Purpose This study was conducted to analyze the differences of physical characteristics focused on the physique, strength, and power for cycling national athletes (Sprint cyclists and Road race cyclists). Methods We measured various factors (e.g., height, weight, body fat ratio, thigh circumference, waist circumference, anaerobic power, isokinetic muscular strength, muscle power, squat jump by 1RM intensity, and so on) for a total 11 male cycling national athletes (5 Sprint cyclists and 6 Road race cyclists). Results First, the body composition showed the significant differences only in weight (p=0.31) and BMI (p=.001) for Sprint cyclists. Second, the values of the anaerobic power for the Sprint cyclists were significantly higher than those for the Road race cyclists only at peak power (p=0.28), whereas there was no significant difference in average power, isokinetic muscular strength, and muscle power between the two groups. Third, the isokinetic trunk flexion muscle (p = .016) for the Sprint cyclists were significantly higher than those for the Road race cyclists. Fourth, the significant difference in Time to Peak Torque was not found between two groups. Fifth, the values for the Sprint cyclists showed the significant difference in all 5 intensity groups (0%, 30%, 50%, 60%, and 80%) (p=.001) of the squat jump. Also, there was a statistically significant difference only in 0% velocity between the two groups, except for exercise intensity. Conclusions From the various measures between two groups, the Sprint cyclists relatively showed the high weight, BMI (muscle mass), and maximum power. Additionally, the isokinetic trunk flexion muscle and the squat jump were higher in the Sprint cyclists than the Road race cyclists. These data may be used as basic data to improve the physical fitness factors related to the athletic performance of the athletes by reflecting them in the effective training plan and evaluation of the athletes.
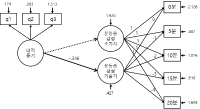
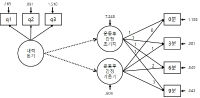
PURPOSE This study compares the effects of video group and metaverse group counseling for student athletes to analyze differences in immersion, sychological skills learning effects, and each approach’s participation experiences. METHODS Twenty-four high school archery students were divided into three groups: a metaverse experimental, a video comparison, and a control group. For the experimental and comparative groups, 10 non-face-to-face psychological skills training sessions were conducted. With the control group, results were compared and analyzed by measuring psychological skills and social presence pre- and post-training. Additionally, analysis of the qualitative effects of psychological skills training was performed. RESULTS The psychological skill test’s quantitative analysis of the video comparison group showed a more significant effect in anxiety control factors than the metaverse experimental and the control groups. Moreover, in the social presence test, both the metaverse and the video groups showed significant differences in social presence and satisfaction; furthermore, Scheff post-verification results showed that the two environments’ satisfaction was significantly higher than that of the control group. Qualitative analysis confirmed that the metaverse and video groups experienced psychological, technical, and relational changes in common. CONCLUSIONS Although the metaverse group using avatars was likely to increase immersion, both the video and the metaverse groups were effective in psychological skills training, suggesting that the training effect may vary depending on the non- face-to-face environment’s stability and participation method. Future studies should examine effects of applying the metaverse platform to sports psychological skills training and various psychological support activities by solving the metaverse environment’s technical limitations.
PURPOSE Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for home training, with exercises or workouts at home, has steadily increased. As a result, the popularity of home training YouTube content, which shows how to use exercise equipment or workouts without professional influence, has also increased. Therefore, this study focused on the characteristics of YouTube home training content (specialization, diversity, and interaction), personal health awareness, exercise awareness, and expectation-confirmation model to identify which required exercise continuation intention through YouTube home training. METHODS SPSS and AMOS software were used to conduct frequency, reliability, and confirmatory factor analyses, as well as to conduct correlation analysis and construct a structural equation model. RESULTS First, health and exercise awareness had a positive effect on confirmation. Second, among the characteristics of home training content, only specialization had a positive effect on perceived usefulness. Third, confirmation had a positive effect on perceived usefulness and viewing satisfaction, perceived usefulness had a positive effect on viewing satisfaction and exercise continuation intention, and viewing satisfaction had a positive effect on exercise continuation intention, which proved the expectation-confirmation model in this study. CONCLUSIONS To increase exercise continuation intention through home training YouTube content, creators need to produce professional content that can stimulate viewers' internal motivation.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the changing trends of swimsuit perception by using SNS big data. Methods By using “swimsuit” and “swimsuit brand” as key words, data was searched through blogs, cafes, Jisiksin(Tip), news, and web documents provided by naver and daum. This study used 2 years of data from January 1st, 2014 to December 31st, 2015 and social matrix program Textom was used for extracting matrix data and analyze them for frequency. To visualize data networking, NetDraw of UCINET6 program was used. Results Through analyzing the popular link words to the key words, it was known that the key words were 'swimsuit brand', 'children's swimsuit', 'rash guard', 'women's swimsuit', and 'model' in the order in 2014, and ‘swimsuit brand', 'rash guard', 'children's swimsuit', 'women's swimsuit', and 'Arena’ in the order in 2015. Second, the median of connectivity values showed that it was high in ‘swimsuit brand', 'women's swimsuit', 'children's swimsuit', 'rash guard', and 'Arena’ in the order in 2014, and ‘swimsuit brand', 'rash guard', 'women's swimsuit', 'children's swimsuit', and 'Arena’ in the order in 2015. Third, th results of CONCOR analysis demonstrated that ‘female customer’, ‘couple swimsuit’, 'rash guard', ‘brand’, 'children's swimsuit', and ‘fashion’ were grouped in 2014, and ‘brand’, ‘fashion’, 'rash guard', ‘purchase factor', and 'children's swimsuit' were grouped in 2015.





PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the factors affecting job stress in fitness instructors, and to elucidate the mediating effects of mindset on the relationship between self-reflection and job stress. METHODS Using convenience sampling, a survey was conducted with 217 male and female fitness instructors nationwide. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 25.0 for descriptive statistics, frequency analysis, and reliability analysis, and AMOS 22.0 for confirmatory factor analysis to validate the measurement tools. SPSS PROCESS Macro v4.0 (Model 4) was utilized to verify the mediating effects of the research model. RESULTS Self-reflection among fitness instructors was found to significantly reduce job stress. A growth mindset was found to have a partial mediating effect on the relationship between self-reflection and job stress among fitness instructors, whereas a fixed mindset did not have a significant impact . CONCLUSIONS The results confirm that self-reflection and having a growth mindset significantly influence the reduction of job stress in fitness instructors.
PURPOSE This study aimed to verify the relationship between adolescent athletes’ julsil, competitive trait anxiety, and self-management. METHODS A total of 370 adolescent athletes who were registered with the Korean Sport & Olympic Committee participated in the survey; 24 insincere responses were excluded from the analysis, leaving a total of 346 participants. After verifying the construct validity of the measurement tool used in the survey, statistical and correlation analyses were performed. The research model was subsequently verified using structural equation modeling. RESULTS Adolescent athletes’ julsil had a significant positive effect on self-management but not on competitive trait anxiety. In addition, self-management was found to have a significant negative effect on competitive trait anxiety, and also completely mediated the relationship between julsil and competitive trait anxiety. CONCLUSIONS Adolescent athletes’ julsil does not increase competitive trait anxiety, but rather plays a role in reducing it by increasing self-management. These findings unveil mechanisms through which julsil can be used to enhance athlete performance.
Purpose The current study investigated the effects of exercise information using social network service(SNS) to identify changes of physical activity and psychological variables among inactive college students. Methods Inactive college students(30 experimental group, 30 control group) were voluntarily participated in the 12-weeks intervention. During this period, the experimental group received exercise information through SNS. And all study participants’ physical activity, stages of physical activity, self-efficacy, motivation, and perceived benefits and barriers were measured at the pre, mid and post intervention. Frequency analysis, chi-square test, 2-way ANOVA RM were conducted to analyze data obtained in the study. All procedures were performed by using SPSS 23.0. Results The exercise information intervention using SNS during 12 weeks had a positive effect on the stages of physical activity of inactive college students, and there were statistically significant differences. In addition, physical activity, perceived benefits and barriers, self-efficacy, motivation positively improved after the intervention, but there were no statistically significant differences between experimental and control group. Conclusions The present study suggests that psychological strategies using various SNS programs have positive effects for inactive college students to increase physical activity and its related psychological variables.

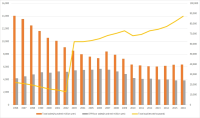
Purpose This research analyzed the Korean and Japanese cycle racing businesses by comparing each country’s total profits and total audience from 1996 to 2016. Methods In this process, it used total profits data and total audience data from 1966 to 2016. The data showed an economic correlation between Korean and Japanese cycle racing businesses by using each county’s economic variables. Results According to regression analysis, the income and audiences of Korean cycle racing industry has been increased as their income level has been increased. However, Japanese cycle racing generally has negative effects between income level and other variables except audiences. Moreover, aging population affects negatively to Korean cycle racing industry. In contrast, aging population is less affects to Japanese cycle racing industry. Furthermore, improvement of employment and unemployment rate affects negatively to Korean cycle racing industry. As a result, Korean cycle racing industry looks like a gambling. On the other hands, Japanese cycle racing industry becoming one of leisure sports industry. Conclusions Korean cycle racing industry has to examine closely Japanese’s restructuring method & result. Also, they have to analyze closely Japanese’s sociocultural variables which explain decreasing profits and increasing audiences. In other words, Korea cycle racing industry needs to various methods to becoming leisure sports industry.

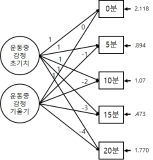
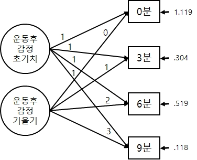
Recent research on exercise and affect has examined participants` affective changes during and after exercise with a longitudinal approach. With regard to this viewpoint, a theoretical model (Dual Mode model) has been presented to explain the different change of affect in an exercise setting and the model identified the impact of psychological factors on the affective changes. However, not only there is little empirical studies on the dual-mode model, but some relevant research has used an inappropriate statistical method (ANOVA), which cannot effectively explain the overall trends in affective change during and after exercise. Exiting research has a limitation to generalize the DM model examining only a certain gender such as active male or inactive female participants. Thus, the aim of present study was to investigate the effect of intrinsic motivation on affective change during and after exercise in participants who do not take part in regular exercise considering gender based difference. 51 inactive university students (M: 36, F: 15) responded a survey measuring intrinsic motivation for running activity and participated in moderate-intensity running exercise to examine affective change during exercise. Therefore, present study examined the influence of intrinsic motivation as a psychological variable on the trend of affective changes during and after exercise based on the dual mode model. Results from the latent curve model analysis revealed that there were decreasing trends of affect during exercise and the trends were individually different. Importantly, the decreasing trends were weaker in the participants with higher intrinsic motivation[FL=-.34, p=.000]. Additionally, participants` affective responses were positively changed after the exercise in general, but the changes were not influenced by intrinsic motivation. Therefore, the decreasing trend of affective change during exercise was weaker in the participants with higher intrinsic motivation, and the positive change in affect after exercise was not influenced by intrinsic motivation.


The purpose of this study was to verify the effect on elementary school students in the exercise start stage by performing a sport psychological skill training to improvement of psychological skill and life skill. Participants were eight elementary school boys volleyball player. The program consisted of psychological skills and life skills in educational counseling model of Visek et al(2009). It was conducted 40-50 minutes a session in total for 22 sessions. Data was collected through a psychological test, worksheet and participant observation, in-depth interviews. The collected data was analyzed to verify difference by paird t-test after pre-middle-post test and to extract meaningful data category. Quantity analysis showed that a result of sport psychological skill test proved a significant difference in willingness to overcome, confidence, concentration, anxiety regulation. Life skill test were no significant differences in all factors. However, the rise of scores was observed on result of the pre-middle paired t-test of life skill during season. Quality analysis showed possibility of goal setting, concentration on the routine, decrease of competitive anxiety, increase of positive thinking, self-understanding and understanding of others, promotion of communication among team members. This sport psychology skill training had a significant effect on the psychological skills of elementary players change. But it seems to be necessary life skills in a more through review of the information.


