The purpose of this study was to analyze the differences among behavioral skills of goalkeeper of K-League and national team and the differences among behavioral skills of goalkeeper according to game the result of match. 5 games of K-League Classic and 10 A matches of the national team in 2013 were analyzed by using Soccer Data Analysis Program and ‘Evermedia HD Capture Station’, which is an HD capture equipment with excellent functions of editing and storage of high-definition video. For statistical analysis process, SPSS Version 21.0 was used to conduct t-test and ANOVA. The results of analysis were as follows: First, the differences among behavioral skills of goalkeeper of K-League and national team were higher in the order of catching factor, kick factor, strategy factor, punching factor. The differences among the specific sub-factors of behavioral skills factors was the highest in crossing catching to be followed by cross punching. And goalkeepers of K-League were higher than those of the national team. In back pass kick factor in kick factor and build-up factor in strategy factor, goalkeepers of the national team were higher than those of K-League. In kick factor, there were significant differences in goal kick (out of play), back pass kick (in play), cross punching, and build-up factors. Second, as for behavioral skills factors of goalkeeper according to the result of match, there were significant differences in catching factor, punching factor, and strategy factor; there were no significant differences in ground kick factor among kick factors; there were significant differences in factors of goal kick, volley kick, and free kick.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the level of factors associated with points and the difference among weight categories after the revision of wrestling competition rules from video images. Factors associated with points were average point per a game, average points according to playing type, the occurring frequency of point according to the skills, the frequency and successful ratio of Parter, and the time zone of points occurred. The video contents were concerned on athletes ranked in 1 - 5 (6 person) at 59, 66, 75 Kg categories of Greco-Roman style in the 2014, 2015 World Wrestling Championship. The analysis was done by watching TV monitor several times. Five quantitative factors were tested between weight categories. As the results, no significant difference was found in average obtained point, but significant difference was found in average lost point (p<.05). Average obtained point showed significant difference in cross effect of the type of game and weight category. And average lost point showed significant difference in the type of game (p<.01) and weight category (p<.05), too. The frequency of point by skills of stand and ground wrestling showed significant difference in weight category (p<.001). However, no significant difference was found in frequency of point by time zone among weight categories. In conclusion, the point obtained and lost and the frequency of it are associated with the type of game and skills included in it of Greco-Roman style wrestling. New training program focused on enforcing the correct type of game and skills in it might be useful for developing the performance.
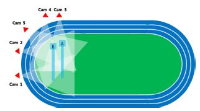
The purpose of the study was to investigate the relationship between the different kinematical variables with respect to the records and techniques performed by the participants during the 2011 Daegu IAAF World Championships Men's Pole Vault Event. Subjects chosen for the study were 8 male athletes who were selected for men's pole vault finals (highly skilled group) and 7 athletes who scored lowest record (skilled group) from the men's pole vault qualifying round. Personal best record of the each subjects were chosen to perform two dimensional (2D) and three dimensional (3D) video analyses. The data were obtained at 60 Hz with the use of five video cameras and digitizing was performed. Kinematical variables were calculated after smoothing the data using 2nd order Low-Pass Butterworth filter at cut-off frequency of 10 Hz and Independent samples t-test was performed to test any differences between two subject groups. The results: during the run-up stage, the horizontal velocity rate of the number of steps and run-up phase was obtained higher in highly skilled group than skilled group. During the take-off phase, deceleration in the horizontal velocity rate was observed in highly skilled group than skilled group. Distinct technical characteristics of distant and lower take-off of the take-off angle (angle of pole support) were also observed in highly skilled group than skilled group. During the pole bending and releasing phase, horizontal velocity was generally higher in highly skilled group than skilled group. It is considered that highly skilled group was able to jump higher as the vertical velocity during the pole bending as well as release phase was much higher in comparison to the skilled group.

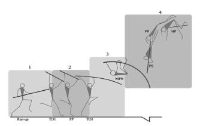
Purpose This study was carried out for the purpose of providing national players of our country by grasping various techniques and difficulty composition of world-level players. Methods For doing so, this research was executed by objecting 9 finalists in parallel bar of 2012 London Olympics and 8 finalists in parallel bar of 2016 Rio Olympics. Collected datum were treated with average, standard deviation, percentage (%) by using SPSS 18.0, and they was analyzed while securing feasibility through expert meeting. Results Research results are same as follows. First, Rio Olympics players appeared higher than London Olympics such like 6,61 points in average D-score of 2012 London Olympics final game and 7.0 points in average D-score of Rio Olympics final game. Second, I group was turned up to prefer Healy technique (34.88%) of D difficulty in two olympics. Third, Ⅱ group carried out Bwd. uprise and salto fwd. p. to sup technique of D difficulty by each 4 players (36.35%) in two olympics, so the technique was displayed as preferred techniques of players. Fourth, Ⅲ group executed at the London Olympics, C difficulty was the most frequently used, but at the Rio Olympics, D difficulty and E difficulty were the most frequent. Fifth, Players in London Olympics and Rio Olympics executed Basket to hdst technique, and it appeared to be most preferred technique by players. Sixth, Ⅴ group executed at the London Olympics, D difficulty was the most frequently used, but at the Rio Olympics, F difficulty was the most frequent. Conclusions These findings will be useful datum to gymnasts and instructors of our country by providing valuable datum in preparing 2020 Tokyo Olympics after grasping preferred techniques and trends of world-excellent players.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to analyze the performance contents of men's floor exercise and to provide basic materials for achieving excellent results at world competitions. Methods Teams ranked 1 - 12 who participated in the World Championships' floor movement group competition selected a total of 59 players by the convenience sampling method and carried out technical statistics, frequency analysis, member variable variance analysis, and post hoc analysis. Results First, as a result of frequency analysis of the difficulty of each group, all the teams ranked 1 to 12 liked the most difficulty of C and found that they do not like the F difficulty the most. Secondly, there was a difference in average for each group's start score, ranking 1st to 4th> 5th to 8th> 9th to 12th place. Thirdly, there was a difference in average of difficulty levels for each group B, C, E, and it became very significant with E difficulty.Results of post hoc analysis B difficulty (9th to 12th> 1st to 4th, 5th to 8th), C difficulty (9th to 12th> 1st to 4th), E difficulty (1st to 4th> 5th to 8th ·9th to 12th). Conclusion These results show that in floor exercise, the art of more than C difficulty and the connection technology of A, B, C, difficulty, E and F, difficult difficulty such as difficulty, creative and dynamic performance composition is excellent It clearly states that it is a condition for getting results.
The purpose of this study was to analysis of moving distance during games, time and heart rate for hockey games using GPS (global positioning systems) by positions in Korea national female athletes. The subjects were Korea national female hockey players (n=13) including 4 forwards, 4 midfields, and 5 fullbacks that participated in five Korea vs. Japan international games. All subjects were wearing GPS throughout the games. The results were as follows: Firstly, the average total travel distance per game was approximately 5.7km and higher in the second half. Physical movement in the games was not different from positions where 70% of physical movement was performed at low intensity and 30% at moderate and/or vigorous intensity, suggesting that the subjects; physical movement was performed at the appropriate level of exercise intensity. Secondly, during the game, the subjects performed physical movement faster than 11km/h for 22 minutes, indicating that the subjects could maintain their physical movement at a relatively faster speed throughout the games. In particular, midfields showed a greater amount of physical movement at moderate speed. Thirdly, the average exercise heart rate was 145bpm, which was equivalent to 60% of HRmax. The subjects maintained their average exercise heart rate greater than 150bpm (above 60% of HRmax) for 40 minutes during the games, indicating that the players had an ability to maintain physical movement at high intensity throughout the games. In conclusion, in spite of the fact that Korea national female hockey players have an ability to maintain physical movement at a relatively faster speed and higher intensity, their physical movement and performance are often affected. Therefore, it is necessary to develop and apply the specific interval training program for national female hockey players that can facilitate the faster recovery from the repetitive physical movement requiring power and speed at high intensity.
PURPOSE This study was conducted to estimate the tendency of psychological factors influencing cycling performance by analyzing the characteristic factors of athlete reputation in the news big-data. METHODS To explore the psychological factors influencing cycling performance, an open questionnaire was conducted on 82 cyclists, and Inductive Content Analyses was performed. Overall, 89,520 news articles were collected through BIGKinds, and forming factors of athlete reputation were derived through LDA topic modeling analysis and inductive categorization. Through regression analysis, time series tendency of the factors of athlete reputation was calculated. Finally, the tendency of psychological factors to influence cycling performance was estimated based on the previously derived results in this study. RESULTS The psychological factors influencing cycling performance were found to be; emotion control, trust capital, cognitive control, motivation and communications with the coach. The forming factors of athlete reputation was found to be; reporting of the sports event, infrastructure creation, analysis to performance, moral issue, social environmental changes and sports gossip. The time series tendency of the forming factors of athlete reputation was found to include the categories of Hot, Warm, Cool and Cold. The psychological factors influencing cycling performance are estimated to expand to exercise performance and moral intelligence. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study suggest that the discussion of psychological factors influencing cycling performance extends not only to exercise performance, but also to moral intelligence, reflecting the socio-cultural context in the discussion of performance.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between performance factors and physical fitness in secondary school female biathlon athletes. Participants in this study were 14 female biathlon athletes. Methods All factors such as aerobic capacity(VO2max, %AT), wingate test(peak power, average power, fatigue index), isokinetic test(trunk, knee, hip, ankle), 1RM test(leg press, chest press, lat pull down), physical fitness(grip, knee and back muscle strength, sit & reach, power, agility) were tested. In order to analyze collected data, pearson product moment and multiple regression analysis were utilized. The results were summarized as follows : First, there was a significant correlation between aerobic. Results The results were summarized as follows : First, there was a significant correlation between aerobic capacity and three factors(standing broad jump, isokinetic test 60° right knee extension)(p<.01). There was a significant correlation between wingate test and four factors(isokinetic test 30° left ankle ever, 30° right ankle ever, 120° left ankle inver, leg press)(p<.10). Conclusion These results suggested new evidence that ankle strength is necessary for performance in female biathlon athletes.


This study aimed to analyze the patterns of service return and the 3rd stroke in relation to the winning and losing points in Badminton men's doubles matches. Especially the comparison of the patterns between rally point and service server game systems was made. Video records of 12 top elite teams were analyzed. As a result, there were significant differences in the total stroke patterns between the rally point system and the server game, and there was a higher offensive stroke tendency. After classification of situations with ‘after the service trial’ and ‘after the service return’, there were high number of winning ratio and offensive stroke in the after the service situations. There were no significant difference in the winning/losing points and winning ratio when the types of 3rd shot attempts were analyzed. I case of the win and lose in service return, there was a significant difference in the server game while not in the rally point system. Offensive stroke ratio in the server’s return categories and the service return strokes’ categories, and was no difference in shots after the return of service in the server team. From the investigation of offensive stroke ratio and winning ratio, there was a high ratio in the rally point system game but no difference in the server game. When aggressive service return took place, rally point system had higher winning ratio, but the server game system did not display such characteristic. Based on these results, recommendations of service anticipation and aggressive plays for Korean Men's doubles game have been suggested.

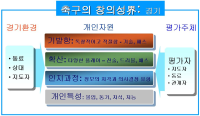
The purpose of this study was to explore a framework of understanding football performance. Researcher review was conducted to organize perspectives for football performance and drew implications as well as drift of football performance based on intelligence approach. Discussions for intelligence had been proceeded in concepts of learning ability, multiple intelligence, successful intelligence, and moral intelligence. Discussions of football performance approaches fitness, skill, and strategies in traditional intelligence aspects. The multiple intelligence perception discusses perspective, mentality, body, and analysis. The successful intelligence perspective deals with creativity, practical intelligence, and football talents. However, specific discussions for moral intelligence have not been progressed yet. FIFA’s social responsibility project and UEFA’s RESPECT campaign reflect that the discussions of football performance develops in a way of the moral intelligence. In European football, issues regarding value, such as RESPECT and against Racism, are currently emerging. Considering the change in the European football, the global football leagues will share the issues related to value in the near future. Given the fact that discussion for intelligence had been proceeded learning ability, multiple intelligence, successful intelligence, and moral intelligence, the moral intelligence will be a main concern in the further football performance discussion. The moral intelligence will be incorporated into football performance evaluations soon. Furthermore, teams and players will strive to place efforts in order for pursuing value and reputation as factors of performance.