Purpose This study was to investigate the systematic application of the life skills program and its effects in a sport setting. Methods Participants were 14 college students(8 males and 6 females) majoring in Taekwondo. Survey tools were utilized to measure items of life skills and journals. Data analyses were conducted by using Excel program and inductive content analysis. Results First, life skills in this study consisted of goal setting, self-talk, imagery, cognitive restructuring. Life skills program has undergone a procedure, such as the introduction, training, development, application, and evaluation. Second, the average scores of life skill variables have been changed according to measured points. Specifically, the average scores of goal setting and self-talk were highly increased over time and the average score of imagery indicated gradual rising line. The average score of negative thought was slightly reduced over time. Third, regarding effects of this program, participants’ responses were categorized into six components; performance enhancement, positive thoughts, chances of change, goal setting, struggling efforts, and motivation formation. Further, participants stated this program was a great opportunity to develop these components. Conclusion The application of life skills program in sport settings will contribute to participants’ life span developmental change in cognitions, emotions, and behavior.



PURPOSE This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the effectiveness of exercise programs in improving physical fitness among middle-aged adults in Korea. METHODS A literature search was conducted using KCI-registered databases on DBpia, RISS, and KISS up to September 21, 2023. The review followed the PICOSD framework (population: middle-aged adults; intervention: exercise program; comparison: did not participate in exercise program; outcome: physical fitness; study design: randomized controlled trials). Two researchers independently evaluated bias using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2). The data was synthesized using the CMA 3.0 program, applying a random effects model to estimate the overall effect size using Hedges’g. RESULTS Out of 914 screened documents, 15 studies were selected, comprising 405 participants. The overall effect size for improving physical fitness was significant (g=0.994, 95% CI: 0.712–1.276). Sub-analysis indicated significant improvements in various components, including muscle strength (g=1.295, 95% CI: 0.909-1.682), muscular endurance (g=0.972, 95% CI: 0.637-1.308), cardiorespiratory endurance (g=1.092, 95% CI: 0.453–1.731), flexibility (g=0.883, 95% CI: 0.555–1.210), muscle power (g=1.421, 95% CI: 0.656– 2.186), and agility (g=1.854, 95% CI: 0.347–3.361) compared to the control group. An additional analysis focusing solely on women revealed a slight increase in effect size, although the order of effect sizes remained consistent across fitness components. CONCLUSIONS This meta-analysis confirms the effectiveness of exercise programs in enhancing physical fitness in middle-aged adults. The systematic review also highlights key considerations for designing exercise programs for this demographic. Future studies should aim to minimize bias and enhance the quality of reporting to ensure more robust results.
PURPOSE This study aimed to apply a capacity building program to sport life skill leaders and to provide cases of this process. METHODS The study participants included four leaders (male=2, female= 2, Mage=37.5) who were managing a sport life skills program at a university. They participated in a capacity building program, which consisted of (a) understanding (leader seminar), (b) application (managing the sport life skills program), and (c) evaluation (leader’s self-reflection), which were conducted in eight sessions. Four leaders conducted self-evaluations using program quality assessment (PQA) during every session, and quantitative and qualitative data were collected. Qualitative data were derived using a cross-case analysis, and quantitative data were used for calculating the effect size after performing the paired t-test. RESULTS Analyzing the reported cases of sport life skill leaders, the use value of the capacity building program was identified. Furthermore, the cases reported by the four leaders enabled observation of how the leader’s capabilities were strengthened. In the paired t-test, the effect size of physical and psychological safety, appropriate structure, supportive relationship, opportunities to belong, support for efficacy mattering, opportunities for life skill building, excluding integration of family, school, and community effort, were all significant. All effect sizes were found to have “very large effects.” CONCLUSIONS The capacity building program played a positive role in strengthening the leaders’ life skill coaching capabilities. These findings have practical implications—chiefly, it is important to strengthen leaders’ or coaches’ capabilities in order to foster life skill development and transfer of student-athletes.
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop a team building program for a middle school soccer team in order to verify its effects. METHODS A total of 50 middle school soccer players participated in the needs analysis, and 10 middle school soccer players participated the preliminary program. In addition, a total of 37 ‘S’ middle school soccer players and 2 coaches participated the final team building program to identify its effects. The team building program was developed through the following sequence: program goal setting, organization of program activities, and the pretest. Three types of questionnaires and a self-report were utilized to verify the effects of the team building program. RESULTS The team building program was developed based on interpersonal relationships, goal setting, and communication. The level of team cohesion, team communication, and coach-athletes interaction significantly increased through this program. Furthermore, the effects of stress relief and self-improvement were revealed through the self-report. CONCLUSIONS The team building program was determined to be effective and has various benefits. It is expected to contribute to the growth of middle school soccer players if coaches actively participate in the program with their athletes.
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop a sports-related human rights education program for college student-athletes. METHODS To do this, literature reviews, individual interviews, and experts’ meeting data were collected. The data were analyzed using content analysis and domain analysis. RESULTS The study involved five steps. First, the literature reviews examined the problems and improvement points regarding previous sports-related human rights education programs. Second, the direction of human rights in sports education programs was developed based on certain development principles and criterion. Third, eight sports-related human rights education lesson plans were developed. Each lesson plan had a format that contained lesson objectives, ice breaking quizzes, core contents, discussion sections, and essential summaries. Fourth, the program was validated using a pilot test. Last, a “human rights in sports” instructor education program was executed. CONCLUSIONS The program can be effectively used among college student-athletes.
PURPOSE This study analyzed the KSPO women’s sports leadership program and foreign cases to suggest policy proposals. METHODS A literature review was conducted involving official webpage of the programs, related technical reports, media resources, and academic articles collected from international and domestic research databases. RESULTS The major results are as follows: (1) The curriculum of current program should be examined and reconstructed to achieve the intended purpose. (2) Since selfawareness is a key factor in demonstrating effective leadership, implementing selfawareness training program should be considered. (3) Mentoring is regarded to be an effective tool in promoting women leadership; therefore, establishing sustainable women mentoring program is required. CONCLUSIONS Despite several limitations, this paper is the first study, to the best of our knowledge, to review and analyze the KSPO women’s sports leadership program comparing foreign cases for the purpose of seeking improvement. As women’s leadership in the field of sport would become even more important in the future, this program should be redesigned to be able to train and nurture leaders so that they can progress to the higher level of decision making in sport organizations.
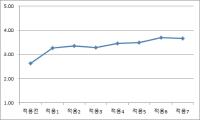
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to apply a life skills program to student-athletes and statistically verify the changes in life skills of the experimental and control group. METHODS Participants were 34 high school Taekwondo athletes (Mage=17.71). They were divided into 18 in the experimental group and 16 in the control group. For eight weeks, the experimental group participated in the life skills program after training and the control group participated in only training as usual. Data were collected by using Life Skills Scale for Student-Athletes (LSSSA), and the participants of two groups filled out the LSSSA before and after the program application. The collected data were analyzed by using repeated measure analysis of variance (ANOVA), and partial η2 (eta squared) was calculated to present the effect size. RESULTS The interaction between time and group was statistically significant in goal setting, coping with stress, positive thinking, and managing emotion among sub-factors of life skills. Partial η2 was interpreted as having a large effect size as it revealed the range of .22 to .51. Therefore, comparing before and after participating in the program, the life skills score of the experimental group among the two groups was significantly improved. CONCLUSIONS Student-athletes who participated in the program experienced positive changes in life skills than those who did not participate in the program.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop an effective college life adaptation program for freshman student-athletes. Methods A total of 160 student-athletes and 5 experts agreed to participate in this study. Four procedures were followed in this study: the needs assessment, the preliminary program development, and the application of the program. For the needs assessment, in-depth interviews were conducted, and the data were analyzed using an inductive reasoning process. Results The results of the needs investigation showed seven need factors and four interruption factors for college life adaptation. In addition, three need factors based on experience and seven interruption factors based on experience were found. The preliminary program was developed based on the needs assessment through the expert meeting, and the program consisted of four stages. Each stage consisted of three sessions, and each session contained a specific topic. The program was provided to nine freshman student-athletes in two months. As a result, the final program which consisted of four stages and thirteen sessions was developed after the reinforcement process based on evaluation of the preliminary program was conducted. Conclusions It is concluded that, the program is able to be expected to help them to understand their roles, have a better sense of responsibility and improve their self-esteem. Therefore, coaches and mental performance consultants should provide the college life adaptation program for freshman student-athletes to reduce their stress and have a better college life.
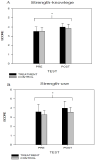
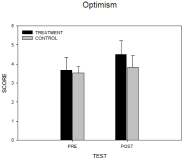
Purpose The goal of this study was to investigate the application effect of strength-based positive psychology intervention to elite archers. Methods Total of 20 elite archers participated in this study. Treatment group consisted of 10 elite archers participated in the strength-based positive psychology intervention for 8 weeks. Each individual responded the questionnaires in pre- and post-treatment sessions. Data were analyzed by repeated-measure ANOVA. Furthermore, archers participated in the program responded to in-depth interviews. Results According to the results, participants in strength-based positive psychology intervention showed that significantly increased strength knowledge, strength use, and optimism in the post–treatment compared to the pre-treatment session while control group did not show significant changes. In addition, archers perceived that there were positive effect on thinking ·coping and their self-confidence and self-esteem enhanced after participating the program. Conclusion The results of this study suggested that strength-based positive psychology intervention has positive impact on athlete’s wellbeing and perception of individuals strength and can be applicable to different sports field.

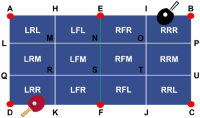
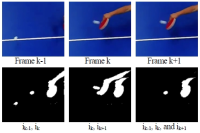
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop algorithms and software that can track the trajectory of table tennis balls using image-processing algorithms to obtain information quickly for under and establish tactics used in table tennis. Methods The algorithms used in the field of computer vision were applied on two matches played by novice and two matches during international competitions by elite athletes. Reliability analysis was performed by comparing the table tennis ball bounce frequency in each zone obtained through the automatic method and the manual method. Results The mean reliability of the two novice games was only 85.1 ± 3.69%, total error was 14.9 ± 3.69%, overestimation error was 52.2 ± 9.78%, and underestimation error was 47.8 ± 9.78%. While the mean reliability of the two international tournaments was 71.8 ± 0.87%, the total error was 28.2 ± 0.87%, overestimation error was 82.0 ± 8.03%, and underestimation error was 19.2 ± 7.75%. Conclusions Although the target reliability of algorithms and software developed in this study was achieved only in novice competitions with 80%, the over-estimation errors were generally high in international competitions, showing the potential for further improvement.