Recent studies focus on Metabolic Equivalent Task (MET) to measure levels of and areas of peoples’ physically active lifestyle because MET more readily translate peoples ’subjectively perceived physicality into standardized scores. MET also allows researchers to clearly understand the relationships between peoples’ physicality and psychological variables. Thus, the purpose of this study was to understand the levels of and areas of MET among Korean middle school students and to analyze the relationships between MET scores and physical self-efficacy. A total of 278 questionnaires were analyzed using SPSS 18.0. Exploratory factor analysis, descriptive analyses, and regression analyses indicated that middle school students’ physically active lifestyle occurred in the order school, leisure, housework, and transportation areas. Female students did more physical activity in the areas of housework and transportation, compared to male students. In contrary, male students did the majority of physical activity in the areas of school and leisure. Physical self-efficacy affected students’ MET scores, especially for vigorous intensity activity. With regard to gender differences, physical self-efficacy affected male students’ MET scores in the area of leisure while female students’ MET scores were affected in the areas of school and housework. The results were discussed in light of methodological and pedagogical perspectives, and future research suggestions were provided in the discussion.
The purpose of this study is to examine the level and difference of sport personalitys of middle school students depending on their quality of sport participation. According to prior research(박정준, 2012; Beller & Stoll, 1996), we decided that faithfulness, cooperation, justice and consideration are the sub-components of sport personalities. The reliability and validity of the Sport Personality Index Questionnaire was verified through Cronbach's α test and confirmatory factor analysis. The survey was conducted from students (n=768) in an urban area of Seoul, thereby level and differences of sport personality were analysed by t-test, one-way ANOVA, and frequency analysis. As a result, male students had higher sport personalitys than female, with regard to the participants'grade, frequency and duration of sports involvement. Disparities of gender and grade were revealed due to the frequency and duration of their sports participation. Regarding the effectiveness of sports activities, school-directed sports activities such as the after school sports programs or mandatory sports club activities had barely influenced building sport personality. In order to build students'sports personalities, specific strategies are sorely needed to increase girl's participation and to enlarge opportunity for regular and consistent participation of middle school students. Moreover, in order to develop participants'sport personality within school-directed sports activities, those programs'development and implementation should be deliberately approached with pedagogical intention and organization.

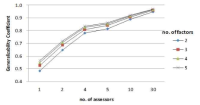
The purpose of this study which is follow up study of Lee and Kim(2015b)'s was to analyse error sources and estimation of reliability in peer review of forced connection method-sportscasting by applying generalizability theory. Generalizability theory quantify error sources of the data measured under certain specific situation set by the researchers. It is an analysis method that the relative influences of each error sources taking from score is determined(G-study), and the effective measurement condition future applicable is provided(D-study). Participants were 10th high school students(N=216). Data were collected from student's peer review results and analyzed using univariate and multivariate generalizability theory. Results showed that error source for video have a more significant impact than other error sources. But the result by analyzing the gender difference was that error source for the interaction of video and participants have a more significant impact than other error source in the case of girls. Peer review used in this study showed high generalizability coefficient and even when reducing the number of video or participants it can maintain the adequate reliability. But generalizability coefficient of boys was higher than girls and specific measurement conditions leading to enhanced reliability were different when analyzing by gender difference. Also, method of analysis which cannot reflect measurement conditions properly estimates the reliability excessive. Discussions were provided in term of the relative influences of each error sources, the effective measurement condition maintaining the Generalizability coefficient of a certain level, and the comparison the Generalizability coefficient with the way of estimation traditional reliability applying univariate and multivariate Generalizability theory taking from score in peer review of forced connection method-sportscasting.



PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze physical activity (sedentary, light, moderate to vigorous physical activity [MVPA]) characteristics of middle school students based on region (urban and rural) and sex. METHODS Data were collected from 216 students across 6 middle schools located in medium-sized urban (3 schools) and rural areas (3 schools), and the relevant physical activity was measured using a three-dimensional accelerometer (GT3X model). The collected data were inputted into the SPSS 20.0, and descriptive analysis and two-way ANOVA based on region and gender were performed (<.05). RESULTS The descriptive statistical analysis resulted in the following achievement rate of the physical activity standard (MVPA 60 minutes/day): 9.4%. The two-way ANOVA showed that the main effect according to gender was found in sedentary activity (F=5.258), light activity (F=6.790), and MVPA (F=32.274); furthermore, the main effect according to region was found in light activity (F=10.888) and MVPA (F=7.876). Interaction effect according to region and gender was found at all intensities, and the gap between rural and urban in male students was larger compared to that of female students. CONCLUSIONS After COVID-19, the level of physical activity among adolescents has worsened; this study found the problem of "decrease in physical activity; increase in sedentary activity" to be more serious among male students in urban areas.
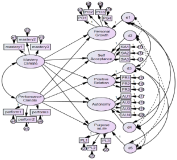
Purpose This study identified the influence of perceived motivational climate on psychological well-being in ballet majors. Methods Participants were 211(male=25, female=186) collegiate students enrolled in ballet department. Measures were The Perceived Motivational Climate in Sport Questionnaire(PMCSQ) and Psychological Well-being Questionnaire. Data were analyzed by using descriptive statistics, reliability test, correlation, and structural equation modeling. Results Results were as follows. First, mastery climate who ballet majors perceive significantly influenced on the five subscales of their psychological well-being: Mastery climate was positively related to personal growth, self-acceptance, positive relation with others, autonomy, and purpose in life. Second, performance climate who ballet majors perceive significantly influenced on the five subscales of their psychological well-being: Performance climate was negatively related to personal growth, self-acceptance, positive relation with others, autonomy, and purpose in life. Model fit indices were acceptable(RMSEA=.070). Conclusion In conclusion, this study indicated that motivational climate who ballet majors perceive was a important situational factor on their psychological well-being.

Purpose The purpose of this sequential mixed-method study is to compare the levels of Moderate to Vigorous Physical Activity (MVPA) between the students with intellectual disabilities and students without disabilities in different types of inclusive physical education classes and to understand why different levels of MVPA occur. Methods For this purpose, 17 students with intellectual disabilities and 102 students without disabilities participated in this study, and the levels of MVPA in inclusive physical education classes were accessed using thee dimensional accelerometers. The collected data were analyzed using independent sample t-test. To understand the different levels of MVPA identified in quantitative analysis, four teachers were interviewed. Results Results showed that different levels of MVPA were found in inclusive physical education classes, and this is because the students with intellectual disabilities had participation constraints and teachers did not have knowledge to deal with those constraints. Considering gender difference, only different levels of MVPA were found among male students, which could be stemmed from few opportunities of cooperative works between male students with intellectual disabilities and male students without disabilities. Considering types of inclusive physical education classes, significant different levels of MVPA were identified in tee ball classes. The reason for this could be that the rule of tee ball is too complicated and too many team tasks for the students with intellectual disabilities to understand and to execute. Conclusions Based on the results, practical teaching strategies to increase levels of MVPA of the students with intellectual disabilities are provided in the discussion section.
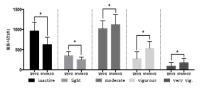
Active participation in Moderate to Vigorous Physical Activity(MVPA) is the indicator of healthy development for adolescents. However, Korean adolescents’ MVPA have continuously declined, and Korean adolescents have lower levels of MVPA compared to adolescents in other countries. Considering this issue, the purpose of this study is to examine the effectiveness of SPARK M-SPAN program to promote adolescents’ MVPA in P.E. classes and to understand how the promotion of adolescents’ MVPA occurs. To collect data, this study used Sequential Mixed Method and GT3X accelerometers. A total of 168 adolescents (84 in an experimental group and 84 in a control group) participated in this study for the quantitative data analysis, and six students and a teacher were interviewed for the qualitative data analysis. Paired t-test showed that students in SPARK P.E. classes experienced the significant decreases of sedentary behaviors(-339.6 sec) and low intensity P.A.(-96.9 sec) at p<.05 and the significant increases of moderate(+99.3 sec), vigorous(+252.4 sec), and very vigorous intensity P.A.(+84.7 sec) regardless of gender difference at p<.05 except for female students’ moderate intensity P.A.. The qualitative data analysis showed that SPARK classes gave students positive learning environments and led them to experience enjoyment and achievement-orientated learning Key teaching strategies of SPARK program and future research suggestions were provided in the discussion section.

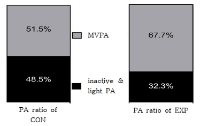

The purpose of this study was to explore Physically Activity Lifestyle pattern & constraints of high school girl in city, and then to propose P.A. promotional ways. I used International Physical Activity Questionnaire Long version and accelerometer to examine outline of P.A. pattern, and photo-voice as qualitative research techniques. The results were as followings. First, sedentary lifestyles of students in G girls' high school was terrible. Accelerometer was said that their inactive time were about 92.4%, however their moderate to vigorous time about 0.76% of the total time of a week. And, school domain of four domains(school, transportation, leisure, domestic chores) were the most active domain of all. Second, P.A. constraints were analyzed as 'because of something no'(time, effort, will, space, physical skills and person) and 'because of something'(smart phone, car, gaze, rules). The key cause were a shortage of time caused by academic based on school curriculum, sedentary leisure and transportation culture. Lastly, I proposed high school girl' P.A. promotional ways in basis of social ecological model.











Recently, there have been diverse types of physical activities supported by government policy in S. Korea. However, these activities may not be effective if they do not reach to moderate to vigorous level. This study designed school physical education system based on SPARK program, which include traditional physical education, sports club based physical activity, after school physical activity, and Saturday physical activity, to evaluate its effectiveness associated with physical fitness and empirical meanings of physical activity. This study employed a mixed method research paradigm for better understanding. Among various mixed method paradigm stances, this study employed "blending strategy" for complementary analysis. First of all, the effectiveness in health condition was evaluated by quantitative data. Specifically, physical fitness and lifestyle were analyzed by Helmas, IPAQ, and Accelerometer respectively. Second, empirical meanings of physical activity were analyzed by both Photovoice and in-depth interview which are qualitative research method. The result of this study first showed that a specially designed school physical activity program based on the SPARK contributed to improve students' physical fitness and lifestyle as well, however, there were important differences between male and female students. Second, physical achievement, alteration of spatiotemporal meaning, and change of societal relationship emerged as important themes. Further, these themes showed that they played an important role to maintain students' motivation in physical activity and consequently physical activity promotion was invigorated in school. Based on these results, we synthesized investment factors and process factors and outcome factors respectively. Finally, we suggested alternative teaching methods and suggestions for following research to overcome gender issues.









