Purpose The purpose of the study is to analyze China's school sports policy by dividing it into the era of four leaders before the current regime. Methods Former Chinese leader Deng Xiaoping's reform and opening up is a big axis that distinguishes China's time, more than 70 years after its founding. Therefore, we discussed the history of Chinese school sports policy by considering the background of the times, the ideology of the former Chinese leaders, and the keynote of the sports policy that influenced the school sports policy. Results The Chinese school sports policy history before and after China's reform and opening up is summarized as having a continuity to “sports as an education for all” and a distinction symbolized by “legislation and scientificization.” Conclusion Deng Xiaoping's reform and opening up has been carried on by the regimes since then, and his guiding ideology and sports policy keynote have had a profound impact on Chinese school sports policy.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to explore the trend of K league exodus and its factors. Methods Qualitative case study was conducted by selecting 9 footballers and 7 their agents as the participants who have migrated from South Korea to China and the Middle East. Results The factors of migration were categorized as three push and pull factors such as economy (individual income and club's profit), policy (employment for foreign and military service) and environment (markets in home and abroad). To understand sport migration in the economic factor, there should be the environmental condition (overseas market) to pay high salaries and transfer fee to individuals and their clubs, and at the same time, the domestic market should be relatively poor environment. In addition, this study overcame limitations of economic and environmental factors by classifying Asian quota system and military service into political factor, and found the specificity (local context) of K league. Conclusions In conclusion, this study can be regarded as the first empirical work on sport labor migration in Korea and valuable as basic data of follow-up studies.
Purpose The purpose of this research is to provide implications for the study of the physical education curriculum in Korea and China by comparatively analyzing the revised high school physical education curriculum in the two countries. Methods Using Bereday(1964)’s four steps of comparison model in education, this study focuses on the format and content of the general high school physical education curricula of Korea and China, each curriculum having been revised respectively in 2015 and 2017. Results First, in terms of format, both countries consider PE a necessity and share similarities in regard to course structure, credit allocation and document format. Nevertheless, though both countries are oriented toward competency-centered education, there are some differences with respect to official education curriculum documents, numbers of subjects and hours of study based on the reality and situation of each country. Second, in terms of content, both countries present various teaching methods and evaluation principles for the sake of acquiring core competence. However, the Korean curriculum prefers to advocate learning of the value of physical activity to achieve core competencies, while the Chinese curriculum prefers to focus on acquiring athletic skills and health knowledge for achieving core competencies. Conclusions After comparing physical education curriculum in both countries, two implications could be obtained. One is that the consistency problem in Korea should be solved between the core competency, the teaching and learning methods and evaluation standards. The other is that, in China, integrated value of physical education should be paid more attention and core competency as well as teaching and learning methods should be considered.
PURPOSE This study aimed to explore the effective and pragmatic idea regarding the development of physical education teacher education (PETE) programs in China. These programs share both similarities and differences in China and Korea, and they are also discussed here. METHODS Six universities reflecting the regional specificities of Korea and China were selected following consultation with experts. Data collected through in-depth interviews, non-participatory observation, literature, and local documents were analyzed and interpreted by using the comparative analysis research method. RESULTS First, when comparing the curriculum, which was divided into liberal arts, major, and teaching subjects in both countries, the ratio of liberal arts and teaching subjects was similar in Korea following major subjects. As for China, major subjects came in first, followed by liberal arts and teaching subjects. Second, the relative pros and cons of preliminary sports teacher education in Korea and China were aimed at nurturing competent sports experts with both expertise and personality. They were generally similar in terms of content dimensions; however, they were found to be different in several areas. Particularly in the case of China regarding the teaching subject, practical subjects that were of pragmatic help to the school field were found to be relatively insufficient. Third, the implications for improving China's preliminary PETE were to emphasize the importance of personality in educational goals at the goal level, and as for the content level, it was necessary to replaced them with classes that could be of pragmatic use in the existing teaching method. Furthermore, at the methodological level, professional training of physical education teachers should be proposed, training them to cultivate character. Finally, more positive changes can be pursued if efforts at the environmental level are well-matched and improved. CONCLUSIONS To improve China's preliminary PETE program, it is necessary to enhance the environment and institutions using various teaching methods to cultivate expertise, such as practical aspects of university-field linkage and preliminary teacher personality education.

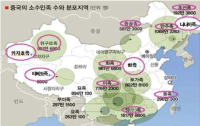
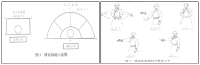
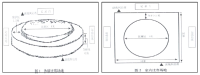
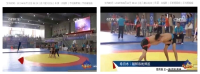
This research begins from the awareness that even though there are different forms of wrestlings in the ethnic minority groups in China, the study on their morphological aspects has reached the limit. Based on the documents and VOD data about these wrestlings of each ethnic group, their morphological characteristics can be verified as follows. First, The postures of Han and Mongolian people take the way of two players standing and playing, and Korean-Chinese people and Hui people take a saddle stance using a thigh band. Second, as for the arenas for the wrestlings, owing to some geographical features and natural environments, they were set up at a specific area during the traditional era using natural objects(grass, lawn, soil, sand). Yet, in the modern times, they have been changed as being installed and run in modernized gyms, sports fields, or parts following the standard of stadium facilities supervised by each organization. Third, with regard to the play wear of wrestling, some parts of the traditional costumes have been transmitted and worn. However, in case of most of the traditional costumes, it has been found out that modernized clothes which take the forms of garments developed since the modern era into consideration are being used. Fourth, in terms of the game equipments of wrestling, certain clothes(uniform, vest), running shoes and a band(a thigh band) should be worn.























[Purpose] This study aims to examine the research trends in Korean women’s sport history and provide suggestions for future research by reviewing journal articles conducted in the last ten years (2007-2016). [Methods] The articles were selected from the Korean Journal of History for Physical Education, Sport, and Dance, which is the only, representative sport history journal in South Korea. 66 articles identified as studies of women’s (or women-related) sport history were analyzed in five categories, including a) period, b) theme/topic, c) purpose, d) method, and e) country. [Results] Specifically, the analysis by period showed that 90% of the research focused on modern and contemporary history, while only 7% of the research was set in pre-modern history. According to the analysis by theme/topic, genre has been studied most often with 36%, followed by figure (20%) and facility/institution/organization (15%). By the criteria of purpose, it was found that the majority of the research (48%) focused on historical evolution and transition, while the research on comparison/relation was of little scholarly interest. Regarding the category of method, textual analysis was used most often, with 70% followed by oral life history (27%). By the criteria of country, the largest ratio of papers studied Korea (75%) while only 3% of studies examined other East Asian countries, such as China or Japan. Comparative, diasporic, or transnational studies were the second most popular subcategory (11%). [Conclusion] According to the results, it was acknowledged that there has been a significant lack of interest in women’s sport history by Korean scholars and “sport herstory” is largely underresearched. In addition, the excessive concentration on a specific period or a particular theme was also exposed. To rectify the biased research practice and promote scholarly growth and enhancement in both academia of Korean women’s sport history and Korean sport history, it is necessary to consider the expansion of historical materials, application of new methodology, cross-disciplinary conversation, and theorization in studying women’s sporting experiences.
This article aims to examine the research trend of sport history by analysing published research articles over the last decade in the Korean Journal of History for Physical Education, and suggest directions of research in sport history based on the results. We have reviewed a total of 264 articles relying on the analytic framework including the criteria of time period, method, nation, theme/topic, and purpose. The research findings are as follows. First, the post-Liberation period has been studied most often with 45.3%, followed by the Japanese Colonization period (20.2%), the Joseon Dynasty period (11.4%), the diachronic research (8.8%), the period from ancient times through Goryeo (8.1%), and the period of Enlightenment (6.2%). The results indicate that most recent studies in the journal unilaterally focus on the Modern and Contemporary history with 71.7%. According to the analysis result by research method, second, more than 90% of the studies have been conducted using qualitative methods while only 0.6% of the papers have adopted quantitative methods. The qualitative methods include textual analysis, participant observation, oral life story, and focus group interview. Textual analysis has been used most often with 74.5%. Oral life story has been second (22.5%), followed by participant observation (2.1%) and focus group interview (0.3%). The findings from this category show that it is still necessary to diversify research methods and vitalize interdisciplinary research. Third, in terms of nation, over 70% of the papers have studied about Korea, and European countries are the second most frequent region in the research trend (8.3%). The nation that follows is China with 6.4%. Although we analysed a Korean journal in sport history, the result exposes the lack of scholarly attention in the studies of sport history to world sport history reflecting comparative perspectives. By the criteria of theme/topic, fourth, genre has been studied most often with 31.7%, followed by figure (14.1%), facility/institution/organization (14.0%), system/policy/event (12.8%), philosophy/ideology/theory (6.7%), remains/relics/documentary material (6.3%), and domestic regions (5.4%). The results show that the recently published research articles have attempted to include a variety of genres in sports, play, and dance. While the topics for figure and facility/institution/organization also receive significant interest, it is limited that the studies mostly focus on male sport figures but female figures are barely explored. Even when female figures are researched, the attempts are observed only in the studies of dance. Fifth, the largest ratio of papers has had the research purpose of historical evolution (37.6%), followed by value/significance (20%), type/characteristic (15.5%), thoughts/ideology/theory (9.1%), origin (6.6%), suggestion/proposal/prediction (5%), comparison/correlation (5%), and concept/terminology (1.2%). The results expose that the studies tend to concentrate on historical evolution relying on chronological description while the research on concept/terminology is of little scholarly interest. Based on what we have found, it is identified that the recent studies in sport history have mostly focused on the historical evolution of a specific sport genre in the Korean Modern and Contemporary history using textual analysis. Consequently, the results suggest that researchers in sport studies need to put in additional effort to expand research topics and methods, and invite comparative perspectives involving inter/cross-national studies.