
Purpose This study was to investigate the systematic application of the life skills program and its effects in a sport setting. Methods Participants were 14 college students(8 males and 6 females) majoring in Taekwondo. Survey tools were utilized to measure items of life skills and journals. Data analyses were conducted by using Excel program and inductive content analysis. Results First, life skills in this study consisted of goal setting, self-talk, imagery, cognitive restructuring. Life skills program has undergone a procedure, such as the introduction, training, development, application, and evaluation. Second, the average scores of life skill variables have been changed according to measured points. Specifically, the average scores of goal setting and self-talk were highly increased over time and the average score of imagery indicated gradual rising line. The average score of negative thought was slightly reduced over time. Third, regarding effects of this program, participants’ responses were categorized into six components; performance enhancement, positive thoughts, chances of change, goal setting, struggling efforts, and motivation formation. Further, participants stated this program was a great opportunity to develop these components. Conclusion The application of life skills program in sport settings will contribute to participants’ life span developmental change in cognitions, emotions, and behavior.


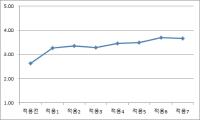

The purpose of this study was to describe psychological changes and variables of injured elite athletes during sport injury rehabilitation. 5 injured elite athletes were selected as participants, and open-ended questionnaires, participant observation, and in-depth interview were used for collecting data. Results from the data were analyzed through transcription, coding, and categorization with inductive method. To validate the results of this study, triangulation, in-depth description, member checks, and peer debriefing were used, and findings of this study were as follow. The participants showed negative psychological state such as fear of return to play and anxiety during the initial rehabilitation program, but their psychological state was changed positively such as recovery of confidence and desire of return to play at the end of program. However, the specific psychological changes of each participant showed several differences according to participant's surrounding environment and situation during the rehabilitation program. All findings have important implications for implementing and developing rehabilitation program, so needs to be investigated further.

Purpose This study aims at investing the educational meanings of school physical education policy by analyzing the direction (ideal goal, goal, objective and program) of the policy in Korea and England. Methods The comparative research design was conducted by the policy literature analysis. In order to clarify the significance of the main discourse embedded the school physical education policy to the educational practice, I used qualitative content analysis based on the interpretive paradigm. Results The school physical education policy in Korea is divided into goal for general students and student athletes for 'happy students and school life', while the policy in England seeks to promote participation of competitive sports through school-community linkage for lifelong sports participation. As a result of the discourse analysis, the ambiguity of school physical education policy due to the complexity of various discourses (e.g. moral development, health, sports) diminishes the effectiveness of policy implementation as well as the teachers’ educational practice. In addition, competition sports discourse has been analyzed to limit the participation of many students in sports and to adversely affect lifelong participation in sports. Conclusions In conclusion, It is necessary to activate theoretical and empirical research that is the basis of building the school physical education policy direction and to establish cooperative governance for the policy implementation. In addition, student participation in lifelong sports and evidence-based policy making and practice are required.

PURPOSE This study aims to analyze research trends on the social capital in sports. METHODS A total of 69 papers published until December 2020 were selected as research subjects. Further, Excel, KrKwic software, and NetDraw function of the UCINET 6 program were used for analysis. RESULTS First, social capital research on sports has shown quantitative growth since 2010. Second, the studies were conducted on sports participants such as general, elderly, college students, adolescents, foreigners, and the disabled, showing the highest frequency of research subjects. Third, quantitative research conducted based on the research method were several. Fourth, single-author studies were the highest. Fifth, as the result of the analysis on the publication journal, the Journal of the Korean Physical Education Association was shown the highest. Sixth, due to frequency analysis of the thesis keywords, “social capital,” “sports participation,” “action intention,” “social capital type,” “living sports participation,” and “youth” were shown the highest. Seventh, as a result of centrality analysis between keywords through the network analysis, “sports participation” in connection centrality, “health-promoting lifestyle” in proximity centrality, and “sports participation” in mediation centrality were found as the highest. CONCLUSIONS The significance of social capital in sports is more important than others because it is a fundamental element for creating a culture where more people can enjoy sports moderately in Korea, where capitalism and liberal democracy were adopted as the governing system. Therefore, this study can be a vital resource significantly contributing to the understanding and active use of social capital, a significant factor in developing sports in Korea.
PURPOSE This study identified a company sports club’s dual characteristics— both for leisure activity and as an extension of work—to provide comprehensive interpretation and understanding of such clubs. METHODS A qualitative case study design was employed, incorporating in-depth interviews, nonparticipant observation, and supplementary data collection from 25 office workers who had participated in an in-house sports club for at least one year. RESULTS Participants reported a wide spectrum of motivations, from voluntary motives such as stress relief and health improvement to more obligatory or organizationally driven motives, including pressure from supervisors or colleagues and expectations related to performance evaluations. The club offered both team sports—which fostered teamwork and a sense of belonging—and individual sports—which offered personal development opportunities. However, some participants experienced blurring of work–leisure boundaries and reemergence of hierarchical organizational culture, leading to conflict and fatigue. CONCLUSIONS Overall, Although company sports clubs have become a welfare program that provides employees with opportunities for leisure and self-development and promote inter-departmental communication and collaboration, they also carry the latent risk of imposing additional burdens and pressures on employees. These findings underscore the need for refined operational strategies and institutional improvements to mitigate negative outcomes and maximize such programs’ original intent.
PURPOSE This study aimed to explore the re-socialization process of college soccer players who rejoin college soccer clubs after dropping out. METHODS A case study approach was employed, and participants were selected using the snowball sampling method. Data were collected through in-depth interviews, participant observation, and literature reviews. The authenticity of the data was validated through triangulation, member checking, and peer debriefing. All research procedures were conducted following approval from the institutional review board. RESULTS The study revealed several key findings. First, participants faced numerous challenges during the re-socialization process into sports, including interpersonal, academic, and emotional difficulties. Second, distinctive features of the re-socialization process emerged, including the determination and effort required for adapting to university life, support from socialization agents within the university, and rapid re-socialization following dropout. Third, experiences within collegiate soccer clubs indicated low barriers to entry for former athletes, academic success through complementary relationships, a hierarchical culture familiar to student-athletes, and enhanced satisfaction in interpersonal relationships and a sense of belonging. CONCLUSIONS This study underscores the importance of institutional support that enables college athletes to participate in sports clubs, facilitating the successful re-socialization of athletes who have dropped out.
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop a team building program for a middle school soccer team in order to verify its effects. METHODS A total of 50 middle school soccer players participated in the needs analysis, and 10 middle school soccer players participated the preliminary program. In addition, a total of 37 ‘S’ middle school soccer players and 2 coaches participated the final team building program to identify its effects. The team building program was developed through the following sequence: program goal setting, organization of program activities, and the pretest. Three types of questionnaires and a self-report were utilized to verify the effects of the team building program. RESULTS The team building program was developed based on interpersonal relationships, goal setting, and communication. The level of team cohesion, team communication, and coach-athletes interaction significantly increased through this program. Furthermore, the effects of stress relief and self-improvement were revealed through the self-report. CONCLUSIONS The team building program was determined to be effective and has various benefits. It is expected to contribute to the growth of middle school soccer players if coaches actively participate in the program with their athletes.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to further understand how out-of-school adolescents’ self-esteem and interpersonal relations have changed in a peer mentoring basketball program and what they have experienced for the program It was action research of qualitative research method. Methods 4 out-of-school adolescents in the adolescents Center of C-si were selected as the participant. The data was collected by in-depth interviews, participant observation, and research journal. The collected data was then analyzed by an inductive categorical system. Results The findings were summarized as follows: the out-of-school adolescents showed somewhat low self-esteem and difficulties of interpersonal relations at an early stage participating in the peer mentoring basketball program. However, their self-esteem and interpersonal relations have been gradually changed during the program. First, they participated in various mentoring activities and self-expression activities. Their self-esteem has been improved as they found their real values, communicated with others, and lived with their confidence. Second, they overcame personal relations with fear and indifference of others, extended personal relations, and sympathized with others to solve the problem that they had as interpersonal relations. Conclusions The out-of-school adolescents has positively changed their self-esteem and interpersonal relations through the peer mentoring basketball program. We expect that out-of-school adolescents could overcome their difficulty and live well their life in the future.


Purpose The purpose of the study is to review the current trends of Korean research on sport volunteering. Methods For the research purpose, 74 KCI-listed articles published were investigated. Results The main topics of 60 articles were sport volunteering and the sub-topic or factor of the other 14 articles was sport volunteering. These articles were classified based on the publishing year, type of journal, academic area, research method, research topic, research sample, volunteer characteristics and volunteer area. Research on sport volunteering has been continuously conducted but the number of related publications has been increased since 2009. Sport volunteer research articles have been published in various sport related journals. However, the majority of the research articles are in the research areas of sport management, sport pedagogy, adopted physical education, and sport policy. Regarding the research method, more than a half of the articles were the ones using quantitative research methods, but qualitative research methods were often used as well. The majority of the research were conducted on volunteers but the research conducted on the beneficiaries of volunteer services were few. Many of the volunteers researched were college students. Event volunteering and educational volunteering were common volunteering areas in the research articles. Conclusions Korean researchers should not only conduct more research on sport volunteering with various topics but also improve the quality of the research after conducting the in-depth review of theories and literature and the better understanding about Korean situation on sport volunteering.
PURPOSE This study examined levels of safety knowledge and practice among recreational sports participants, focusing particularly on impacts of gender, age, injury experience, and exercise-level profile. In sports environments, understanding these factors is essential for developing targeted strategies to promote safe behaviors. METHODS Survey data from 7725 participants engaged in regular recreational sports activities were analyzed. Latent Profile Analysis was employed to categorize participants based on their injury experience and exercise levels, resulting in two profiles: Group 1 (moderate or severe injury experience with intermediate exercise levels) and Group 2 (mild injury experience with beginner exercise levels). Three-way ANOVA was then used to evaluate relationships between these profiles and safety knowledge and practice levels. RESULTS Results revealed significant differences across sex, age, and profile groups. Compared with women, men demonstrated higher levels of safety knowledge and practice, which were likely influenced by greater exposure to high-intensity sports and risk-taking tendencies. Adolescents exhibited the highest levels of safety knowledge and practice linked to structured safety education, but these levels declined in early adulthood and then increased again in middle age due to growing health awareness and preventive motivations. Furthermore, participants in Group 1 consistently showed higher levels of safety knowledge and practice than those in Group 2, highlighting injury experience’s role in shaping safety behaviors. CONCLUSIONS These findings underscore the importance of developing gender-specific safety education programs, age-appropriate interventions, and training initiatives tailored to beginning participants. Future research should evaluate these strategies’ long-term impact on safety practices and injury prevention in diverse sports settings.