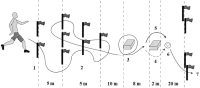
[Purpose] This study aimed to examine the effects of complex physical training on exercise and football performances in youth football players. [Methods] The subjects (n=16) were randomly assigned to either a complex physical training group (CPG, n=8) or a control group (CON, n=8). CPG was performed the complex physical training for 50 minute per day, and 2∼3 times per week, for 8 weeks. Exercise performance (health related physical fitness, skill related physical fitness, Y-balance and functional movement screen; FMS) and football performance (juggling, speed dribbling, shot passing, long kick and triple hop) were measured before and after 8 weeks complex physical training. [Results] Sit-up (p=0.002), sit and reach (p=0.040), 50-m run (p=0.031), side step (p=0.005), single-leg standing with eyes closed (p=0.040), plank (p=0.023), dominant composite score (p=0.002) and non-dominant composite score (p=0.005), deep squat (p=0.009), inline lunge (p=0.042), active straight leg-raise (p=0.015), rotary stability (p=0.049), total score(p=0.001), speed dribbling (p=0.030), dominant triple hop (p=0.001) and non-dominant triple hop (p=0.032) were statistical significant interactions between group and time. [Conclusion] Our findings indicate that complex physical training has beneficial effects on performance improvement of exercise and football in youth football players.


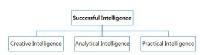
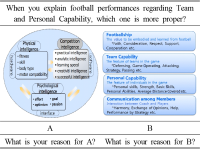
This study was to analyze the hierarchical importance of successful intelligence in Football coaches and players. In order to explore the hierarchical importance of successful intelligence 24 football coaches(under AFC A course) and 20 Korea Football Association U15 Players were responded to analytic hierarchy process questionnaires. In the Analytic Hierarchy Process, football coaches and players completed the AHP Questionnaire with creative intelligence, analytical intelligence and practical intelligence. The hierarchical importance order of successful intelligence for coach and player were analytical intelligence, practical intelligence, and creative intelligence respectively. Evaluation of hierarchical importance of successful intelligence for coach is analytical intelligence(.542), practical intelligence(.278), creative intelligence(.181) in order. Evaluation of hierarchical importance of successful intelligence for coach was analytical intelligence(.684), practical intelligence(.161), creative intelligence(.155) in order. The hierarchical importance of successful intelligence for coach and player were similar each other. Analytical intelligence, was evaluated most important factor for coach and player in successful intelligence. Successful intelligence is important issue for sport performance. More consider needs to Successful intelligence for sport psychology researchers.




PURPOSE This study aims to provide policy recommendations for the development of women’s football and the enhancement of the Women’s University Football League (WUFL) by examining participant satisfaction and meaningfulness of football. METHODS To achieve this goal, we distributed survey questionnaires, including 5-point Likert scale and open-ended questions, and subsequently analyzed 153 responses using qualitative data analysis software, N-vivo. RESULTS Our findings reveal that female students actively engaged in the WUFL express high overall satisfaction. Furthermore, participants perceive football as a source of happiness, an energy booster, and a platform for new experiences. Their involvement in football goes beyond typical leisure; it is regarded as a form of serious leisure. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS Based on these results, we propose actions such as fostering and elevating amateur women’s competitions, promoting female students’ participation in football, and developing a comprehensive strategy for increasing women’s enjoyment of playing football.
PURPOSE This study explores injury attributions accepted by serious football participants, specifically intermediate and advanced players. METHODS Utilizing Q methodology, 25 Q-samples and 33 P-samples were selected, and Q-classification was conducted. Principal component factor analysis through the PQ method (vers. 2.35) was employed for data analysis, and types were interpreted and named based on the Q-sample with a Z-score of ±1.0 or higher. RESULTS Results categorized injury attributions accepted by the participants into four types: 'Type I: Facility/ Human Resource Responsibility Type,” 'Type II: Luck/Other Responsibility Type,” 'Type III: Self Responsibility Type,” and 'Type IV: Insufficient Safety Education.” This study provided academic and policy discussions by reclassifying four types according to their internal and external location and controllability. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, this study emphasizes the relevance of all four types of injury attribution to policy considerations. Ensuring participants' right to participate in safe and enjoyable sports requires addressing facilities/human resources, education, and insurance as major policy components of sports safety.
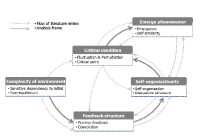
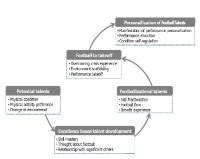
Purpose This study was aimed at interpreting the football talent development stages based on complexity theory. Methods The data for this study was gathered through literature review and in-depth interviews that were analyzed by thematic analysis. Literature review of the studies regarding complexity theory revealed the features of complexity theory and five football players participating in the K-league were interviewed. Gathered materials were analyzed by the thematic analysis. Initial codes and potential themes of football talent development stages, the conception and potential themes of the complexity theory were interpreted by metaphorical analysis. Results Results of literature review were as follows: analysis frame of complexity theory were organized environment of complexity, feedback structure, self-organization, critical condition and emergent phenomenon. The football talent development stages, interpreted as a result of literature review, were divided into Potential Talents, Excellence based Talents Development, Footballizational Talents, Football to Takeoff and Personalization of Football Talents. The stages were specifically materialized as follows: Potential Talents was materialized into physical condition, physical activity preference and change of environment. Excellence based Talent Development was materialized into skill mastery, thoughts about football and relationship with significant others. Footballizational Talents was materilized into skill fractionation, football flow and growth experience. Football to Takeoff was materialized into overcoming crisis experience, performance scaffolding and performance takeoff. Personalization of Football Talents was materialized into manifestation of performance personalization, performance evolution, condition maintenance. Conclusion Football talent development stages, interpreted by means of complexity theory, were divided into Potential Talents stage, Excellence based Talent Development stage, Footballizational Talents stage, Football to Takeoff stage and Personalization of Football Talents stage. Utilization of this study as a fundamental resource of football talents development programs and as a means to understanding football talents development is looked forward to.

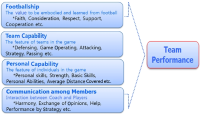
Purpose The following study was conducted to suggest and verify the validity of the concept of team performance, which has previously been considered as the total sum of individual performances. Method The concept of team performance was extracted by a conductive content analysis and an exploratory factor analysis of the data gathered from middle school football players. To verify the validity of the extracted concept, football experts' opinions were collected. Results The idea of team performance, categorized by Footballship, Team Capability, Personal Capability, Communication among Members, has been taken differently from the total sum of individual performances. Footballship is the virtue that should be materialized, and simultaneously earned during the game. Team Capability is a available resource for team's performance, Personal Capability is a available resource for a player's performance, and Communication among Members is the intimacy of communication between coaches and players. The conglomeration of experts' opinions on the concept of team performance and its components shows that team performance is evidently different from the total sum of individual performances. Conclusion The following study has been conducted to suggest and verify the validity of the concept of team performance. Team performance exists, standing distinct from the sum of individual performance, and understanding the concept of team performance will contribute not only to understanding performance, but also to improve the effectiveness of training and managing the team. Interest of the sport society is looked forward to.

PURPOSE This study aimed to extract football coaches’ categories of performance evaluation factors (PEF) and examine the reflective characteristics of the football coaches’ player and casting judgments. METHODS PEF were extracted through an open-ended questionnaire and categorization from 80 AFC C or higher football coaches. Reflection was calculated in player and casting judgments through an analytic hierarchy process. The difference between the football coaches’ player and casting judgments was examined using SPSS 21.0. RESULTS First, the PEF of football coaches were categorized into four general categories: physical intelligence, psychological intelligence, growth potential, and competition intelligence. Second, the importance of football coaches’ player judgments were reflected by the PEF as football intelligence, situation judgment, football talent, tactical understanding, tactical operation, etc. The importance of the casting judgment were reflected by the PEF as tactical understanding, mediative skills, fitness, tactical operation, situation judgment, etc. Third, a statistically significant difference was noted between player and casting judgments. Football coaches tended to value growth potential and talent as sub-factors in the player evaluations. Football coaches’ PEF were aligned with the importance of player and casting judgments in psychological and competition intelligence as sub-factors such as skills, physical, attitude, passion, etc., but differed from physical intelligence and growth potential as sub-factors including mediative skills, physical, football talent, and tactical understanding. CONCLUSIONS In the football coaches’ player evaluations, the idealistic principle centered on growth potential. However, in the casting evaluation, the realistic principle centered on victory takes effect.
Purpose This study examines legal and institutional aspects of FA Compensation System (FACS) which was introduced by Korean professional football league in 2013. Methods This legal analysis reviews the current FACS in lights of several provisions of human rights in the Constitution and other relevant rules of law. Results First, the FACS violates Article 15 of the Constitution that protects 'freedom of choice to workplace' arguably implied under the 'freedom of occupation' provision since the system restricts a player's transfer within the league by requiring a transfer fee paid by the destination team even if the player has acquired the free agency status and his current contract is expiring. Second, the FACS would likely be unconstitutional according to precedents decided by the Constitutional Court and the National Human Rights Commission on the ground that 'freedom of occupation' is closely related to the rights to pursue happiness under Article 10 of the Constitution. Conclusions Based on the legal interpretations, the study argues complete abolition or significant revision of the FACS. This project calls for follow-up studies and further policy-making efforts given the practical magnitude and scholarly merits of the issue.
The purpose of this study was to examine psychological capital acquisition through Asian Games Participation. 17 of national women football players were completed Psychological Capitals Questionnair. The psychological capital consists of optimism, psychological skills, self-management, collective efficacy, and performance perception was investigated after the team call-ups and before the team-release. The data was analyzed by paired t-test. As results, Korean women football players’ collective efficient and performance perception showed a statistical significance at the beginning of the team call-ups but optimism, psychological skills, and self-direction did not show statistic significances. The team-harmony, interpersonal-management, team-power, sufficient training, trust in coach, efficient communication, and psychological football factors, which were subfactor of football players’ psychological capital, showed statistical significances. However, confidence, concentration, goal-setting, imagery, willpower, anxiety-control, mental-management, life-management, training-management, innate-behavior management, physical-management, football skills, mediative skills, and football intelligence factors did not have statistic significances. These results demonstrate that effects of mega sporting events-like experiences and psychological factors’ variability and inflexibility according to weather changes should be considered when it comes to discussion of psychological factors regarding players’ performance. It is expected that this study would be a fundamental resource for understanding of psychological influences through participations in mega sporting events and discussions about further psychological interventions for teams with environmental consideration as well as methodological developments which could measure effects of the psychological interventions.
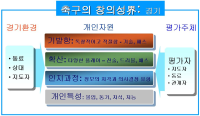
The purpose of this study was to explore a framework of understanding football performance. Researcher review was conducted to organize perspectives for football performance and drew implications as well as drift of football performance based on intelligence approach. Discussions for intelligence had been proceeded in concepts of learning ability, multiple intelligence, successful intelligence, and moral intelligence. Discussions of football performance approaches fitness, skill, and strategies in traditional intelligence aspects. The multiple intelligence perception discusses perspective, mentality, body, and analysis. The successful intelligence perspective deals with creativity, practical intelligence, and football talents. However, specific discussions for moral intelligence have not been progressed yet. FIFA’s social responsibility project and UEFA’s RESPECT campaign reflect that the discussions of football performance develops in a way of the moral intelligence. In European football, issues regarding value, such as RESPECT and against Racism, are currently emerging. Considering the change in the European football, the global football leagues will share the issues related to value in the near future. Given the fact that discussion for intelligence had been proceeded learning ability, multiple intelligence, successful intelligence, and moral intelligence, the moral intelligence will be a main concern in the further football performance discussion. The moral intelligence will be incorporated into football performance evaluations soon. Furthermore, teams and players will strive to place efforts in order for pursuing value and reputation as factors of performance.