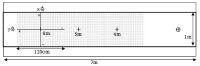
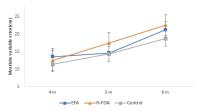
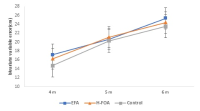
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the effectiveness of the holistic focus of attention(H-FOA), presented as an alternative attention concept, to explore effective attention focus for the skilled performer. Methods KPGA's experts (N = 24) were selected and randomly assigned to external focus, overall focus and control groups. Experiments were conducted in the putting competition of the target distance (4m, 5m and 6m). Performance was measured for accuracy. Results Interestingly, the control group showed the high putting performance accuracy (MRE). In addition, the holistic focus of attention group was able to identify performance similar to the control group. The effect of external attention focus could not be confirmed. Conclusions Results of this study indicate that external focus may be unnecessary for skilled golfers. Rather, holistic focus of attention is highlighted for the improvement of players’ attentional focus under pressure.



Purpose This study was designed to develop a curriculum for pre-service golf coaches at universities to enhance the coaches’ competencies to counsel athletes on the field. Methods This study was conducted in accordance with the revised and supplemented procedures for the national competency standard (NCS) based curriculum development outline under the level of application of individual instruction-level classes among the types of curriculum development. Results The results were as follows: First, the elements of the counseling competence were guided by conflict resolution counseling, psychological skills training, guidance counseling, coordination and Intervention, and relationship formation. Second, the curriculum was adopted as a curriculum for sports psychology, theory and practice of counseling, counseling practice and super-vision, and psychological skills training, and non-disciplinary activities were participation in group and personal counseling, and an open counseling case study. Third, the feasibility of the curriculum was calculated in the range of 0.8 to 1.0 for all areas to be reasonable. Conclusions The results of this study have structured the counseling competencies required for pre-service golf coaches. Based on this, the results of the study suggest counseling courses in the curriculum of university. This is expected to ultimately seek to improve the coaching field by enhancing the capacity of the coaches.
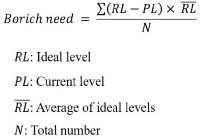



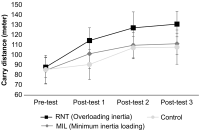
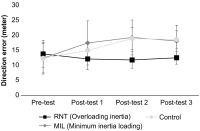
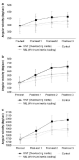
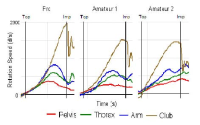
[Purpose] We examined the influence of reactive neuromuscular training (RNT) on golf swing coordination. RNT aims to induce proper coordinative movement by exaggerating the performer’s mistakes. Therefore, we applied RNT using inertia overloading to golfers who have problems with kinematic sequence during a golf swing. [Methods] To examine the effect of 12 weeks of RNT on golf swing coordination, we employed a ball tracking system (launch monitor) and motion analysis system (inertia sensors) were taken on four consecutive periods (pre-test and post-tests 4, 8, and 13 weeks later). Thirty Korean male cadets were divided into three groups based on inertial loading and practiced 7-iron golf swings combined with specific group tasks twice per week. [Results] At pre-test, most participants reached maximal angular velocity near the impact timing (95-100%). However, the deceleration timing of the maximum angular velocity of the proximal segments gradually moved toward mid-downswing as the training sessions proceeded, with the RNT group ultimately outperforming the two control groups. Additionally, the RNT group showed a significantly higher maximum angular velocity in the thorax and wrist. [Conclusion] Our results suggest that RNT can be sufficient to elicit and effective whole-body coordination pattern. Considerable follow-up research is needed on the use of RNT for various sports tasks and the effects of expertise on RNT results.



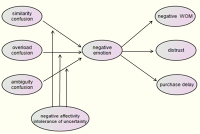
Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify how the three variables of consumer confusion proneness affect consumers' negative emotion, word of mouth, trust and decision postponement during the process of purchasing golf club. Futhermore, this study looked through the moderating effect of the personal characteristics in the relation between consumer confusion proneness and negative emotion. Method A total of 850 questionnaires were used for data analyses(i.e., frequency analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, structural equation modeling) with PASW 18.0 and AMOS 18.0. The results of the study are as follow. Results First, all of the subordinate factors of consumer confusion proneness had a significant effect on the consumer's negative emotion. Second, consumer's negative emotion had a significant effect on negative WOM. Third, consumer's negative emotion had no significant effect on distrust. Fourth, consumer's negative emotion had a significant effect on decision postponement. Fifth, the moderating role of negative effectivity partially had a significant influence in a relation ship between confusion proneness and negative emotion. Sixth, the moderating role of intolerance of uncertainty had a significant influence in a relation ship between confusion proneness and negative emotion. Conclusion The results of this study contributed to provide fundamental information on over all golf industry as in service providing point of view as well as development and application relate to it.

This study reviews whether it is valid to impose the National Sports Promotion Fund (“NSP Fund” hereafter) on green fees of private golf course. NSF Fund has a problem with the Framework Act on the Management of Charges (“MCF Act” hereafter), relevant statute of the fund, in that, in spite of requirements of MCF Act, purposes of imposing NSF Fund are not prescribed precisely and clearly, and “restrictive and supplementary” imposing principles of NSF Fund are not observed. Moreover, although discrimitive imposement of NSF Fund, which is not levied on fees of other sports facilities and public golf course, implies better economic abilities and consequent more abilities of payment of private golf membership, such discrimination is rarely meaningful now that golf has become highly public pastime like those exempt facilities and membership is of little avail to make a profit through speculation. As a result, current way of imposing NSF fund is highly likely to violate the principle of horizontal equity of tax burdens not constitutional rights to equality. Consequently, NSF Fund, which does not keep the principle nor the constitutional rights, should be repealed or improved.

Purpose: The purpose of the present study was to identify the difference of overall putting accuracy and/or distance control among three visual conditions; executing putt focusing vision on the near target(ball), focusing on the far target(hole), and with no vision. In order to satisfy ecological validity, the test was held not on the synthetic putting green in a laboratory, but on the outdoor real putting green. Methods: A putting green with slight slope and minimal break was selected as the test site. The test was held at 8.5m uphill, 13m uphill, 8.5m downhill, and 13m downhill. Twenty participants were asked to putt the ball as close to the target as possible. They were also asked to adhere to their own pre-putt routine having enough time of visual fixation toward the hole to get distance and direction cues. Each Participant putted a total of 12 balls putting 3 balls on each distance-slope experimental condition. Overall putting accuracy score represented actual distance (in meter) from the far target(hole) to the ball rest. Distance control score represented it from the near target(original ball position) to the ball rest. Repeated measure ANOVA was used to verify the raw data. Results: Putt from 8.5m uphill and putt from 13m downhill were revealed to have statistically significant difference only in distance control by visual focus conditions. Putt focusing vision on the ball was the best at 8.5m uphill. Putt focusing vision on the hole was the best at 13m downhill. However, there was no significant difference in overall putting accuracy by visual conditions. Discussion & Conclusion: The results of our study are interesting and valuable from two aspects. First, the presumption is that overall putting accuracy on the real putting green has no significant difference by visual conditions because it is affected by various factors, i.e. memory of distance, slope, break, turf condition, impact quality, body alignment, etc. Second, no consistent evidence was detected that specific visual condition, especially executing putt focusing vision on the hole, was the best for distance control.

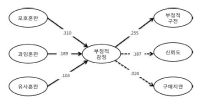
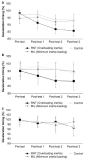
The ever-increasing golf club market made difficult and brought confusion to most of amateur golfers to differentiate and choose suitable clubs for them. Therefore, the purpose of study was to examine how consumer confusion proneness affects consumer’s negative emotion, negative word of mouth, trust and decision postponement, during the process of purchasing golf clubs. 450 questionnaires were distributed to recreational golfers in 6 different golf-driving rages and 4 golf courses located in Seoul, Gyeonggi and Gangwon area with a return rate of 98.4% (n=443). Total of 432 questionnaires were used for data analyses with PASW 18.0 and AMOS 18.0. The results of the study are as follow. First, all of the subordinate factors of consumer confusion proneness had a significant effect on the consumer’s negative emotion. Second, consumer’s negative emotion had a significant effect on negative word of mouth. Third, consumer’s negative emotion had a significant effect on trust. Fourth, consumer’s negative emotion had no significant effect on purchase postponement.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to investigate the applicability of proprioceptive-dependent training as an effective physical training method by analyzing the effects of proprioceptive-dependent training on the accuracy of perceived and actual distance as well as the correlation between the changes in the two variables. METHODS Thirty-six male college students took part in the experiment. Participants were beginners with no previous experience in golf or less than five times of experience. They were randomly assigned to one of three groups; proprioceptive-dependent training, visual-dependent training, and control, maintaining the same sample size per group. The experiment was carried out in the order of pre-test, practice section, and post-test. In the pre-test, putting was tested to assess the accuracy of perceptual and actual distance in the 1-15m distance in a random order using a digital putting analyzer. In the practice section, proprioceptive-dependent and visual-dependent training groups practiced a total of 90 putting, six times per distance with the eyes closed or open. The post-test was the same as the pre-test. The accuracy of perceived and actual distance and the correlation between the changes in the two variables were analyzed using the calculated absolute errors. RESULTS The results of this study showed that there was no difference between groups in pre-test. In contrast, in post-test, the absolute error was significantly decreased in the order of proprioceptive-dependent training, visual-dependent training, and control group in the three distance conditions. Besides, for the proprioceptive-dependent training group and visual-dependent training group, there was a significant positive correlation between the changes in the accuracy of perceived and actual distance. CONCLUSIONS These results provide insight into the applicability of proprioceptive-dependent training for enhancing motor performance by showing the effects of proprioceptive-dependent training on perceived distance, actual distance, and the correlation between the two variables.

The purpose of this study was to identify problems that consumer and golf expert faced with and determine types of similar golf membership in Korea through analysing status of golf semi-membership. In addition, as the law related to golf facility was examined, current issues to improve management system of golf semi-membership were diagnosed, some improvements were deducted. In order to achieve the purpose of this research, case-study, expert interview, survey, examination of typical legal-system and expert advisory meeting were conducted. The results were as follows: First, the type of golf semi-membership was classified by 7. Second, the result of survey from consumer who experienced in purchasing golf semi-membership revealed that the number of experienced respondents was more than the unexperienced. Also, awareness of golf semi-membership brings positive effect to development of golf industry. According to the result of IPA, it was required that the current situation of golf semi-membership market would be improved and managed properly. Third, the results from investigating legal system in Korea showed that provision for reducing property loss associated with illegal contracts might be needed. Eventually, in order to minimize the property loss, complementary of membership contract, mandatory of information discloser, enacting provisions against violation and introduction of cooling-off system would be required.

PURPOSE This study explains how the combination of autonomy support (A) and holistic attentional focus (HF) affects golf putting performance among beginners. METHODS A total of 72 novice golfers were randomly assigned to (1) external focus (EF), (2) HF, (3) A–EF, (4) A–HF, (5) A, and (6) control groups, and their putting accuracy and consistency were measured. RESULTS The experimental findings showed that the group that received only A showed better accuracy than the control group in the acquisition stage and that the best accuracy and consistency were observed when A and HF were combined. The A–HF group maintained their accuracy even after the test. CONCLUSIONS Functional performance can be enhanced simply by providing A, and more positive effects can be expected when A interventions are implemented with HF than with EF.