
This study aimed to explore the types of traumatic event experienced by Volleyball players and then prepare to take-off the serial process of posttraumatic growth to schematize a causal network by organizing the factors for overcoming adversity. Participants experiences were collected by distributing open-ended questionnaires to 77 professional Women's volleyball players in 2013-2014 and collected data was categorized by inductive content analysis. These results were schematized by the causal network. As a result of the study, according to the trauma were categorized into four general areas: member conflict, competence loss, physical injury, and coach conflict and the emotions relative to the trauma were categorized into four general areas: powerlessness, pressure, dejection, and hostility also coping factors were categorized into three general areas: social support, intervention strategies, and psychological control. Finally, positive growth emerged as psychological leap, performance improvement, psychological maturity, and emotional stability. And as a result of the categorized study, bring about a better understanding to the posttraumatic growth by causal network. Based on the study results, that volleyball players experienced a positive development on themself after overcoming the problem that they had suffered psychological scars from a traumatic event. In doing so, they contributed to the formation of resources that helped them in their positive lives. In this regard, this study expects to provide the players who have been scratched in mind because of the traumatic experience.





The purpose of this study was to describe psychological changes and variables of injured elite athletes during sport injury rehabilitation. 5 injured elite athletes were selected as participants, and open-ended questionnaires, participant observation, and in-depth interview were used for collecting data. Results from the data were analyzed through transcription, coding, and categorization with inductive method. To validate the results of this study, triangulation, in-depth description, member checks, and peer debriefing were used, and findings of this study were as follow. The participants showed negative psychological state such as fear of return to play and anxiety during the initial rehabilitation program, but their psychological state was changed positively such as recovery of confidence and desire of return to play at the end of program. However, the specific psychological changes of each participant showed several differences according to participant's surrounding environment and situation during the rehabilitation program. All findings have important implications for implementing and developing rehabilitation program, so needs to be investigated further.
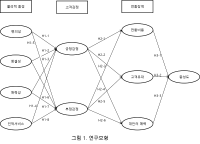
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between physical environment, customers' emotions, switching barriers and loyalty among water ski resort users in Gyeonggi-do and Gangwon-do province. Convenience sampling method was used, 277 of the questionnaires were selected as the ultimately valid sample. Data were analysed by SPSSWIN 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 program using frequency analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, confirmatory Factor Analysis(CFA) structural equation model(SEM). The research findings are as follows. First, relations between physical environment and customers' emotions, attractiveness, cleanliness, convenience and human service had a significant positively impact on positive emotional response. convenience, attractiveness, human service, and cleanliness had a significant negatively impact on negative emotional response. Second, relations between customers' emotions and switching Barriers, positive emotional response did not have a significant impact on switching cost and interpersonal relationship, but positive emotional response had a significant impact on attractiveness of alternatives. negative emotional response had a significant impact on switching cost, interpersonal relationship and attractiveness of alternatives Third, relations between switching barriers and loyalty, switching cost did not have a significant impact on loyalty. but interpersonal relationship and attractiveness of alternatives had a significant impact on loyalty.

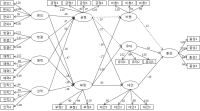
Recent studies focus on Metabolic Equivalent Task (MET) to measure levels of and areas of peoples’ physically active lifestyle because MET more readily translate peoples ’subjectively perceived physicality into standardized scores. MET also allows researchers to clearly understand the relationships between peoples’ physicality and psychological variables. Thus, the purpose of this study was to understand the levels of and areas of MET among Korean middle school students and to analyze the relationships between MET scores and physical self-efficacy. A total of 278 questionnaires were analyzed using SPSS 18.0. Exploratory factor analysis, descriptive analyses, and regression analyses indicated that middle school students’ physically active lifestyle occurred in the order school, leisure, housework, and transportation areas. Female students did more physical activity in the areas of housework and transportation, compared to male students. In contrary, male students did the majority of physical activity in the areas of school and leisure. Physical self-efficacy affected students’ MET scores, especially for vigorous intensity activity. With regard to gender differences, physical self-efficacy affected male students’ MET scores in the area of leisure while female students’ MET scores were affected in the areas of school and housework. The results were discussed in light of methodological and pedagogical perspectives, and future research suggestions were provided in the discussion.

The purpose of this study was (1) to develop a archery lesson using forced connection method-sportcasting for cultivating collaborative problem-solving competencies, and (2) to apply and to examine the responses of students after physical education(PE) lesson. A archery lesson of Understanding-Performance-Appreciation step was developed according to LfPE(Lee, 2014) using backward curriculum design. Participants were tenth grade students (N=148) in a high school. Open-ended question used to collect the data. The analysis of data indicates that students expressed features in lessons. Six features are (a) 朋友信之, (b) 君子不器, (c) 能竭其力, (d) 觀其所由, (e) 溫故知新, (f) 思而不學. In-depth interviewers were carried out for further analysis of the answers to the questionnaires. The results are as follows. First, 朋友信之 means lesson cultivating collaborative problem solving competencies. Second, 君子不器 means pleasant and funny lesson. Third, 能竭其力 means lesson cultivating self management ability. Fourth, 觀其所由 means lesson cultivating appreciativeness for archery. Fifth, 溫故知新 means lesson improving the status of PE teacher and school. This study concluded that a archery lesson generated fun and interest for students. Implication for developing lesson using LfPE, utilize and transform forced connection method-sportcasting in PE were discussed.


This study aims to provide an in-depth study on K-League players' perception and preparation process on retirement. In order to achieve the purpose, data collection was conducted in two major ways; face-to-face interviews and questionnaires from 10 currently working players. The result of study is based on inductive analysis. First of all, sense of expectation and concern, limited scope of secondary job, and necessity for career education are appeared in terms of players' perception. Second, preparation process on retirement is concluded in two categories; personal development activities(non-professional and inefficiency) and financial preparation. Thirdly, difficulties in the procedures of retirement preparation are categorized into ‘limited time and isolated lifestyle caused by staying in club house ’ and ‘lack of educational programs regarding retirement’. Depending on the results of this study, opportunities confined to retired players are supposed to be enlarged to currently working players. In addition, football club and K-League federation need to support players not only to enhance performance but also to prepare retirement.
The purpose of this study was to examine psychological capital acquisition through Asian Games Participation. 17 of national women football players were completed Psychological Capitals Questionnair. The psychological capital consists of optimism, psychological skills, self-management, collective efficacy, and performance perception was investigated after the team call-ups and before the team-release. The data was analyzed by paired t-test. As results, Korean women football players’ collective efficient and performance perception showed a statistical significance at the beginning of the team call-ups but optimism, psychological skills, and self-direction did not show statistic significances. The team-harmony, interpersonal-management, team-power, sufficient training, trust in coach, efficient communication, and psychological football factors, which were subfactor of football players’ psychological capital, showed statistical significances. However, confidence, concentration, goal-setting, imagery, willpower, anxiety-control, mental-management, life-management, training-management, innate-behavior management, physical-management, football skills, mediative skills, and football intelligence factors did not have statistic significances. These results demonstrate that effects of mega sporting events-like experiences and psychological factors’ variability and inflexibility according to weather changes should be considered when it comes to discussion of psychological factors regarding players’ performance. It is expected that this study would be a fundamental resource for understanding of psychological influences through participations in mega sporting events and discussions about further psychological interventions for teams with environmental consideration as well as methodological developments which could measure effects of the psychological interventions.

This study was to verify the structure of efficacy related to performance perceived by short-track athletes when playing a match. Therefore, 50 players answered open questionnaires and 200 players participated in construct validity verification, a total of 250 players of short-track members of national, business and university team were sampled during the research phase. The data was analyzed through the study procedures. The results were as follows: First, efficacy structure of players during the match were categorized into three groups as game managing strategy(including course management, race control, match management and selective attention ability), psychological control ability(including positive imagery, match competition, competitive spirit, ability to handle hardship, anxiety control, and patience), and physical usage of ability(including physique, endurance, and quickness). Second, the result of the first construct validity verification through exploratory factor analysis showed 7 factors in 29 items as game management, course management, psychological control, physical use, coping with hardship, speed control and psychological stability. Finally, as a result of confirmatory factor analysis, short-track self-efficacy showed the 5 factor in 15 items except for coping with hardship and psychological stability.

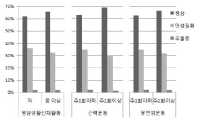
This study examined the association between physical activity (PA) and the prevalence of chronic disease and chronic depression. Additionally, the relationships between PA and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among general population, categorized by healthy, chronic disease and depression were investigated. Cross-sectional data includes 9,739 participants (4,351 males, 5,659 females, over 19 years old) who completed physical activity, chronic disease and HRQoL questionnaires from The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Complex samples frequency, descriptive, cross-tab and logistic analysis were used. Estimated prevalence of chronic disease and depression were significantly different between PA levels and frequency. Based on odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI), participating in lower levels of daily PA including less resistance and flexibility exercise were associated with an increased likelihood of chronic disease. Less frequency of resistance PA was also associated with an increased likelihood of depression. Estimated prevalence of HRQoL was different according to PA in the healthy and chronic disease populations. Adjusted OR and confidence intervals represented through lower levels of daily PA and less frequency of resistance PA were associated with an increased likelihood of poor HRQoL in the chronic disease population. No significant OR between PA and HRQoL in the depression population was observed.

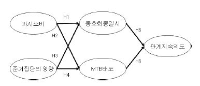
This study was aimed at empirically analyzing the impact of conspicuous consumption of MTB club members and influence of the reference group on club identification, MTB attitude, and relation continuity intention through structural equation modeling. To accomplish the objective, 250 adult men and women who were involved in MTB clubs in Seoul, Gyeonggi, and Chungcheong areas were surveyed. As for sampling method, self-administered questionnaires were sent out through the mail, which were collected through visits. To verify the proposed structural model, SPSS WIN Ver. 21.0 and AMOS 18.0 were used. It led to the following results. First, conspicuous consumption didn't have a positive impact on club identification. Second, conspicuous consumption had a negative impact on MTB attitude. Third, the influence of reference group had a positive impact on club identification. Fourth, the influence of reference group had a positive impact on MTB attitude. Fifth, club identification had a positive impact on relation continuity intention. Sixth, MTB attitude had a positive impact on relation continuity intention.
