Purpose The purpose of this study is to conduct a typological classification of female recreational sport participants' coaching experience. Methods Q methodology was conducted using 25 Q-samples and 25 P-samples. Data were analyzed using PQmethod software. Results Four types were categorized: communication and character-oriented (I), function and immersion-oriented (II), process and fun-oriented (III), and function and inclusion-oriented (IV). These types were re-categorized as 'non-functional value-oriented (I, III)' and 'functional value-oriented (II, IV)'. Conclusion This study also made efforts to explore the value and norm that female participants expect from sport participation, which provided a variety of perspectives on social, psychological and philosophical discussions about woman sport. In addition, each type and its characteristics can be used as meaningful basic data in teaching method (coaching theory) for woman sport.

The purpose of this study was to analysis of perception types for gender equality of middle school students in P.E. class. 90 students in the specialized middle school located in K city, were selected for the subjects based on the theory of Q methodology. Q samples were 31 Q statements finally extracted from the total of 120 statements after the experts' consultation. The final 35 selections were surveyed to be forced distribution by the respondents to the statement of their positive, neutral, negative frequency distribution of the total score nine points. Factor analysis was conducted by QUANL-PC program and the following conclusions were derived by the factors centered on those over one. First, the image types for middle school students in the coed physical education class on gender equality were appeared into total of 4 categories, physical education classes without discrimination, peer-cooperative to create friendly atmosphere, physical education class to the possibility for anyone, gender equality class and there were subjective differences in each types. Second, five Q statements commonly formed among each types of the physical education on gender equality for coed middle school students were derived.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to conduct a typological classification of female college students in sport studies regarding perceived career barriers. Methods Q-methodology was used to identify female college students’ viewpoints on carrier barriers. The Q sample was distilled from 76 statements (64 from literature reviews and 12 in-depth interviews) to 25 statement after conducting literature review, in-depth interviews and surveys with open-ended questions. The P sample for this study was 30 students around Seoul and PQmethod software was used for data analysis. Results Three distinct views were extracted: First type of ‘career opaque’, revealed that students have failed to find their own aptitude and interest. Second type of ‘sexual discrimination-male centered’, implied students’ concerns about discriminating factors in relation to marriage and pregnancy for the job they desire. Third type of ‘Insufficient experience and qualification’, indicates students perceive their lack of experience or qualification required for their career. Conclusions The identification of these three viewpoints could provide insights that can be used to design more segmented and detailed career policies for female college students in sport studies.

PURPOSE This study seeks to explore the subjectivity regarding leisure constraints perceived by college student-athletes. METHODS Based on Q methodology as an analysis framework, 25 Q-samples and 25 P-samples suitable for the research purpose were selected, and Q-classification and Q-factor analysis were conducted. RESULTS The leisure constraints were categorized into “Type Ⅰ: Psychological constraints,” “Type Ⅱ: Financial constraints,” and “Type Ⅲ: Spatio-temporal constraints.” The three types provided discussions on “strong athlete identity of student-athletes,” “role conflict between students and athletes,” “core competencies of student-athletes,” “current student-athlete support project,” and “school sports camp training.” CONCLUSIONS College student-athletes’ leisure constraints are closely related to strong athlete identity, anxiety about enjoying leisure, cost burden, and closedness of camp training, and each type provided new perspectives on discussions related to Korean student-athletes.
PURPOSE This study explores injury attributions accepted by serious football participants, specifically intermediate and advanced players. METHODS Utilizing Q methodology, 25 Q-samples and 33 P-samples were selected, and Q-classification was conducted. Principal component factor analysis through the PQ method (vers. 2.35) was employed for data analysis, and types were interpreted and named based on the Q-sample with a Z-score of ±1.0 or higher. RESULTS Results categorized injury attributions accepted by the participants into four types: 'Type I: Facility/ Human Resource Responsibility Type,” 'Type II: Luck/Other Responsibility Type,” 'Type III: Self Responsibility Type,” and 'Type IV: Insufficient Safety Education.” This study provided academic and policy discussions by reclassifying four types according to their internal and external location and controllability. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, this study emphasizes the relevance of all four types of injury attribution to policy considerations. Ensuring participants' right to participate in safe and enjoyable sports requires addressing facilities/human resources, education, and insurance as major policy components of sports safety.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to classify the subjectivity of re-socialization barriers among retired footballers. Methods Q methodology was conducted to identify constraint factors contributing to social adjustment and reemployment perceived by 28 P-samples. Results Re-socialization barriers were classified as ‘Type I: Internal-constraint’, ‘Type II: External-constraint’, ‘Type III: Internal-conflict’, and ‘Type IV: External-conflict’. These types provided a variety of academic and practical discussions, depending on where the barriers are taken from (internal and external) and what depends on them (objective conditions and subjective ideas). Conclusions This study focused on the subjective structure of retired footballers and complemented traditional methodology focusing on hypothesis testing. Therefore, each type found in this study provides useful information not only in follow-up study on retired athletes, but also in policy-making decision such as support projects.


PURPOSE This study aimed to categorize consumers’ subjectivity on public value of citizen professional football club. METHODS Q-sample and Q-classification charts were developed based on theoretical background of the public value of citizen football clubs, and in-depth interviews with consumers were conducted using the Q-methodology. Q-classification and Q-factor analyses were conducted by selecting local residents as P-samples. RESULTS The public value of citizen football clubs was confirmed as ‘Type I: club-city win-win’, ‘Type II: social integration’, and ‘Type III: culture-led’. These types are contrary to previous studies that mainly focused on management and marketing, such as financial profitability and soundness, regional economic impact, and commercial value. This is the result of examining the public value of the citizen football club from based on the subjectivity of consumer, and it differs from that in previous studies. CONCLUSIONS This study reconfirmed the specificity and role of citizen football clubs in commercialized professional sports. It showed that citizen clubs must adopt organizational goal and operation method that are different from profit sports organizations (clubs).
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the badminton players psychological disturbance and coping strategies types and characteristics. Methods To achieve the purpose of this study, an open-ended questionnaires were used targeting 194 badminton players, 25 Q samples were selected by collected data as the self – statement. Q samples were classified depending on their subjective experience by P samples composed of active badminton players who had more than eight years of athletic career; this data were coded and analyzed by VARIMAX rotation. Results The results revealed by the Q methodology were below. First of all, the first type is named as (Internal Disturbance - Passive Coping) type. The first type is psychologically disturbed by internal factors, and negative about external coping strategies. Second, the second type showed the higher awareness of coping strategies than the other types; It was named as (Active Coping) type. Third, The third type recognized the burden of victory and self-confidence, and it was named as the type of (Victory Obsession). Conclusion In the badminton competition, the deterioration of concentration and judgment ability because of psychological disturbance has a serious effect on the performance. Therefore, based on the results of this study, it will be possible to improve the performance by appropriate psychological intervention through the characteristics of the athletes.

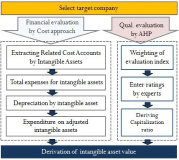
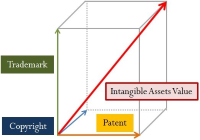
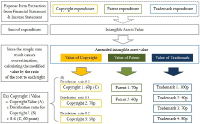
Purpose In the field of sports industry, the intangible assets of sporting companies often show discrepancies between accounting information and corporate value because of conservative current accounting standards. Therefore, this study intends to present a valuation model of intangible assets of sports industry based on cost approach, as a part of a method of capitalizing intangible property expenditures. And we tried to verify the valuation model of intangible assets derived from the research on actual sports companies. Methods To accomplish the purpose of the study, reviewing the literature on various related precedent studies and examining related valuation methodology, legal basis, and representative valuation models were utilized. And to verify the effectiveness of the derived model, Tobin q values were derived and compared. A simple regression analysis was used to verify the explanatory power of the derived model. Results The financial evaluation was conducted based on the cost approach, which enables relatively objective evaluation through the existing financial statements, and a valuation model with the procedure of duplicating the AHP evaluation to reflect the characteristics of the individual intangible assets was presented. In addition, in order to verify the proposed valuation model, the valuation was conducted by putting the accounting information of the sports companies into the intangible asset valuation model presented in this study. As a result of the statistical analysis on the evaluation results, the intangible asset value evaluation model presented in this study is proved to be significant based on statistically high explanatory power. Conclusion Therefore, if it is possible to appropriately evaluate the enterprise value of sports companies through the intangible asset valuation model based on the cost approach presented in this study, various types of technology financing will be possible in the sports industry. And this is expected to accelerate the growth of the sports industry in the future.