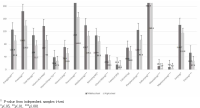
Purpose This study aimed to evaluate the nutrient intakes and diet quality of national youth badminton players participating in summer camp training in 2016. Methods Total of 40 middle school players and 60 high school players were included in the study. Two players with skipped meals were excluded from the final target. Food intake data for the 3-day using 24-hour recall method were obtained and analyzed using the CAN-pro 5.0 (Web ver. Korean Nutrition Society, Korea). Differences in nutrient intakes and diet quality were compared between middle school players and high school players using independent samples t-test. Results Intakes of vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin B6, folic acid, calcium, chloride, magnesium, and zinc in both groups were lower than (RNI) recommended intakes of KDRIs. On the other hand, intake of sodium significantly exceeded the recommended nutrient intake (RNI) of KDRIs in both groups. The NARs (Nutrient Adequacy Ratio) of vitamin C, vitamin B6, folate, calcium and zinc were less than 0.75 in both groups. The NARs of 11 nutrients except for folic acid were significantly lower in high school players. The MAR (Mean Adequacy Ratio) of middle school players was 0.78, significantly higher than 0.64 of high school players. The INQs (Index of Nutritional Quality) of vitamin C, vitamin B6, folic acid, calcium and zinc were less than 0.75 in both groups. The INQs of vitamin A, vitamin B6 and zinc were significantly lower in high school players. On the other hand, the total DDS (Dietary Diversity Score) of high school players was 3.88, significantly higher than 3.29 of middle school players. The DDS of fruit group as well as milk and dairy group were particularly low. Conclusions The results suggest that balanced diet managed by professional dieticians along with nutrition education should be implemented to improve nutrients intake and diet quality of national youth badminton players.

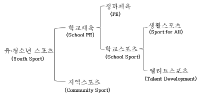
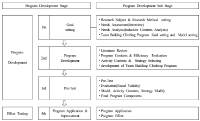
Purpose and Methods The purpose of this study is to clarify the concepts of ‘youth sport policy’ and policy areas as an alternative to school physical education concept and to provide a core conceptual framework for the development and implementation of youth sports policy in the future. Results The notion of youth sport policy is a process of seeking rational decision-making and optimal alternatives to solve the social problems associated with sports participation of youth in elementary school(aged 6 years) to high school(aged 18 years). The concept of 'youth sport' can reflect modern culture rather than 'school physical education' and it can be seen as more future oriented for lifelong participation in sports. The areas of youth sport policy are classified into physical education, school sport, and community sport. Physical education refer to the physical education classes operated by the Ministry of Education, and the school sport refers to the sports activities that take place throughout the school. Community sport is sports activities that are carried out outside the school by the choice of youth, which is the area where cooperation between the public sector and the private sector is needed. Conclusion In conclusion, healthy and active life for youth is required to establish cooperative governance of related organizations in order to ensure proper linkage between youth sport policy areas. Through this, it is necessary to solve the social problems of youth and promote their lifelong enjoyment of sport more consistently, efficiently and effectively.


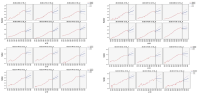
The present study has been carried out with a purpose of a long term estimation for the body size and BMI (Body Mass Index) of Korean children and youth using ARIMA, a time series model. In order to select an estimation model for the optimum time series, among the time series analysis method of SPSS22.0 statistic programs, a multivariate ARIMA (p,d,q) model has been selected that has an input series (physical education facility, time spent for physical education, animal source foods, GDP deflator, animal source food intake ratio), using annual average data of height, weight, and BMI data from 1965 to 2015. Among the several optimal measurements in ARIMA model with estimation variables, an optimal RMSE-based model (RMSE: Root Mean Square Error) has been selected. Using this model, the estimation model and estimated values of children’s height, weight, and BMI have been suggested for each age group. The results are as the following. The trend estimation of height follows a logistic curve, with both male and female groups showing increasing trends. The weight has a trend of increasing ratio higher than height. BMI also shows a trend curve similar to weight. The estimation model has been mostly ARIMA(0,1,0). In particular, the average BMI has been estimated as 22-23 for male students in 6th, 8th, 9th, 11th and 12th grade in 2030. This indicates the recent increasing obesity as children and youth occupy most of daily time for play culture that is far from physical activities, such as computer games, smartphone games, and video games at home.




The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of team building climbing program on happiness, social development, self-esteem, stress, and depression of the youth. The participants consisted of 27 university students. The self-report instruments were compose of happiness scale, social development inventory, self-esteem scale, stress inventory, and depression scale. Qualitative data were participants’ perception about the effects of team building climbing program. Firstly, team building climbing program had positive effect on happiness of the youth, while climbing program had not significant effect on happiness of the youth. Secondly, both team building climbing program and climbing program had positive effect on social development of the youth, while team building climbing program was significant higher than climbing program in post-time. Thirdly, team building climbing program had positive effect on stress of the youth, while climbing program had not significant effect on stress of the youth. Fourthly, both team building climbing program and climbing program had positive effect on self esteem of the youth, while there were not significant between team building climbing program and climbing program in self esteem of post-time. Fifthly, both team building climbing program and climbing program had positive effect on depression of the youth, while there were not significant between team building climbing program and climbing program in depression of post-time. Limitations of this study and future implications were discussed.

The purpose of the study is to find the impact of social and economic factors in physical activity of children and youth. This study utilized the data from 4th Korean Children and Youth Panel Study(KCYPS), and the analysis were carried out based on the starting sample of 2,009 from ‘the elementary 4 panel’ and 1,978 from the ‘middle school 1 panel’ and 1,984 from the ‘high school 1 panel’, 5,971 full data were used in the final analysis. Data were processed using hierarchical regression analysis and it was statistically validated at the significance level of 0.05. First, Pearson r and Spearman ρ showed that all variables are statistically significant correlations. Second, among the first factors of personal and family characteristics, household income level(B=.113), family composition(B=-.049) and parental education (B=.060) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, parental education (B=.027) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Third, among the second factors of community-level characteristics, Gini coefficient (B=-.810), wealth concentrating (B=.120) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, the Gini coefficient (B=-0.315) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Additional factors that determine the coefficient of variation in the level 2 were found to be 0.623 and 0.001 respectively. Therefore, second factors of community-level characteristics are added such as Gini coefficient, wealth concentrating were explained to children and youth exercise time during physical activity 62.3%(p<.01) and subjective evaluation of physical education in grades 0.1%(p<.01). predictive power to
The purpose of this study was to examine the current status of school sport club(SSC) participation and to explore relationship between school sport participation and positive youth development. In order to do this, a survey was conducted with 403 elementary, middle, and high school teachers who are currently taking charge of SSCs, and also individual interviews were conducted with 22 students. In addition, the youths' developmental asset questionnaire was administered with 412 middle school students. The survey results from 403 teachers showed that SSCs have potential to contribute to positive youth development because teachers are placing an emphasis on character development as well as physical and social development through SSC activities. In addition, participants who regularly participate in physical activities had higher internal and external developmental assets than non-participants or irregular participants. Specifically, students participated in SSC more than twice a week had higher internal and external assets than students participate once a week. In addition, participants who engage more than one hour per session had higher internal and external assets except constructive use of time and social competence. Discussion and implications for organizing SSCs to provide developmental contexts and contents for positive youth development were provided.
The purpose of the study was to determine relationship of abdominal fat, adipocytokine, bone mineral density, and bone turnover markers in obese male adolescents. Twenty four male adolescents (obese: 12, normal: 12) volunteered to participate in the study. Anthropometry and skeletal maturity were measured. Body composition and bone mineral density were estimated by DXA (Hologic, QDR-4500, USA). Abdominal fat with total adipose tissue (TAT), visceral adipose tissue (VAT), subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT), and visceral adipose tissue to subcutaneous adipose tissue ratio (VSR) were estimated by computed tomography (ECLOS, HITACH, Japan). Blood samples were obtained for and analysis of adipocytokines including leptin and adiponectin. Bone turnover markers, osteocalcin (OC), bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BALP) for bone formation markers and N-terminal telopeptide (NTx), C-terminal telopeptide (CTx) for bone resorption markers were analysed. All data were analyzed utilizing SAS 9.3 (SAS Institute, NC, USA). Independent t-test was used to evaluate the differences between obese adolescents and normal adolescents. Pearson correlation analysis was applied to figure out the relationship between abdominal fat, adipocytokines, bone mineral density, and bone turnover markers. Multiple regression analysis was used to find out the factors of abdominal fat which influence on bone mineral density. A level of significance was set at p<.05. The results of the study indicated that fat tissue (p<.001), percent body fat (p<0.001), TAT (p<.001), VAT (p<.001), and SAT (p<0.001) were significantly higher in obese adolescents than normal adolescents. However bone mineral contents were significantly higher in normal adolescents. Normal adolescents have significantly higher whole body BMD and lumber BMD than obese adolescents. Abdominal fat including VAT and SAT related negatively with whole body BMD and lumbar BMD. Leptin related negatively with BMD whereas adiponectin related positively with BMD. NTx for bone resorption marker related positively with abdominal fat. Visceral adipose tissue was a predictor for whole body BMD and lumbar BMD in explaining 46% and 32% in adolescents. In conclusion, obese male adolescents have lower whole body BMD and lumbar BMD than normal adolescents. Abdominal fat including VAT and SAT related negatively with whole body BMD and Lumbar BMD. And leptin and adiponectin were closely related with BMD. Finally, visceral adipose tissue was a predictor for whole body and lumbar BMD in adolescents.
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effects of motion analysis and image training using self-modeling with visual cues on the skill performance, imagery, and sports confidence of adolescent female soccer players. METHODS The participants were elite soccer players from two girls’ high school soccer teams divided into an experimental group (D girls’ high school, n=16) and a control group (I girls’ high school, n=13). The experimental group underwent motion analysis and image training when performing penalty kicks, short kicks, and long kicks using self-modeling with visual cues, while the control group underwent training using self-modeling videos without visual cues. Before and after the training, the evaluation score was calculated according to kick performance, and the imagery and sports confidence factors were measured. For the statistical analysis of all collected data, descriptive statistics, the Friedman test, the Mann-Whitney U test, and two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance were used. RESULTS First, on the motion analysis using self-modeling with visual cues, the experimental group’s penalty kick and short kick scores were improved and differed significantly, but no significant change was noted in long kick score. Second, as a result of image training using self-modeling with visual cues, all visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability factors of the experimental group improved except for the auditory factor, and the interaction effect was confirmed. In addition, the stated sports confidence of the experimental group was improved and the interaction effect confirmed. CONCLUSIONS The analysis of kick motion using self-modeling with visual cues was effective for the penalty kicks and short kicks of adolescent female soccer players. Moreover, this study confirmed that the analysis of kick motion improved the visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability sub-factors of imagery and significantly affected the players’ stated sports confidence.
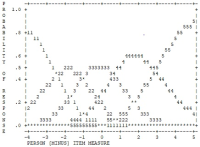
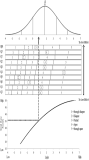
Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine item goodness-of-fit and the optimal categorization of an instrument measuring Korean elite young soccer player’s self-esteem using a two-facets Rasch model (item parameters and person parameters). Methods 10-item Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale (RSES) with five response categories was administered to 366 elite young soccer players from the Korea football association. The Rasch analysis was conducted by WINSTEPS 3.65. Results First, the model fit the data well. Second, 5-category rating scale did function well. Third, a item-person map illustrated the distribution of RSES items and person’s level of self-esteem. Fourth, the separation reliability of the items and person was shown to be an acceptable degree of confidence, respectively. Lastly, there was statistically significant difference in self-esteem between starting players and bench players, which supported the known-difference evidence of validity. Conclusion These findings provided additional support for the suitability of the RSES in assessing self-esteem of Korean elite young soccer players.



Purpose The purpose of this study was to further understand how out-of-school adolescents’ self-esteem and interpersonal relations have changed in a peer mentoring basketball program and what they have experienced for the program It was action research of qualitative research method. Methods 4 out-of-school adolescents in the adolescents Center of C-si were selected as the participant. The data was collected by in-depth interviews, participant observation, and research journal. The collected data was then analyzed by an inductive categorical system. Results The findings were summarized as follows: the out-of-school adolescents showed somewhat low self-esteem and difficulties of interpersonal relations at an early stage participating in the peer mentoring basketball program. However, their self-esteem and interpersonal relations have been gradually changed during the program. First, they participated in various mentoring activities and self-expression activities. Their self-esteem has been improved as they found their real values, communicated with others, and lived with their confidence. Second, they overcame personal relations with fear and indifference of others, extended personal relations, and sympathized with others to solve the problem that they had as interpersonal relations. Conclusions The out-of-school adolescents has positively changed their self-esteem and interpersonal relations through the peer mentoring basketball program. We expect that out-of-school adolescents could overcome their difficulty and live well their life in the future.

