on the inductively categorized results. The results are as follows. First, regarding strategies for maintaining positive momentum, 188 raw data were collected and classified into three category (keeping pace, dominating the play, and psychological facilitation) and 10 sub-category (including speedy resumption of the game, attacking weak points, and fighting shout). The results suggest that badminton players maintain positive momentum by using strategies to control the speed and tempo of the game at their preferred pace, implement special techniques, exploit their opponent’s weaknesses, and cheer or talk amongst themselves to motivate each other and communicate with their partners and coaches. Second, regarding strategies for overcoming negative momentum, 293 raw data points were collected and classified into three category (time outs, psychological reminders, and changes in plays) and 11 sub-category (including delaying the game, seeking social support, and play change). The data demonstrate that badminton players overcome negative momentum using strategies to intentionally delay the game and exchange equipment, focus on performance cues, and interact with their coaches and partners to change plays and prevent errors. It is hoped that these study findings will inform efforts to provide psychological support that is effective in increasing the odds of winning for the national badminton players in the Asian Games and the Olympic.

The purpose of this study was to verify the effect on elementary school students in the exercise start stage by performing a sport psychological skill training to improvement of psychological skill and life skill. Participants were eight elementary school boys volleyball player. The program consisted of psychological skills and life skills in educational counseling model of Visek et al(2009). It was conducted 40-50 minutes a session in total for 22 sessions. Data was collected through a psychological test, worksheet and participant observation, in-depth interviews. The collected data was analyzed to verify difference by paird t-test after pre-middle-post test and to extract meaningful data category. Quantity analysis showed that a result of sport psychological skill test proved a significant difference in willingness to overcome, confidence, concentration, anxiety regulation. Life skill test were no significant differences in all factors. However, the rise of scores was observed on result of the pre-middle paired t-test of life skill during season. Quality analysis showed possibility of goal setting, concentration on the routine, decrease of competitive anxiety, increase of positive thinking, self-understanding and understanding of others, promotion of communication among team members. This sport psychology skill training had a significant effect on the psychological skills of elementary players change. But it seems to be necessary life skills in a more through review of the information.



PURPOSE This study aimed to understand the changes in the exercise behavior of participants in the exercise-psychological counseling program. METHODS This study sampled adult female participants of C diet camp in Seoul, who were in stages 2~3 of the “Stages of Change Model.” A total of 60 participants were randomly assigned to the counseling group (n=30) and control group (n=30). During the 12 weeks of study, all subjects participated in the diet camp program C. The counseling group participated in the exercise psychological counseling program once a week, while the control group participated in recreational activities instead. Exercise adherence, outcome-expectancy, and satisfaction were measured once every four weeks. Latent growth models were used to analyze the measured data. RESULTS Exercise adherence, outcome-expectancy, and satisfaction in the counseling group exerted a statistically significant positive effect. A statistically significant positive effect on the change of exercise adherence variable was observed in the control group, but the trend was only 1/4 of that of the counseling group. In the control group, exercise outcome-expectancy and exercise satisfaction did not have a statistically significant outcome. CONCLUSIONS The exercise counseling program is an essential intervention strategy that enhances participants’ exercise adherence, outcome-expectancy, and satisfaction. Therefore, a positive change in exercise behaviors occurs.
PURPOSE This study explored psychological experiences in long jump competitions and examined the continuity of psychological experiences over time. METHODS A total of 28 adult long jumpers, 18 men and 10 women, were provided data through in-depth interviews. Data on psychological experiences were extraced through inductive content analysis, while continuity by period was analyzed by calculating the response frequency ratio using Excel. RESULTS First, the psychological experience in the long jump competition was categorized as fundamental, competition intelligence, emotional control, and communication capacity experience. Second, in long jump competitions, results showed that jumpers experienced mixed feelings of anxiety and pressure, self-confidence, and concentration in the first period; peer communication and analysis thinking were necessary in the second period; practical intelligence and pressure control were important in the third period; learning ability and creativity were crucial in the fourth period; learning ability and coach communication were applied in the fifth period; and fighting spirit and creativity were present in the sixth period. Third, the psychological experience of long jumpers by period, basicphysical strength was maintained; competition intelligence increased in the second and fourth periods; communication skills increased until the fifth period, and decreased after; while emotional control decreased. This reflects the contextual changes over time andthe change in competition records owing to that. CONCLUSIONS In the long jump competition, psychological experience changes by period and affects competition records. This study will contribute to further understanding of psychological continuity.
This study conducted to explore K-League (Korea Professional Football League) referees’ psychological experience and coping strategies just after the moment of wrong judgment. Open-ended questionnaire were conducted on 35 full-time referees who participated in the K-League winter training camp. The data were categorized by inductive content analysis. The results were as follows. Psychological experience yielded 45 raw data points, which were based on the following 10 sub categories; increased anxiety, rumination wrong judgment, concern about reprimand, and feeling apologetic; and four general categories including, psychological fragmentation, feeling helpless, concern about reputation, and acknowledgment of wrong judgment. Thus, K-league referees experience a psychological turbulence just after the moment of the bad calls and worsen feelings of helplessness about the wrong decisions. Also, K-league referees worry about further disadvantages following the misjudgement and admit their bad calls feeling sorry for teams and athletes who were in the incidents. Coping strategies yielded 55 raw data points from which the following categories were identified 11 sub categories; increasing concentration, attempting to forget wrong judgment, apologizing on wrong judgment, and change in thinking; and four general categories including, emotional self-support, avoiding situation, correcting the error and thinking, and changing of refereeing approach. Therefore, K-league referees enhance their concentration in order to not reoccur wrong judgement after the moment of the mistakes and try to forget the incidents of wrong judgement. Also, K-league referees apology to the teams and athletes who experienced the bad calls and make efforts to correct the mistakes if possible. Moreover, K-league referees try to modify a criteria of judgement in order to manage aftereffects of wrong judgement and make decisions correctly by approaching the scenes of the wrong judgement. The study emphasizes the importance of referee psychological stability on the field and the need for psychological support. The study is expected to encourage further research on sports referees in Korea to ensure they receive appropriate psychological support.
The purpose of this study was to examine psychological capital acquisition through Asian Games Participation. 17 of national women football players were completed Psychological Capitals Questionnair. The psychological capital consists of optimism, psychological skills, self-management, collective efficacy, and performance perception was investigated after the team call-ups and before the team-release. The data was analyzed by paired t-test. As results, Korean women football players’ collective efficient and performance perception showed a statistical significance at the beginning of the team call-ups but optimism, psychological skills, and self-direction did not show statistic significances. The team-harmony, interpersonal-management, team-power, sufficient training, trust in coach, efficient communication, and psychological football factors, which were subfactor of football players’ psychological capital, showed statistical significances. However, confidence, concentration, goal-setting, imagery, willpower, anxiety-control, mental-management, life-management, training-management, innate-behavior management, physical-management, football skills, mediative skills, and football intelligence factors did not have statistic significances. These results demonstrate that effects of mega sporting events-like experiences and psychological factors’ variability and inflexibility according to weather changes should be considered when it comes to discussion of psychological factors regarding players’ performance. It is expected that this study would be a fundamental resource for understanding of psychological influences through participations in mega sporting events and discussions about further psychological interventions for teams with environmental consideration as well as methodological developments which could measure effects of the psychological interventions.
PURPOSE This study compares the effects of video group and metaverse group counseling for student athletes to analyze differences in immersion, sychological skills learning effects, and each approach’s participation experiences. METHODS Twenty-four high school archery students were divided into three groups: a metaverse experimental, a video comparison, and a control group. For the experimental and comparative groups, 10 non-face-to-face psychological skills training sessions were conducted. With the control group, results were compared and analyzed by measuring psychological skills and social presence pre- and post-training. Additionally, analysis of the qualitative effects of psychological skills training was performed. RESULTS The psychological skill test’s quantitative analysis of the video comparison group showed a more significant effect in anxiety control factors than the metaverse experimental and the control groups. Moreover, in the social presence test, both the metaverse and the video groups showed significant differences in social presence and satisfaction; furthermore, Scheff post-verification results showed that the two environments’ satisfaction was significantly higher than that of the control group. Qualitative analysis confirmed that the metaverse and video groups experienced psychological, technical, and relational changes in common. CONCLUSIONS Although the metaverse group using avatars was likely to increase immersion, both the video and the metaverse groups were effective in psychological skills training, suggesting that the training effect may vary depending on the non- face-to-face environment’s stability and participation method. Future studies should examine effects of applying the metaverse platform to sports psychological skills training and various psychological support activities by solving the metaverse environment’s technical limitations.