
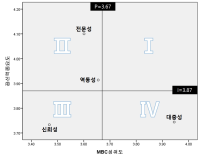
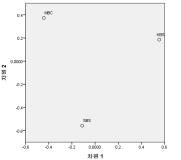
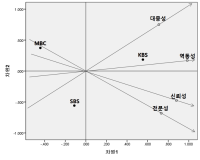
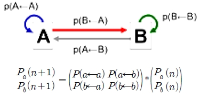
The purpose of this study was to evaluate sports commentators’ public confidence by the difference between media recipients’ expected level on the public confidence and their perceived outcomes, and to investigate how such characteristics are perceived by media recipients. The questionnaires were given out to people in Seoul and Gyeonggi province, who have experience of having watched the 2014 FIFA World Cup Brazil. The samples were collected by snowball sampling method and a total of 218 questionnaires were chosen as final validity sample. For data analysis, frequency analysis, exploratory factor analysis, paired t-test, importance-performance analysis (IPA), PROXSCAL analysis, and a multiple regression analysis were done by using PASW 21.0. The derived results are as follows: First, according to results from IPA analysis, the Quadrant I is a status-quo area, which is inclusive of the professionalism of KBS and SBS commentators. The Quadrant Ⅱ is a concentrated effort-oriented area, which includes dynamics of KBS and SBS commentators, and professionalism and dynamics of MBS commentators. The Quadrant Ⅲ is an inferiority ranking area, which contains popularity of KBS and SBS commentators, and reliability of MBC commentators. The Quadrant Ⅳ is a rejection of overexertion area, which incorporates reliability of KBS and SBS commentators and popularity of MBC commentators. Second, according to results from MDS analysis in terms of the characteristics of public confidence, an order of KBS>SBS>MBC appeared in the fields of professionalism, reliability and dynamics, and an order of KBS>MBC>SBS appeared in popularity.



PURPOSE This study aimed to develop and implement a customized mental plan program to facilitate an optimal psychological state and peak performance among para shooting athletes. It also sought to empirically verify this program’s psychological effects by focusing on improvements in concentration, confidence, and relaxation. METHODS A total of six para shooting athletes who had earned medals in the Paralympic Games underwent six program sessions that were designed and implemented based on attention-related psychological factors identified through open-ended surveys and in-depth interviews. RESULTS The athletes’ attention was facilitated by task-focused behavior, breathing control, performance routines, and physical condition management. Meanwhile, their concentration was hindered by task-irrelevant thoughts, negative physical states, and external distractions. These factors were further categorized according to competition phase: the day before, precompetition, and during competition. Based on the statistical analysis, significant improvements were observed in the athletes’ concentration, confidence, and relaxation. CONCLUSIONS The custom program was practically effective as an intervention for psychological skills tailored to experienced para shooting athletes’ individual needs. The findings offer valuable insights for developing strategies supporting the psychological states of athletes in disabled sports.
PURPOSE This study explores the factors influencing eco-friendly behavioral intentions during sports spectating and infers the causal structure linking each variable to eco-friendly behavioral intentions. METHODS A total of 364 sports fans participated in the survey that collected data on Knowledge of Climate Change (KCC), Awareness of Climate Change (ACC), Attitude of Climate Change (ATT), Subjective Norm of Climate Change (SN), Perceived Behavior Control of Climate Change (PBC), and Behavioral intention to Reduce Single-Use Plastic (INT) during sports spectating. The validity of the measurement was examined through confirmatory factor analysis. Based on the validated data, latent variables’ average scores were reconstructed as input variables for the Bayesian Network, along with demographic characteristics. RESULTS The results of Bayesian network learning indicated that ACC, ATT, SN, and PBC variables directly influence INT. ACC affects ATT and SN, while ACC is influenced by KCC and sex. Conversely, PBC influenced INT but showed no association with the other input variables. SN was found to have the greatest impact on INT during sports spectating, while the influence of PBC was relatively low. CONCLUSIONS The causal structure inferred in the current study using Bayesian network learning provides insights into the previously underexplored relationship structure explaining eco-friendly behavioral intentions of sports fans in the field of sports science. The findings of this study can serve as empirical evidence for sports-related organizations to develop strategies and decision-making processes to promote sustainable sports spectatorship.
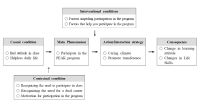
Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the process of participation in the PEAK program of collegiate athletes based on grounded theory. Methods In-depth interviews were conducted with 12 athletes from Y University who were registered in Korea Taekwondo Association. The collected data were analyzed by using the open coding, axis coding, and selective coding of the grounded theory, completed the paradigm model among the extracted concepts, and extracted the core categories through the story outline. Results As the result of data analysis, 'participating in the PEAK program' was found as the central phenomenon, and the causal situation was 'bad attitude in class' and 'helpless daily life'. The contextual conditions were 'recognition of the need for class participation and dual career' and 'motivation to participate in the program', and the intervening conditions were 'factors that hinder participation in the program' and 'factors that help program participation'. The action/interaction strategies were ‘caring climate’ and ‘promoting transfer’, and depending on the consequence, ‘learning attitude change’ and ‘life skill change’ appeared. Conclusion Participants improved their learning attitude through the PEAK program and confirmed the possibility of life skills transfer. It is hoped that this study can lead to implementation of various studies and discussions about life skills and transfer.

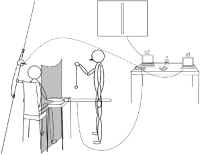
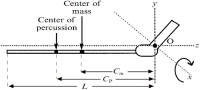
Purpose This study measured the haptic extroperception accuracy, that is, judging one hit position in a hand-held object. Especially, what factors associated the estimation of contact position when the impact is made at the grasped implement by hitting the ball. Methods Relative frequency and conditional probability based analysis verified that perceivers influenced not only the amount of pressure distinguished impressions by the coefficient of restitution but also the pressure distributions encoded impressions by the distance from the hand to the impact. Results Results conformed to previous invariant characteristic on dynamic touch in showing that perceiving the location of the impact of grasped objects, including dominant perceiving selectively modality, is constrained by inertial properties with such success requires appreciating the location of the implement’s center of percussion. Conclusion Investigated in this planes captured as a mechanical factor, we would suggest a broader hypothesis for further research into the effects of the rotational inertia related to haptic position accuracy in the hand-held object, and leading to different estimates of system function providing an account of generalization that accommodates of its varied aspects.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to provide useful information on the improvement of performance by measured the psychological-physiological stresses experienced by elite shooters during a competition. Methods Thirty-eight elite shooters participated in this study (Male = 13, Female = 25). Psychological stress was measured and used for this study based on the stress factors found in the elite target stress study by Park(2015). The cortisol, a physiological stress hormone, was measured using saliva. Results The reliability of the psychological stress sub-factor pre-post analysis results showed no statistically significant. The concentration of cortisol measured on the day before the competition (0.1704 µg/dL) significantly increased immediately before the competition (0.3558 µg/dL). Cortisol immediately before the competition showed negative correlation (r=-.361, p=.036) with the competition score, and the regression variable of cortisol was 13%. Conclusions In this study, physiological stress had a negative effect on elite shooters performance compared to psychological stress.

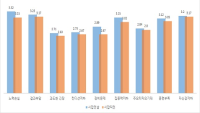


The purpose of this study was to explore and confirm Kumi-kata related factors of muscle strength by performance level in Korea elite female judoists. In order to achieve this purpose, 14 elite female judoists participated to this study. The subjects were divided to two groups (World Class Group and Non-World Class Group) according to their world ranking level(by ranked 30th). The analysis factors were repeated grip strength, Kumi-kata specific pulling strength and isokinetic strength of trunk joint. The results were as follows: Firstly, World Class Group had significantly higher repeated grip strength as compared to non-world class group (p<.001). Secondly, World Class Group had significantly higher specific Kumi-kata pulling strength as compare to non-world class group (p<.05). Finally, The differences between the two groups for isokinetic strength of trunk joint were non-significant. The results of this study indicates that a strong relationship exist between Kumi-kata related specific muscle strength and performance level in korea elite female judoists.

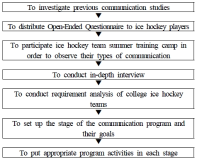
This study was designed to develop a communication training program for college ice hockey teams and examine the effects of this program. College ice hockey players and coaches participated in this study. The various types of data were collected and analyzed to assess the needs of the program and to develop the program with expert meetings. To analyze the effects of the developed program, questionnaires, experience reports, and in-depth interviews were conducted as measures. The results of this study are as follows. First, ice hockey team communication consisted of eight factors (i.e., sympathy, respect, trust, two-way verbal communication, firm expression of opinion, training program communication, developing rapport, and cohesion). Thus, the program developed based on eight factors and consisted of three stages of total 12 sessions which was 90 min to 100 min long. Second, this program increased communication satisfaction, coach-athlete interaction, group cohesion and exercise effectiveness, and these quantitative results were statistically significant. Moreover, qualitative analysis revealed that this program enhanced sympathy, social cohesion, and task cohesion among participants as well as positively changed their communication skills better than before. The communication training program which was developed through this study could provide basic information of a communication training program in the sports domain and positively influence overall sports team effectiveness and performance.


This study aimed to explore the types of traumatic event experienced by Volleyball players and then prepare to take-off the serial process of posttraumatic growth to schematize a causal network by organizing the factors for overcoming adversity. Participants experiences were collected by distributing open-ended questionnaires to 77 professional Women's volleyball players in 2013-2014 and collected data was categorized by inductive content analysis. These results were schematized by the causal network. As a result of the study, according to the trauma were categorized into four general areas: member conflict, competence loss, physical injury, and coach conflict and the emotions relative to the trauma were categorized into four general areas: powerlessness, pressure, dejection, and hostility also coping factors were categorized into three general areas: social support, intervention strategies, and psychological control. Finally, positive growth emerged as psychological leap, performance improvement, psychological maturity, and emotional stability. And as a result of the categorized study, bring about a better understanding to the posttraumatic growth by causal network. Based on the study results, that volleyball players experienced a positive development on themself after overcoming the problem that they had suffered psychological scars from a traumatic event. In doing so, they contributed to the formation of resources that helped them in their positive lives. In this regard, this study expects to provide the players who have been scratched in mind because of the traumatic experience.





Purpose The purpose of this study was to provide basic data for spectators group of Taekwondo performance efficient marketing activities through market segmentation from characteristics, perceived values of the Taekwondo performance spectators. Methods The subjects of this research were Kukkiwon, Taekwondowon and 1,021 questionnaires were finally used for the analysis. The results of this research were drawn by frequency analysis, CFA(confirmatory factor analysis), reliability analysis, cluster analysis (hierarchical and K-means), cross-tabulation analysis and One-way ANOVA were used for data processing through SPSS 22.0 and AMOS 22.0. Results As results of the analysis, It was subdivided into three clusters (such as group of male college students, man group of low perceived value and high degreed women group of low pragmatism). Conclusions The significant differences of the characteristics and perceived value appeared from each cluster. Cluster 1: A group of male college students, and the highest perceived value for Taekwondo performance. Cluster 2: A group of male, and a low perceived value for Taekwondo performance. Cluster 3: A group of high degreed women and a low pragmatism of perceived value. Therefore, a practical marketing strategy was needed for each groups.