
This study was to verify the structure of efficacy related to performance perceived by short-track athletes when playing a match. Therefore, 50 players answered open questionnaires and 200 players participated in construct validity verification, a total of 250 players of short-track members of national, business and university team were sampled during the research phase. The data was analyzed through the study procedures. The results were as follows: First, efficacy structure of players during the match were categorized into three groups as game managing strategy(including course management, race control, match management and selective attention ability), psychological control ability(including positive imagery, match competition, competitive spirit, ability to handle hardship, anxiety control, and patience), and physical usage of ability(including physique, endurance, and quickness). Second, the result of the first construct validity verification through exploratory factor analysis showed 7 factors in 29 items as game management, course management, psychological control, physical use, coping with hardship, speed control and psychological stability. Finally, as a result of confirmatory factor analysis, short-track self-efficacy showed the 5 factor in 15 items except for coping with hardship and psychological stability.

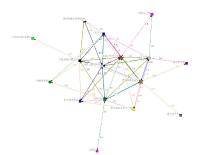
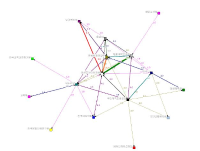
The purpose of this study was to investigate structural characteristics and participants` roles & functions of sport policy network in Korea, by social network analysis on structural characteristics of sport policy network and AHP analysis on participants` roles and functions. For that, 21 executive officers from 19 organizations and agencies related to sports policy were selected as study subjects, and, the materials collected from whole twice surveys on them were analysed by Ucinet 6 and Expert Choice 2000 program. As the results, the governmental organizations like the Blue House and Ministry of CultureㆍSports and Tourism composed the central position group of sport policy network of Korea, and took the main functions of planing and arrangement within their main roles of policy agenda formation and policy decision, so, sport policy network of Korea could be called centralized network by government. And, in cases of private agencies, Korea Sports Council composed the central position group only in policy network of professional sport, Korea Council of Sport for All of sport for all, and Korea Sports Association for the Disabled of disability sport, and, each of them took the main roles and functions of policy execution in their fields, so, it was obvious that the private agencies were divided into their own sport policy areas.

PURPOSE This study comprehensively examined the aerodynamic and flight characteristics of modern soccer balls, focusing on their design evolution and performance attributes. METHODS The aerodynamic characteristics of five types of World Cup balls (2006 Germany World Cup, 2010 South Africa World Cup, 2014 Brazil World Cup, 2018 Russia World Cup, 2022 Qatar World Cup) and five types of Euro tournament balls (EURO2008, EURO2012, EURO2016, EURO2020, EURO2024) were examined, along with their respective design changes. RESULTS Through detailed analysis, significant variations in aerodynamic properties among soccer balls used in various tournaments were identified. Recent advancements have resulted in faster transitions towards critical Reynolds numbers, indicating improved stability in flight trajectories. This enhancement was attributed to the augmentation of surface roughness, which plays a crucial role in enhancing aerodynamic stability and overall performance. 2D simulations simulating powerful goalkeeper kicks revealed distinct differences in flight distances among different soccer balls; the Jabulani ball used in the 2010 World Cup exhibited the longest flight distance, while that of the 2024 Euro ball was the shortest. CONCLUSIONS Variations in surface texture significantly impact aerodynamic properties, affecting flight distance, arrival time, and height. This study underscores the significant design enhancements in modern soccer balls that optimize aerodynamic stability and performance, with modifications aimed at improving flight characteristics and enriching player experience.
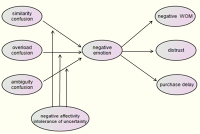
Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify how the three variables of consumer confusion proneness affect consumers' negative emotion, word of mouth, trust and decision postponement during the process of purchasing golf club. Futhermore, this study looked through the moderating effect of the personal characteristics in the relation between consumer confusion proneness and negative emotion. Method A total of 850 questionnaires were used for data analyses(i.e., frequency analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, structural equation modeling) with PASW 18.0 and AMOS 18.0. The results of the study are as follow. Results First, all of the subordinate factors of consumer confusion proneness had a significant effect on the consumer's negative emotion. Second, consumer's negative emotion had a significant effect on negative WOM. Third, consumer's negative emotion had no significant effect on distrust. Fourth, consumer's negative emotion had a significant effect on decision postponement. Fifth, the moderating role of negative effectivity partially had a significant influence in a relation ship between confusion proneness and negative emotion. Sixth, the moderating role of intolerance of uncertainty had a significant influence in a relation ship between confusion proneness and negative emotion. Conclusion The results of this study contributed to provide fundamental information on over all golf industry as in service providing point of view as well as development and application relate to it.

PURPOSE This study conducted a longitudinal analysis of physical activity levels and characteristics of middle-school boys and girls over a three-year period before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. METHODS This study used a sequential mixed-methods research design. In the quantitative study; three-dimensional accelerometers were used to measure weekly physical activity and sedentary time over three years (2019, 2020, and 2021) among 33 middle-school boys and girls, and the data were analyzed using repeated measures analysis of variance. In the qualitative study, data were collected and analyzed through focus group interviews with five participants. RESULTS The quantitative study indicated a significant increase in sedentary behavior and significant decrease in low-intensity activity and MVPA during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. In the second year of the pandemic, no significant difference was observed in sedentary behavior, low-intensity activity, and MVPA compared to the data collected in the first year. During the pandemic’s first year, qualitative study identified the following physical activity problems: “lockdowns,” “sedentarization of leisure,” and “reduced structured physical activity.” The following reasons were identified for the lack of improvement in physical activity during the second year: “intensified sedentary lifestyle habits,” “weak social networks,” and “lack of energy to exercise.” CONCLUSIONS The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a significant decrease in physical activity and a significant increase in sedentary behavior among middle-school students in South Korea, and even as the environments for physical activity have recovered, the physical activity problems of the early stages of the pandemic have not improved.
PURPOSE For student-athletes to be able to successfully dedicate themselves to training and competition, the following key factors play an important role: The coach, team climate, and individual motivational characteristics. To test this hypothesis, the structural relationships between having a perceived autonomy support, a caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment were analyzed. METHODS Participants were 297 high school athletes registered with the Korea Olympic Committee (203 males, 94 females, Mage=17.88 years). Data were collected using sports climate questionnaires for autonomy support, caring climate scale, basic psychological needs scale, and sport commitment measurement. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling. RESULTS The model’s fitness was indicated by x2/df=2.797 (x2=106.288, df=38), CFI=.977, TLI=.967, RMSEA=.078 (90% CI=.061, .096). Examining the various path coefficients revealed that coach autonomy support had a positive effect on the athlete’s caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment. The caring climate had a significant effect on basic psychological needs, but did not have a statistically significant effect on sport commitment. Finally, basic psychological needs had a positive effect on sport commitment. CONCLUSIONS Coach autonomy support fosters a caring climate, and athletes who are able to perceive this are able to dedicate themselves to their sport since their basic physiological needs are met. Therefore, coaches should use appropriate coaching strategies to enhance athletes' autonomy and foster a caring climate, as both are essential factors for meeting athletes' psychological needs and promoting sport commitment.
PURPOSE Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for home training, with exercises or workouts at home, has steadily increased. As a result, the popularity of home training YouTube content, which shows how to use exercise equipment or workouts without professional influence, has also increased. Therefore, this study focused on the characteristics of YouTube home training content (specialization, diversity, and interaction), personal health awareness, exercise awareness, and expectation-confirmation model to identify which required exercise continuation intention through YouTube home training. METHODS SPSS and AMOS software were used to conduct frequency, reliability, and confirmatory factor analyses, as well as to conduct correlation analysis and construct a structural equation model. RESULTS First, health and exercise awareness had a positive effect on confirmation. Second, among the characteristics of home training content, only specialization had a positive effect on perceived usefulness. Third, confirmation had a positive effect on perceived usefulness and viewing satisfaction, perceived usefulness had a positive effect on viewing satisfaction and exercise continuation intention, and viewing satisfaction had a positive effect on exercise continuation intention, which proved the expectation-confirmation model in this study. CONCLUSIONS To increase exercise continuation intention through home training YouTube content, creators need to produce professional content that can stimulate viewers' internal motivation.

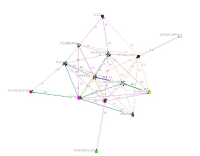
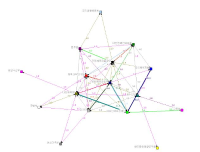
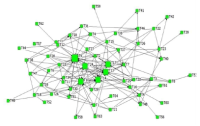
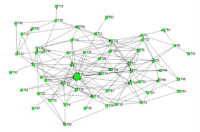
Previous work has shown that coaches sought information from several sources; however, there was a strong reliance on learning from other coaches within their social networks. There has been limited research examining the nature of these social networks with other coaches (Trudel and Gilbert 2004). Thus the purpose of this study was to examine the structures of coaches’ social networks of Korean rhythmic gymnasts. Research questions were: (1) What are the network structures of Korean rhythmic gymnasts’ coaches? (2) What structural parameters contribute to coaches’ network structures, and (3) Is there an association between coaches’ network and flow of information in their networks? A total of 37 coaches of youth rhythmic gymnasts (6-18 years old) participated in this study. Each of those coaches was asked to complete a Name Generator Questionnaire (i.e., list four names that you have a close relationship with) and general socio-demographic survey. Data were analyzed using social network analysis tools such as UCINET, p-net, and Quadratic Assignment Procedure. Analysis of network centrality, density, and strong components showed that (1) homophily was identified in the structure of coaches’ social networks (2) homophily (e.g., by gymnasts’ ranking, mentor coaches) contributed to the total social network of coaches, and (3) interacting only with close coaches in the network, coaches received information about coaches/coaching from the strong ties rather than weak ties (Granovetter, 1973). This study also has strong links to Wenger’s (1998) community of practice which posited that groups of people share a common characteristic in practice.


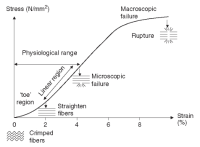
Vertical jumping is one of basic skills in many sports activities. Maximizing vertical jumping performance requires large “power”, which implies that one should generate force against the ground in a short period of time. In order to gain better understandings of how human musculo-skeletal system mechanically functions to achieve maximal power in vertical jumping, the proposed “dynamic catch” mechanism, one of “power amplification” mechanisms through the role of muscle-tendon interaction, was specifically reviewed base on the morphological and mechanical characteristics of lower limb muscle-tendon complex. By understanding basic structural and functional features of human muscle-tendon interaction, this review aims to provide basic scientific information for training and rehabilitation and promote convergence researches in related areas, such as sports biomechanics, mechanical engineering, and sports medicine.


PURPOSE This study explores the factors influencing eco-friendly behavioral intentions during sports spectating and infers the causal structure linking each variable to eco-friendly behavioral intentions. METHODS A total of 364 sports fans participated in the survey that collected data on Knowledge of Climate Change (KCC), Awareness of Climate Change (ACC), Attitude of Climate Change (ATT), Subjective Norm of Climate Change (SN), Perceived Behavior Control of Climate Change (PBC), and Behavioral intention to Reduce Single-Use Plastic (INT) during sports spectating. The validity of the measurement was examined through confirmatory factor analysis. Based on the validated data, latent variables’ average scores were reconstructed as input variables for the Bayesian Network, along with demographic characteristics. RESULTS The results of Bayesian network learning indicated that ACC, ATT, SN, and PBC variables directly influence INT. ACC affects ATT and SN, while ACC is influenced by KCC and sex. Conversely, PBC influenced INT but showed no association with the other input variables. SN was found to have the greatest impact on INT during sports spectating, while the influence of PBC was relatively low. CONCLUSIONS The causal structure inferred in the current study using Bayesian network learning provides insights into the previously underexplored relationship structure explaining eco-friendly behavioral intentions of sports fans in the field of sports science. The findings of this study can serve as empirical evidence for sports-related organizations to develop strategies and decision-making processes to promote sustainable sports spectatorship.