[Purpose] This study was designed to explore Yuna Kim’s psychological strengths and the contextual factors, which led her to obtain the gold medal and the reflection of peak performance and preparation at the 2010 Olympics. It was hoped that by sharing the experience of one of the top athletes, other athletes would learn from her and prepare themselves better for Olympics in the future. [Methods] A case study method was applied with a qualitative approach. To obtain the purpose of the study, five in-depth interview sessions including introductory and member checking procedures were conducted. The interviews were recoded and transcribed verbatim, and content analysis was used to inductively analyse the data. [Results] The four general dimensions that were discovered in the results included Social-external Factors, Personal Traits, Coping Strategies, and Peak Performance. The social-external factors consisted of social support and attached/detached relationships while personal traits were personality traits, confidence and motivation. Coping strategies to overcome external and situational pressures were detached coping and resilience whereas peak performance was reflected on flow and the state of being mindful. [Conclusion] In conclusion, Yuna Kim’s strength was parallel with the previous research on the top athletes and other findings such as adaptive perfectionism and a sense of rivalry in the research were discussed.


The purpose of this study was to explore and confirm Kumi-kata related factors of muscle strength by performance level in Korea elite female judoists. In order to achieve this purpose, 14 elite female judoists participated to this study. The subjects were divided to two groups (World Class Group and Non-World Class Group) according to their world ranking level(by ranked 30th). The analysis factors were repeated grip strength, Kumi-kata specific pulling strength and isokinetic strength of trunk joint. The results were as follows: Firstly, World Class Group had significantly higher repeated grip strength as compared to non-world class group (p<.001). Secondly, World Class Group had significantly higher specific Kumi-kata pulling strength as compare to non-world class group (p<.05). Finally, The differences between the two groups for isokinetic strength of trunk joint were non-significant. The results of this study indicates that a strong relationship exist between Kumi-kata related specific muscle strength and performance level in korea elite female judoists.

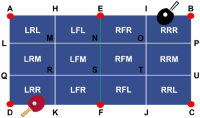
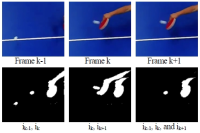
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop algorithms and software that can track the trajectory of table tennis balls using image-processing algorithms to obtain information quickly for under and establish tactics used in table tennis. Methods The algorithms used in the field of computer vision were applied on two matches played by novice and two matches during international competitions by elite athletes. Reliability analysis was performed by comparing the table tennis ball bounce frequency in each zone obtained through the automatic method and the manual method. Results The mean reliability of the two novice games was only 85.1 ± 3.69%, total error was 14.9 ± 3.69%, overestimation error was 52.2 ± 9.78%, and underestimation error was 47.8 ± 9.78%. While the mean reliability of the two international tournaments was 71.8 ± 0.87%, the total error was 28.2 ± 0.87%, overestimation error was 82.0 ± 8.03%, and underestimation error was 19.2 ± 7.75%. Conclusions Although the target reliability of algorithms and software developed in this study was achieved only in novice competitions with 80%, the over-estimation errors were generally high in international competitions, showing the potential for further improvement.




Purpose The purpose of this study was to find out the physical characteristics of Wushu athletes by comparing the differences on the results of physical fitness between the male athletes of the Wushu national team Taolu and the Sanda group. Methods Measurement of basic and professional fitness based on muscle function, targeting 37 men Wushu national team players (24 taolu, 13 Sanda) in the selection and evaluation contests twice in 2018 and 2019. Body composition, isometric muscle strength, flexibility and equilibrium, anaerobic power, and isokinetic muscle strength. The fitness factors were divided into two groups, Taolu and Sanda. Results First, body fat rate of the Sanda athlete group was significantly lower than that of the taolu athlete group (p<.01). Second, in the isometric muscle strength category(back muscle strength, grip strength), the Sanda athlete group had higher muscle strength than Taolu athlete group, but there was a statistically significant difference only in the left grip strength (p<.01). Third, in terms of flexibility and equilibrium, the taolu players were significantly higher in all items(p<.001). Fourth, in the anaerobic power, the taolu athlete group had higher both the peak power and the mean power, and there were a significant differences(peak power: p<.01, mean power: p<.001). Fifth, isokinetic muscle strength was significantly higher in the right knee flexion of the taolu athlete group (p<.01), and lumbar extensor muscle was significantly higher in the Sanda athlete group (p<.05). Sixth, in the isokinetic strength ratio, the knee flexion ratio of the Sanda athlete group were significantly higher on the left and right knee flexion and extensor ratios (p<.05). In addition, in the lumbar flexor and extensor ratios, the group of Sanda athlete group were significantly higher on the lumbar extensor(p<.05). Seventh, there was no significant difference between two groups in isokinetic muscle power. Conclusions The results of this study can be used as basic data to improve the efficiency of technical and physical training through the analysis of the characteristics of Taolu and Sanda. The effectiveness of this training will help to improve the performance.
PURPOSE Recreation specialization theory, which is characterized by a unique development process and progress, has been found to have varied pathways that develop in different patterns based on each dimension of recreation specialization. This study aimed to investigate how each sub-dimension of specialization changes as the degrees of experiential participation (frequency, period, and intensity of participation) and goods investment (expenditure) of the scuba divers increase. METHODS In the summer of 2021 (May-August), a purposive sampling method was used to collect samples from young scuba divers, and 278 copies of valid data were used for the final analysis. Frequency analysis, descriptive statistical analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, curve estimation analysis, and hierarchical regression analysis were performed using SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 24.0 ver. RESULTS The findings were as follows. First, the quadratic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the scuba divers’ participation intensity and cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations based on experience. Second, the cubic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the participation period, frequency of participation, and cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations of scuba divers. Third, the cubic nonlinear model was identified as the optimal model for the relationships between the expenditure cost of scuba divers and the cognitive, behavioral, and affective recreation specializations in the center of the goods. As the period, frequency, and expenditure of scuba diving participants increased, the relevant cognitive, behavioral, and affective specializations did not progress in a linear manner; instead, they went through an intermediate maintenance stage and developed to a higher level. CONCLUSIONS Progressive and meaningful consumption of experiences and goods further promotes recreation specialization. Any future follow-up study should identify a trade-off point in the development of the recreation specialization in a step by step manner.

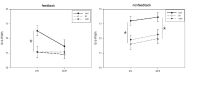
[Purpose] Perception plays an important role in understanding the environment or related objects in order for humans to perform physical movements more effectively. Sometimes they create different movements with different perceptions. Especially, visual perception errors that occur in sports situations can have a considerable effect on performance. Accurate knowledge of the environment in this process of perception is important in performing movements or actions. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of learning formation on perception using Muller-Liar illusion diagrams. To measure this, we compared the feedback group that induced knowledge learning and the control group that did not provide knowledge To see if there is a difference. Therefore, in this study, we have provided a visual feedback that can establish the cognitive awareness of the actual stimuli length to subjects, and investigated the changes in their matching action responses. [Methods] A total of 32 young and healthy subjects were randomly divided into two groups (Feedback and Non-Feedback groups). Subjects were asked to match the stimulus size with their index fingers and thumbs. Initially (pre-test), three different visual stimuli (inward, outward, and no arrows) were randomly presented 60 times (20 times each) and the grip sizes were recorded using the Liberty Motion Analysis System (Polhemus Co., America). Then, video clips of two lines merging each other were presented as feedbacks. Post-test protocol was identical to the pre-test protocol. The data were analyzed using the 3-way ANOVA with one RM factor (2 x 3 x 2). [Results] Results showed a significant 2-way interaction effect. Post-hoc results showed significant interaction between stimulus shape and pre/post-tests only in the experimental group. There was a significant decrease in the grip size after feedback in the OUT condition of experimental group. However, in the control group, there was no interaction between stimulus shape and pre/post-tests. [Conclusion] Overall, current results indicates that, while visual illusion can affect the action, the provision of visual feedback can establish the awareness of actual stimulus size and suppress the influence of illusion on action.

PURPOSE This study aimed to apply a capacity building program to sport life skill leaders and to provide cases of this process. METHODS The study participants included four leaders (male=2, female= 2, Mage=37.5) who were managing a sport life skills program at a university. They participated in a capacity building program, which consisted of (a) understanding (leader seminar), (b) application (managing the sport life skills program), and (c) evaluation (leader’s self-reflection), which were conducted in eight sessions. Four leaders conducted self-evaluations using program quality assessment (PQA) during every session, and quantitative and qualitative data were collected. Qualitative data were derived using a cross-case analysis, and quantitative data were used for calculating the effect size after performing the paired t-test. RESULTS Analyzing the reported cases of sport life skill leaders, the use value of the capacity building program was identified. Furthermore, the cases reported by the four leaders enabled observation of how the leader’s capabilities were strengthened. In the paired t-test, the effect size of physical and psychological safety, appropriate structure, supportive relationship, opportunities to belong, support for efficacy mattering, opportunities for life skill building, excluding integration of family, school, and community effort, were all significant. All effect sizes were found to have “very large effects.” CONCLUSIONS The capacity building program played a positive role in strengthening the leaders’ life skill coaching capabilities. These findings have practical implications—chiefly, it is important to strengthen leaders’ or coaches’ capabilities in order to foster life skill development and transfer of student-athletes.
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine contemporary sports reality and its problems through the feature-length independent film <Not Out>, which focused on baseball, a popular sport, and highlighted its rather dark side. METHODS The researcher performed a textual analysis using the perspective of critical theory. RESULTS Gwang-ho was the hero of a walk-off hit in the national baseball competition final, who suffered from three career strikes during his third year of high school and thought that he had bright future ahead of him. Before the amateur draft, Gwang-ho boldly rejected the proposal of a trainee contract from a professional team (strike 1), then he was subsequently not selected in the amateur draft (strike 2), before he applied for the college entrance examination for baseball specialties, and was eventually rejected. (strike 3) In the end, he was able to enter college through a bribe given by his father (not-out situation). CONCLUSIONS <Not Out> is a film based on a true story, and it showcased the realities of elite sports by revealing the dynamics of society and school, where the main character responded with reluctance and indifference. This movie highlighted the realities of delinquency, violence, abusive language, bribe, and violations of the right to learn and how these have continued to evade the law despite being thought to be gone.
This study was to explore and confirm factors of sport psychology counseling needs in Korean elite coaches. In order to achieve this purpose, 56 elite coaches in Korean Olympic training center at Taereung and Jincheon responded on open-questionnaire and 260 coaches responded on survey. Open-ended questionnaire responses were analyzed by inductive content analysis and collected survey data were analyzed by exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory analysis. The results were as follows: Firstly, sport psychology counseling needs of elite coaches were competition preparation, negative athlete-coach relationship, athlete private problems, performance degradation, pressure on performance result, injury management, team cohesion degradation, motivation, training management, different gender athlete control, athletes drop out, pressure from outside, conflicts with colleagues, neglecting from athletes, feeling of incompetence, emotional control problem, and so on. Secondly, based on these responses, closed-ended questionnaire was developed, surveyed, and analyzed. Exploratory factor analysis illustrated that sports counseling needs of coaches were performance enhancement strategies, unreasonable pressure, negligence on training, coaching stress, competition result stress, conflicts with athletes. Finally, confirmatory factor analysis showed that construct of sport counseling needs illustrated appropriate fit indices values. The results of this study contributed to provide fundamental information on coaching education program and sport psychology counseling program development and application. Consequently, it will help coaches to control their mind at coaching in training and competitions.

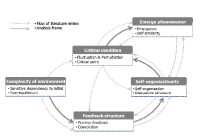
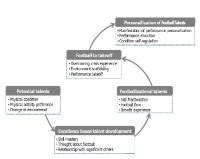
Purpose This study was aimed at interpreting the football talent development stages based on complexity theory. Methods The data for this study was gathered through literature review and in-depth interviews that were analyzed by thematic analysis. Literature review of the studies regarding complexity theory revealed the features of complexity theory and five football players participating in the K-league were interviewed. Gathered materials were analyzed by the thematic analysis. Initial codes and potential themes of football talent development stages, the conception and potential themes of the complexity theory were interpreted by metaphorical analysis. Results Results of literature review were as follows: analysis frame of complexity theory were organized environment of complexity, feedback structure, self-organization, critical condition and emergent phenomenon. The football talent development stages, interpreted as a result of literature review, were divided into Potential Talents, Excellence based Talents Development, Footballizational Talents, Football to Takeoff and Personalization of Football Talents. The stages were specifically materialized as follows: Potential Talents was materialized into physical condition, physical activity preference and change of environment. Excellence based Talent Development was materialized into skill mastery, thoughts about football and relationship with significant others. Footballizational Talents was materilized into skill fractionation, football flow and growth experience. Football to Takeoff was materialized into overcoming crisis experience, performance scaffolding and performance takeoff. Personalization of Football Talents was materialized into manifestation of performance personalization, performance evolution, condition maintenance. Conclusion Football talent development stages, interpreted by means of complexity theory, were divided into Potential Talents stage, Excellence based Talent Development stage, Footballizational Talents stage, Football to Takeoff stage and Personalization of Football Talents stage. Utilization of this study as a fundamental resource of football talents development programs and as a means to understanding football talents development is looked forward to.