PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of COVID-19 on elite youth athletes by investigating their activities and eating habits before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. METHODS This study included 917 elite adult athletes from 19 sports and were grouped into 6. The questionnaire included items regarding demographics, physical activity, sleep, and eating habits before and after COVID-19. A total of 44 questions requiring subjective short answers were included. Statistical significance was set at p< 0.05. RESULTS After COVID-19, vigorous and moderate activity decreased across all sports; however, light activity increased in almost sports. Time spent sitting increased across all sports. The difference in the number of meals consumed varied among sports, and the number of competitions decreased in all sports. CONCLUSIONS The COVID-19 pandemic appears to be finished but has not ended yet. Athletes must determine the best way to maintain their physical, physiological, and psychological states close to their original abilities. Determining this will provide the greatest impact on the return of athletes after COVID-19; this study will be helpful.
Purpose This study focuses on accessibility to sports facilities that can be classified into structural leisure constraints. The purpose of this study is to explore exploratory analysis of the types of reservation methods and payment methods, which are the initial stages of consuming sports facilities, and to explore inconveniences that consumers feel when making reservations. Methods A quantitative research method was used to derive the results, and data were collected through a questionnaire survey method. The collected data were analyzed by technical statistics focusing on the reservation method, payment method, and inconvenience during reservation. Results As a result, it was found that the main types of reservation methods and payment methods were homepage, homepage/telephone, telephone, homepage/app, and account transfer and card payment, respectively. In the case of inconvenience, the procedure was complicated, address and location, and reservation method were identified as the main matters. Conclusions Efforts must be made to secure both the convenience and publicity of accessibility at an early stage, such as reservation methods and payment methods for sports facilities.
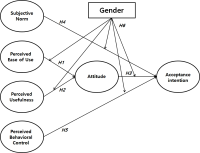
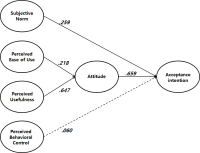
Purpose The current study was aimed to examine acceptance intention of sports wearable smart device using the Technology Acceptance Model and Theory of Planned Behavior. Methods Data were drawn from 357 consumers who had experience purchasing sports products. Data were analyzed through frequency analysis, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling using SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 program. Results First, perceived ease of use had a positive effect on attitude. Second, perceived usefulness had a positive effect on attitude. Third, attitude had a positive effect on acceptance intention. Fourth, subjective norm had a positive effect on acceptance intention. Fifth, perceived behavioral control did not affect acceptance intention. Sixth, differences of path coefficients between attitude and acceptance intention, subjective norm and acceptance intention were significant according to gender. Conclusion The significance of this research is to provide the basis of positioning strategy for domestic companies of sports wearable smart device.


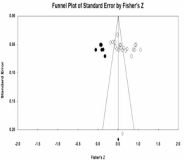
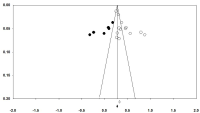
[Purpose] The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect size of the relationship between team identification and their intention to attend sport events and intention to purchase licensed team merchandise using a Meta-analysis. [Methods] To accomplish the purpose of the study, multiple databases were visited (e.g., RISS, KISS, Library of National Assembly) and studies were collected using the keyword of team identification. Through the search process, total of 92 studies were identified, among which 20 studies provided Pearson correlation coefficients between team identification and intention to attend and 13 studies between team identification and intention to purchase licensed team merchandise. The 33 studies were analyzed using Comprehensive a Meta Analysis(CMA) program. The analyses were done using random effect model assuming there were significant heterogeneity among the studies included. [Results] The overall effect size between team identification and intention to attend sport games was .567 and .403 for between team identification and intention to purchase licensed team merchandise, which can be classified as large effect size(Cohen, 2013). Sub-group analyses were done using types of publication(journal article vs. thesis). The results of the sub-group analyses indicated that the effect size differences were statistically insignificant. [Conclusions] As indicated in many previous studies, team identification was found to be a significant predictor of sport consumers’ behaviors. However, future studies need to find the reasons of heterogeneity in effect sizes.

PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the decision-making process for consumers participating in sports centers based on an extended goal-directed behavior model (EMGB), and to provide empirical data for establishing effective operation strategies for sports centers, including additional risk perception of consumers during pandemic. METHODS A total of 446 surveys were used as the final sample. For data analysis, SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 were used for frequency analysis, correlation analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation model analysis. RESULTS Except for hypothesis 2 and 9, all of the hypothesis were chosen. CONCLUSIONS The findings suggested that extended goal-oriented behavior models can increase consumers' cognitive and emotional factors through emotional aspirations, suggesting that a lower risk perception of COVID19 increases their desire to participate in sports centers, and provides academic fundamental data on how to increase and activate sports centers.
PURPOSE The outdoor camping market size is expected to hit a new high in 2021 as the popularity of outdoor activities surges due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The purpose of this study was to investigate the structural relationships among servicescape, perceived value, flow and behavioral intention, focusing on participants of international outdoor camping exhibition. METHODS Demographic analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation modeling analysis were perfomed. RESULTS The findings suggest that (1) all servicescape factors (attractiveness, cleanliness, accessibility and responsiveness) have a positive effect on perceived value, (2) attractiveness, cleanliness and responsiveness are significant predictors of flow, (3) perceived value affects both flow and behavioral intention, and (4) flow also significantly impacts behavioral intention. CONCLUSIONS These findings highlight that high quality servicescape can result in enhancing a positive perceived value and flow, and in turn leading to behavioral intention of consumers. Hence, it is recommended for practitioners and staff of the exhibitions to considering the strategies for improving servicescape factors in order to achieve their goal.

This study classified and analyzed groups of spectators of professional baseball through market segmentation and predicted the sports consumer behavior by using artificial neural networks model and logistic regression model. The results of hierarchical cluster analysis, K-means cluster analysis, cross-tabulation analysis and one-way ANOVA using PASW 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 suggest five clusters of consumer segments and by using Modeler 14.1, artificial neural networks model was made to predict the data. By using artificial neural networks model and logistic regression model, hit ratio was grasped about the spectator satisfaction and future consumption behavior. The results are as follow: The hit ratio were high in ‘cluster 5’ for artificial neural networks model(spectator satisfaction: 71.3%, future consumption behavior: 99.3%) and logistic regression(spectator satisfaction: 71.8%, future consumption behavior: 96.5%). Furthermore, cross-tabulation and one-way ANOVA was performed to understand the cluster's characteristic which had highest hit ratio about the spectator satisfaction and future consumption behavior. And through this marketing strategy was suggested.

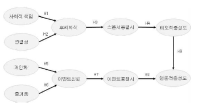
The purpose of this study was to develop a model of relationship intensification, identification formation, and loyalty achieved through mutual effect within participants of sports sponsorship. Through this, the study aims to provide guidance to businesses for establishing and developing sports sponsorships. In order to achieve the objective, two identification paths were used to understand the process of deepening consumer-sponsor relationship in professional volleyball title sponsorships. The target of this study is 'NH Nonghyup' a valleyball title sponsor in 2014-2015. A survey was conducted on 264 home crowd members of Korea Air, Samsung fire, Kepco, Woori card, OK saving bank and Hyundai capital based in metropolitan regions. Sampling method was Convenience Sampling Mode, and questionnaire has been structured to be self-administerd type. SPSSWIN Ver. 21.0 and AMOS 18.0 have been used for data processing. The results were as follows: Frist, the study showed that the connection between consumer-sponsor mutual effect positively influence "we-ness." "We-ness" in turn positively affected sponsor identification, and sponsor identification in turn positively affected attitudinal loyalty. Second, the personalization and enjoyment in consumer-event mutual effect positively affected event trust, and event trust in turn positively affected event identification, and event identification in turn positively affected behavioral loyalty. Third, attitudinal loyalty positively impacted behavioral loyalty.

PURPOSE This study first investigated how different types of sport team logos (emblem vs. mascot) influence consumer behavior through warmth and competence and then examined the moderating effects of consumer characteristics (gender) and contextual cues (perceived competence) on these relationships. METHODS A nationwide sample of adults age 20 was selected using quota random sampling based on gender. A 2 (logo type: emblem vs. mascot) × 2 (gender) × 2 (contextual cue: high competence vs. low competence) experimental design was employed, with participants randomly assigned to each group. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) with Mplus 8 was employed to assess the measurement model’s reliability and validity, and hypothesis testing was conducted through structural equation modeling (SEM), measurement invariance tests, and multigroup SEM analysis. RESULTS Findings indicate that anthropomorphized mascot logos, compared to emblem logos, generate more positive attitudes and psychological responses (warmth and competence) to the team. Gender’s moderating effect on the relationship between logo type and consumer perceptions (warmth and competence) was not significant, but contextual cues’ moderating effect was partially significant. CONCLUSIONS This study highlights of perceived warmth and competence’s crucial role in shaping consumer attitudes toward sports teams through logo design. These findings offer meaningful insights for sports teams and marketers to optimize branding strategies and enhance fan engagement.
PURPOSE This study aimed (1) to analyze the behavioral intention and use behavior among the consumers of online home training contents via YouTube by employing the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT); (2) to test the moderating effects of risk perception toward the coronavirus (COVID-19) infection, and 3) to test differential impacts of generational difference across millennial and baby boom generations. METHODS A total of 400 questionnaires were distributed, and 383 samples were used for the final analysis after excluding 17 incomplete responses. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 22.0. RESULTS It was found that (1) the performance expectancy, the effort expectancy, and the social influence had positive effects on behavioral intention; (2)the facilitating condition had negative effects on the use behavior; (3) the behavioral intention had positive impact on the use behavior. Moreover, the risk perception toward the COVID-19 infection did not have moderating impacts on the UTAUT model, whereas generational differences did. CONCLUSIONS Our results suggest that the marketing strategy that improves exercise performance, convenience, and social influencing factors may be key to home training customers' behavioral intention and use behavior. Furthermore, home training material makers should recognize that the features and infrastructure required for the two generations are distinct and develop a separate marketing strategy for each.