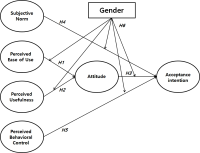
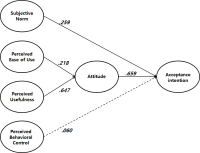
Purpose The current study was aimed to examine acceptance intention of sports wearable smart device using the Technology Acceptance Model and Theory of Planned Behavior. Methods Data were drawn from 357 consumers who had experience purchasing sports products. Data were analyzed through frequency analysis, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling using SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 program. Results First, perceived ease of use had a positive effect on attitude. Second, perceived usefulness had a positive effect on attitude. Third, attitude had a positive effect on acceptance intention. Fourth, subjective norm had a positive effect on acceptance intention. Fifth, perceived behavioral control did not affect acceptance intention. Sixth, differences of path coefficients between attitude and acceptance intention, subjective norm and acceptance intention were significant according to gender. Conclusion The significance of this research is to provide the basis of positioning strategy for domestic companies of sports wearable smart device.



Purpose This study was to explore construct of fear and courage behavior overcoming the fear and relationship between fear and courage in competition. Methods Total 65 national athletes of combat sports(Judo, Boxing, Taekwondo, Fencing) responded to open questionnaire about fear and courage behavior in competition. The data was analyzed by triangle verification and content analysis. Results Firstly, the fear of combat sports athletes consisted of five factors, which were negative consequences, lack of preparation for a game, concerns of performing one’s best, expectation of significant others, and internalized ego threat. Secondly, courage behaviors to overcome fear were self-effort, self-suggestion, self-conviction, selfish self-regulation, social self-control, self-analysis, and acceptance of experience. Finally, there were the relationship between fear and courage in competition. Conclusion These results will contribute to provide useful information for combat sport athletes and coaches in different level to cope with competition fear.

The current study aimed to examine behavioral intentions of online sports products consumers using the Extended Goal-directed Behavior Model. The questionnaires were distributed to consumers who had experience of purchasing sports products online. Data collected from 282 respondents were analyzed mainly using structural equation modeling. The results were as follows: First, attitude and subjective norm had a positive effect on desire. Second, perceived behavior control did not affect desire but had a positive effect on behavior intention. Third, positive anticipated emotions had a positive effect on desire and negative anticipated emotions had a negative effect on desire. Fourth, prior knowledge did not affect desire and behavior intention. Fifth, frequency of past purchase behavior did not affect desire, but had a positive effect on behavior intention. Lastly, desire had a positive effect on behavior intention.



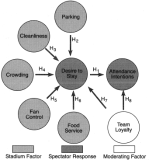
This study employed a sportscape model to analyze environmental impact on spectators’behavior. In addition, the loyalty construct in the sportscape model was reanalyzed based on the theoretical framework. Five hundred questionnaires were distributed to the spectators of World University Taekwondo Championship, and 418 questionnaires were used for data analyses. The analyses of measurement and structural models were conducted using SPSS 18.0 and EQS 6.2 programs. The results indicated that the measurement model showed acceptable reliability and validity. The structural analysis showed that five stadium factors (parking, cleanliness, crowding, food service, and fan control) have significant effects on spectators’ desire to stay and to revisit the stadium. Loyalty also positively affected revisit intention. This study emphasizes sport environment to make spectators revisit and provides future research suggestions to improve the sportscape model.



PURPOSE This study examines organizational autonomy through a public sports governance lens and diverse theoretical perspectives by discussing the longstanding conflicts between the Korea Sports Council and the Ministry of Culture, Sports, and Tourism (MCST) in the context of the Korean Sport and Olympic Committee’s (KSOC) reorientation under President Ryu Seung-min in 2025. METHODS This research adopted Verhoest et al.’s (2004) analytical framework of organizational autonomy to perform a comprehensive literature review that includes scholarly articles, government reports, public institution disclosure documents, and media sources. Expert meetings were also conducted using the naturalistic inquiry method to gather opinions. RESULTS First, this study redefined sport governance as a collaborative partnership between the government and public sport organizations rather than being based merely on traditional government-centric control. Second, public sport organizations’ organizational autonomy has five dimensions: managerial, structural, legal, interventional, and financial autonomy. Third, the KSOC shows high structural and legal autonomy, moderate managerial and interventional autonomy, and low financial autonomy. Fourth, the KSOC’s unique organizational attributes and history allow it to maintain a relatively higher autonomy compared with other public organizations. CONCLUSIONS Amid ongoing debate over its autonomy and independence, the KSOC must balance autonomy with accountability and foster stronger collaborative relations with the MCST to reassert its foundational mission as a public sport organization and help develop stronger and more effective public sport governance.
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop and implement a customized mental plan program to facilitate an optimal psychological state and peak performance among para shooting athletes. It also sought to empirically verify this program’s psychological effects by focusing on improvements in concentration, confidence, and relaxation. METHODS A total of six para shooting athletes who had earned medals in the Paralympic Games underwent six program sessions that were designed and implemented based on attention-related psychological factors identified through open-ended surveys and in-depth interviews. RESULTS The athletes’ attention was facilitated by task-focused behavior, breathing control, performance routines, and physical condition management. Meanwhile, their concentration was hindered by task-irrelevant thoughts, negative physical states, and external distractions. These factors were further categorized according to competition phase: the day before, precompetition, and during competition. Based on the statistical analysis, significant improvements were observed in the athletes’ concentration, confidence, and relaxation. CONCLUSIONS The custom program was practically effective as an intervention for psychological skills tailored to experienced para shooting athletes’ individual needs. The findings offer valuable insights for developing strategies supporting the psychological states of athletes in disabled sports.
PURPOSE This study investigated the differences in plantar pressure distribution when using three breathing techniques during heel raises. METHODS The subjects were 29 professional dancers aged 20 to 30 years with more than 10 years of experience. Pressure distribution according to breathing method during heel raise was measured for 10 seconds while controlling the raise speed and gaze. The three breathing techniques were randomly ordered. Peak pressure, contact area and time, displacement, and absolute velocity of the center of pressure trajectory were measured using Emed®-le from Novel GMBH. Plantar pressure was analyzed by dividing it into a total of 12 areas (masks): five toes, five metatarsals, the midfoot, and the hindfoot. RESULTS Using the teeth occlusion breathing technique, the peak pressure on the first metatarsal was significantly reduced, the contact time of the second metatarsal was significantly longer, and the displacement of the center of pressure trajectory was significantly shorter. Additionally, during the phase of the forefoot retainer, the velocity of the center of pressure trajectory was significantly reduced. CONCLUSIONS The teeth occlusion technique reduces peak pressure, increases contact time and area, and decreases the displacement and velocity of the center of pressure trajectory, demonstrating an efficient method for maintaining balance in ballet movements. This technique can potentially enhance stability and prevent injuries in ballet dancers.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of different resistance training structures on basic physical fitness, 1-repetition maximum (1RM), and isokinetic shoulder and knee muscle functions in male college students. METHODS Forty college students were divided into four groups: control group (CG, n=10), compound set training group (CSG, n=10), pyramid set training group (PSG, n=10), and superset training group (SSG, n=10). Excluding CG, each group performed a different resistance exercise method at an intensity of 60~80% 1RM for 60~90 min, three times a week for eight weeks. To compare the effects of resistance training structures, we confirmed body composition, basic physical fitness, 1RM, as well as isokinetic shoulder and knee functions. RESULTS Results indicated that the PSG exhibited the most significant improvement in relative peak torque in isokinetic shoulder and knee testing compared to the other groups. Additionally, all exercise groups positively affected back strength, 40m sprint, and 1RM compared to the CG, although no significant differences were observed among exercise groups. CONCLUSIONS The findings suggest scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of pyramidal resistance training in improving isokinetic shoulder and knee muscle functions in male college students.
PURPOSE This study explores injury attributions accepted by serious football participants, specifically intermediate and advanced players. METHODS Utilizing Q methodology, 25 Q-samples and 33 P-samples were selected, and Q-classification was conducted. Principal component factor analysis through the PQ method (vers. 2.35) was employed for data analysis, and types were interpreted and named based on the Q-sample with a Z-score of ±1.0 or higher. RESULTS Results categorized injury attributions accepted by the participants into four types: 'Type I: Facility/ Human Resource Responsibility Type,” 'Type II: Luck/Other Responsibility Type,” 'Type III: Self Responsibility Type,” and 'Type IV: Insufficient Safety Education.” This study provided academic and policy discussions by reclassifying four types according to their internal and external location and controllability. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, this study emphasizes the relevance of all four types of injury attribution to policy considerations. Ensuring participants' right to participate in safe and enjoyable sports requires addressing facilities/human resources, education, and insurance as major policy components of sports safety.
Circadian rhythm (CR) is an intrinsic process that changes in a cycle of approximately 24h/day to maintain body homeostasis. It is mainly controlled by the central command through the suprachiasmatic nucleus, and modern society features can disturb the central CR, contributing to various diseases. Recent studies have provided evidence that extrinsic factors, such as regular physical activity (RPA) and timerestricted feeding (TRF), can also alter the CR peripherally, emphasizing RPA and TRF as the non-therapeutic methods for circadian misalignment (CM). Therefore, this review scrutinizes the regulatory mechanism of CR and summarizes the relationships between CM and various diseases. In addition, by reviewing studies investigating the prevention or improvement of CM via RPA and TRF, the value of circadian biology research that can directly affect health, physical function, and lifespan is summarized. By introducing the scientific evidence for RPA and TRF to maintain and improve CR, we tried to emphasize the importance of regular exercise and healthy eating habits to people in the modern world who have difficulty maintaining CR.